Introduction to the Body Systems
450 likes | 1.2k Vues
Introduction to the Body Systems. March 27, 2007 BY: BRIANNA SHIELDS. DO NOW. 1. Which member of a food chain can directly utilize the sun’s energy? 2. Which member of a food chain is responsible for breaking down dead and decaying matter and returning it to the soil?

Introduction to the Body Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction to the Body Systems March 27, 2007 BY: BRIANNA SHIELDS
DO NOW • 1. Which member of a food chain can directly utilize the sun’s energy? • 2. Which member of a food chain is responsible for breaking down dead and decaying matter and returning it to the soil? • 3. In which type of symbiotic relationship do both organisms that are involved benefit?
GOAL • To understand how the body systems function together to maintain homeostasis in the body.
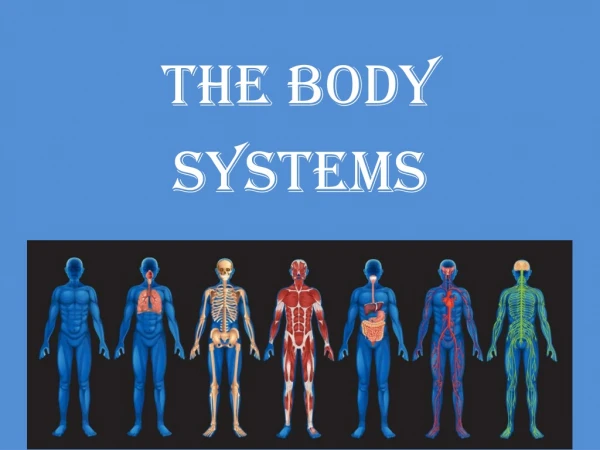
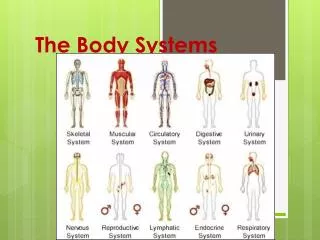
CELL ORGAN SYSTEM TISSUE ORGAN
Organization in the Body • Cell--> smallest unit of life • Tissue--> made of many similar cells • Organ--> made of many similar tissues • Organ System--> several organs working together
CELL TISSUE ORGAN ORGAN SYSTEM Blood Cells Blood Tissue Heart Circulatory System EXAMPLE
EPITHELIAL NERVE CONNECTIVE MUSCLE BLOOD Protects other tissue Sends/receives messages Supports/protects body Allows movement Carries oxygen, food through body TYPES OF TISSUE
Digestive Breaks down food into small bits for cells to use Body Systems Overview
Peristalsis- involuntary squeezing of food through the digestive tract Digestive System
Pathway of Digestion 1. MOUTH- Digestion begins, starches broken down (saliva and teeth) 2. ESOPHAGUS Food passes through (peristalsis)
Pathway of Digestion STOMACH Chemical & Mechanical digestion (proteins broken down) SMALL INTESTINE Most digestion happens, digestion is completed- find villi for absorbing nutrients
Pathway of Digestion LARGE INTESTINE Stores & eliminates undigested food ANUS Solid waste passed out
Respiratory Lungs take in O2 which is combined w/ nutrients for energy Body Systems Overview
Pathway of oxygen 1. Mouth/ nose 2. Trachea 3. Two bronchial tubes 4. Bronchi branches 5. Air sacs 6. Capillaries Blood picks up OXYGEN in capillaries of air sacs The waste CARBON DIOXIDE is dumped off Respiratory System
Circulatory Blood transports oxygen from lungs to cell, and wastes from cell to lungs Body Systems Overview
Pathway of Blood Blood is pumped by the heart & carried by 3 types of blood vessels: Arteries- carry blood away from heart (carries CO2) Veins- carry blood to heart (carries O2) Capillaries- tiny, thin walls so O2 and CO2 can pass through Circulatory System
Nervous Receiving and sending messages Body Systems Overview
Stimulus Response Pathway Made of nerve cells (NEURONS) 1. Senses send signals (stimulus) to brain 2. Brain decides how to respond (response) 3. Nerves carry response to proper part Nervous System
Excretory Ridding body of wastes (water, heat, urine, CO2, salt) Body Systems Overview
Excretory System: Label your Diagram Skin Lungs Kidneys
Organs of Excretion LUNGS- excretes CO2, water, heat SKIN- excretes water, salt, heat KIDNEYS- excretes water, salt, urine Excretory System
Organ of elimination ANUS/LARGE INTESTINE- gets rid of feces (s0lid waste) Excretory System
Reproductive Sex cells combine to make offspring (sperm + egg = fertilization) Body Systems Overview
Endocrine Glands make and release chemical regulators into the blood: hormones to respond to changes inside & outside the body Body Systems Overview
GLANDS Pituitary- controls all other glands Thyroid- regulates metabolism Thymus- fights infection Adrenals- fights body stress Islets of Langerhans- Produces insulin to control blood sugar levels Gonads/Testes- makes sex cells Endocrine System
Muscular Allows body to move Muscles only contract (pull)- they don’t push Body Systems Overview
Types of muscles VOLUNTARY (skeletal) Can control them Are attached to bones Work in pairs Muscular System
Types of muscles INVOLUNTARY (smooth) Can’t control them Found in blood vessels, organs, digestive tract Muscular System
Types of muscles Cardiac (Heart) Smooth, Involuntary Muscular System
Skeletal Protects organs, allows movement, makes cells Body Systems Overview
Joints How do bones move? 3 type of joints Ball & Socket- allows twisting (hips) Hinge- move in one direction (elbow) Slightly moveable- limited movement (vertebra & ribs) Skeletal System
Bones Blood cells made in marrow- have calcium Skeletal System
Cartilage Softer, flexible bone Skeletal System
Ligaments Holds bone together at joints Skeletal System
Tendons Cordlike tissue that attaches muscle to bone Skeletal System
WEBSITES • Heart and Brain Virtual Body • My Body for Kids: Brain/Nervous System • My Body for Kids: Heart/Circulatory System • Yucky Body Facts • Interactive Body Review Games • Innerbody.com