Strategies for Promoting Positive Behavior and Managing Disruptive Actions in the Classroom
260 likes | 417 Vues
Effective classroom management is essential for fostering a conducive learning environment. Understanding that all behaviors serve a purpose, educators should not take misbehavior personally. Strategies include anticipating behaviors, establishing clear rules, and using positive reinforcement. Address techniques for identifying the reasons behind negative behaviors, such as anxiety or lack of structure. Employ proactive measures like routines and practice scenarios, and maintain a calm, neutral demeanor when addressing disruptions. Build student strengths and provide choices to promote engagement.

Strategies for Promoting Positive Behavior and Managing Disruptive Actions in the Classroom
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Behavior Management Promote positive behaviorPrevent disruptive behavior
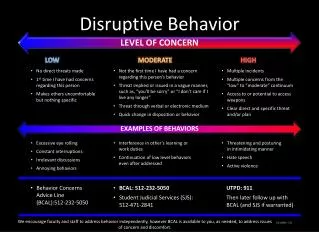
All Behaviors serve a purpose • Behavior is a form of communication • Behaviors may be attention seeking • Behaviors may occur to avoid work • Behavior may occur to escape from the environment. • Do not take misbehavior personally
Behavior Disability Types • Oppositional Defiant • Persistent temper tantrums • Argues with adults • Refusal to comply with requests • Annoys others • Vindictive
Behavior Disability Types • Conduct Disorder (severe behavior) • Overt aggression toward people or animals • Destruction of property • Deceitfulness of theft • Serious violation of rules, truancy
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder • Difficulty in sustaining attention • Failure to give close attention to details in school work • Difficulty in organization • Impulsiveness • Restlessness, fidgeting, or talkativeness • Difficulty waiting for turn • Interrupts conversations
Get Up and Dance • Yes !!! • Bust a move • Freestyle • When in doubt knee bounce • Move it!
Depression and Anxiety Disorders • Insomnia • Loss of energy/fatigue • Poor concentration • Feelings of worthlessness • Excessive worrying • Reluctance and refusal • Mood changes
Why negative behaviors? • Difficulty transitioning • Difficulty understanding or following directions (especially if there are multiple steps) • Frustration with performing a skill • Lack of structure • Sensory overload
Effective Strategies • Be proactive – anticipate student behaviors • Plan clearly how you will address behaviors. Ignore, apply consequences, take a break, or redirect • Implement predictability and routine
The Learning Environment • Establish class rules and procedures • Post rules • List three to five rules • Use simple positive language • Add pictures and demonstrate • Connect actions with words
Our Class Rules • Do your best • Respect others • Be safe • Follow directions • Share, be kind and help others
Practice Rules • What does the rule look like when someone is following or not following? • What does it sound like when someone is following or not following? • Develop practice scenarios to show rules and consequences.
Cooperation, Kindness, Honesty • What does this look like? • What does this sound like?
Class Management • Expectations clearly communicated • Routines and timelines • Protocols – enter and exit class, water, bathroom, emergencies, fire drills, equipment • Stop Signal established and practiced • Boundaries
Time to Dance • Get up out of your seat and move • Wave your arms • Get oxygen in your lungs • Jump up and down, twist, shake, or whatever • Have fun
Teacher behavior when addressing disruptive behaviors • Maintain a calm disposition • Use a neutral Voice • Present clear concise instruction • Provide opportunities for student choice • Build on student’s strengths • Use humor when appropriate
Negative Comments: • What’s the matter with you? • Excuse me !!! • What is your problem? • How many times to I have to tell you? • Shut Up !!! • Do I have to come over there? • You are always a problem. • You are the worst kid I know.
Positive Comments: • You are a good listener today. • I am really proud of you for putting the ball away. • Way to be, John! I like how you shared with Mark. • Khalid you did a good job today and raised your hand when you had something to say. • Michele you were helpful and kind to Patty.
Appropriate Consequences • What types of consequences can you use in your class? • Remember the goal is for students to learn to change their behavior and be responsible.
Behavior Correction Strategies • Private verbal comment – Be specific • Agreed upon signal for correction • Student checklist or contract • I messages “I want you to …….. “ • Logical and consistent consequences • Time out, take a break, cool down, use a distracter • Physical restraints and touching
Positive Reinforcements • What types of reinforcement are appropriate? • Identify immediate and delayed reinforcements.
Positive Reinforcement • Verbal Comments • Word Wall – signs • Gestures – thumbs up, smiles, clapping • Proximity control or change student location • Tokens – tangible items • Favorite objects – toys, stickers • Food – candy, or favorite texture or taste • Time – free time, time with teacher
AVOID !!! • Picking teams • Elimination games • Human targets • Waiting in long lines • Long complex instruction • Exercise as a consequence
Consider the appropriateness of: • The constant use of large group activities. • High level competition with an emphasis on winning and loosing. • Posting scores for fitness achievement. • Watching one student perform for all others.
Bullying of and by students with disabilities • Can occur before, during and/or after class. • Verbal comments – put downs • Physical hitting, shoving, bumping • Hitting with equipment • Rejection by peers
Documenting Behaviors • Be descriptive • Record over several class sessions. • What action is the student doing? Alone or with others • When does the behavior occur? • What is the intensity? Distracting or destructive • Where does the behavior occur • How frequent is the behavior occurring?