Plant Structure and Function The Plant Body
510 likes | 1.17k Vues
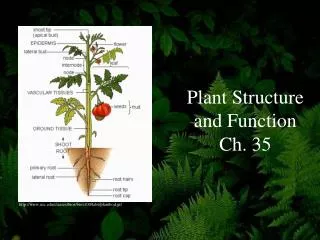
Plant Structure and Function The Plant Body. Chapter 24. Vascular plant tissue includes all of the following EXCEPT meristem. sieve tube cells. vessels. tracheids. companion cells. Answer: a. Which is CORRECT about monocots? Vascular bundles in the stem are in a ring.

Plant Structure and Function The Plant Body
E N D
Presentation Transcript
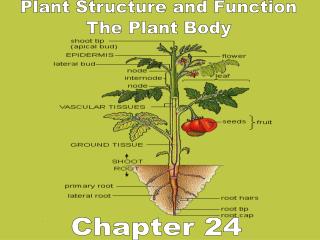
Plant Structure and Function The Plant Body Chapter 24
Vascular plant tissue includes all of the • following EXCEPT • meristem. • sieve tube cells. • vessels. • tracheids. • companion cells. Answer: a
Which is CORRECT about monocots? • Vascular bundles in the stem are in a ring. • Their floral parts are usually in 3’s. • They usually have taproots. • The veins in the leaves are netlike. • All of the above. Answer: b
Cortex, mesophyll, epidermal cells, and pith • all consist of • parenchyma. • collenchyma. • schlerenchyma. • both b and c • all of the above Answer: a
To observe the process of mitosis in plant • roots, a student should examine the root’s • root cap. • zone of maturation. • meristem tissue. • pericycle. • endodermis. Answer: c
Which of the following tissue types gives rise to all other plant tissues? a. parenchyma b. collenchyma c. schlerenchyma d. xylem e. phloem Answer: a
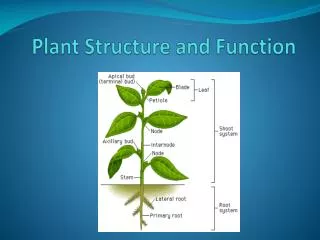
stem root internode node petiole leaf blade Asexual (vegetative) organs
flower seed fruit Sexual Organs
root hairs guard cells Epidermal Tissue cork glands
parenchyma collenchyma Least specialized Ground Tissue (Filler) sclerenchyma
Vascular Tissue (Stele)
Plants constantly grow in specialized areas only! Meristem (embryonic tissue)
ground meristem (ground tissue) protoderm (epidermis) procambium (vascular tissue)
taproot (dicot) First root grows straight down ex. Beet fibrous root (monocot) Anchor/ hold soil ex. grss Secondary growth adventitious root pericycle Dicots- from vascular tissue Grow from lower nodes of stem
parasitic mutualistic haustoria mycorrhizae (fungus)
Soybean root nodules, each containing billions of Bradyrhizobium bacteria
Terminal bud Produces new cells that elongate, increasing length Continually differentiating Primary growth Mature non-woody stems (herbaceous) Most monocots Shoot Apical Meristem
rhizome stolon tuber tendril corm
spines tendril Modified leaves bulb insect catching
Secondary growth Woody Stems Second and subsequent years Lateral meristem
Spring wood: wide vessels for transport Summer wood: more fiber and tracheids (less vessels) Spring wood + summer wood = annual ring
Cork Cambium Cork Wood Bark
Which is CORRECT about monocots? • Vascular bundles in the stem are in a ring. • Their floral parts are usually in 3’s. • They usually have taproots. • The veins in the leaves are netlike. • All of the above. Answer: b
Vascular plant tissue includes all of the • following EXCEPT • meristem. • sieve tube cells. • vessels. • tracheids. • companion cells. Answer: a
Cortex, mesophyll, epidermal cells, and • Pith all consist of • parenchyma. • collenchyma. • schlerenchyma. • both b and c • all of the above Answer: a
Which of the following tissue types gives rise to all other plant tissues? a. parenchyma b. collenchyma c. schlerenchyma d. xylem e. phloem Answer: a
To observe the process of mitosis in plant • roots, a student should examine the root’s • root cap. • zone of maturation. • meristem tissue. • pericycle. • endodermis. Answer: c