Vision-Controlled Robotic Arm
70 likes | 361 Vues
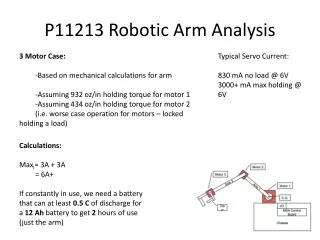
Austin Hou - RISE. Vision-Controlled Robotic Arm. Objectives . Communicate with and control a CRS F3 robotic arm Integrate computer vision into the system. Hardware. Hardware . F3 Robotic arm with 6 degrees of freedom The same arm that was used in the Human Genome Project

Vision-Controlled Robotic Arm
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Austin Hou - RISE Vision-Controlled Robotic Arm
Objectives • Communicate with and control a CRS F3 robotic arm • Integrate computer vision into the system
Hardware • F3 Robotic arm with 6 degrees of freedom • The same arm that was used in the Human Genome Project • High precision, made for performing tasks that require little human input • CRS C500 controller • Allows for serial communications with another device for commands, diagnostics, etc. • Connects to a controller pendant that has a range of abilities that is used through a keypad
Software • Main section: serial communication through python • Robot is normally controlled through proprietary software (Robcomm) • By taking over serial communication when the connection is made, the input/output stream can be redirected • The main section accepts user input, writes it to serial, waits for outputs, and repeats.
Software • Modules • Control can be redirected to a module • Main module is simpleCV control • A red dot is waved in front of the webcam • This is recognized, and based on the position of the dot, the arm moves • Another module controls through a front-mounted camera • Any webcam mounted to the front will do • If a dot is detected, the robot will move to face it • Smaller modules • Keyboard control (WASDQE)