Neutron edm
80 likes | 244 Vues
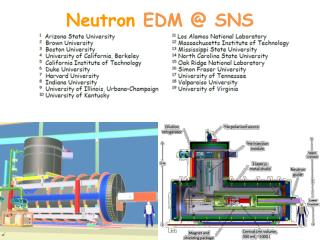
Neutron edm. Philip Harris, on behalf of the CryoEDM collaboration: Rutherford Appleton Laboratory University of Oxford University of Sussex ILL University of Kure. Technology. Neutrons in. HV in. (NB sensitivity/day is actually closer to ).

Neutron edm
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Neutron edm Philip Harris, on behalf of the CryoEDM collaboration: Rutherford Appleton Laboratory University of Oxford University of Sussex ILL University of Kure
Technology Neutrons in HV in
(NB sensitivity/day is actually closer to ) Sensitivity Achieved 60% polarisation in source, but must improve Successfully produced, transported, stored UCN, but need to reduce losses Successfully applied 10 kV/cm (same as previous expt); aiming for 20-30 kV/cm RT-edm: 130 s. So far we have 62 s cell storage time.
Room-temperature expt final sensitivity ~2E-25 ecm/day • Took 12 years of incremental developments from known technology • Systematics limited (geometric phase effect) • We can come within factor 4-5 of this in 2012 by • increasing detector area x10: technology now proved • refurbishing damaged detector-valve: in hand • applying ~70 kV (previously ~40 kV): should be straightforward • opening beam aperture from 43 to 50 mm: depends on radiation levels • retaining polarisation: superconducting material has been removed • There may be additional improvements beyond this • a peak above background (detector improvement) • Polarisation to 60% (improved guide field) • Increasing cell storage lifetime (insulator bakeout) (we will achieve these by 2014) Sensitivity in 2012
Mid-2013: Have to vacate current location. ILL will shut down for a year; we will move to new dedicated beamline. • New beam 4x more intense; and dedicated • Due to become operational mid-2014 • Beam must then be characterised (9A flux, divergence, stability, polarisation) • We will then have access to the area (late 2014) to move our apparatus into it. • M&O uplift requested to fund move and infrastructure in new location. Shutdown and move to new beamline
Not yet fully costed • Major upgrade to experiment: • Cryogenics design changes: • Pressurise the liquid helium: increase E field x 2-3 • Upgrade from two-cell to four-cell system • 2 x neutrons • Cancellation of some systematic effects • Installation of inner superconducting magnetic shield • B-field stability improves x1000, for systematics • Construction of non-magnetic SCV • Improves depolarisation: better T2 • Overcome geometric-phase systematic error • Net result: • Order of magnitude improvement in sensitivity • Commensurate improvement in systematics Upgrade 2013-15: Upcoming PPRP request
Without upgrade, we may reach factor ~3 better stats than RT-edm (possibly better if storage lifetime improves significantly). • Systematics is a different matter. • Back-to-back cells (4-cell system) provide important cancellations • Completely non-mag SCV would eliminate most of geometric-phase systematic (which limited RT-edm). 1 nT/m very difficult otherwise. • Magnetic shielding controls fluctuations, reduces broadening of Ramsey fringes • Changes to cryogenics would increase reliability (reduce down-time), reduce manpower burden, reduce He consumption... • With upgrade, should reach factor ~10 improvement in stat sensitivity, with commensurate improvement in systematics. Sensitivity and systematics