The Body Systems
250 likes | 391 Vues
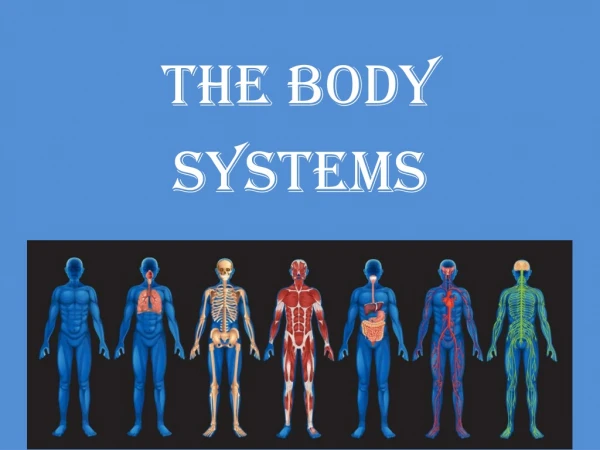
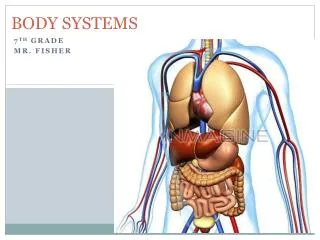
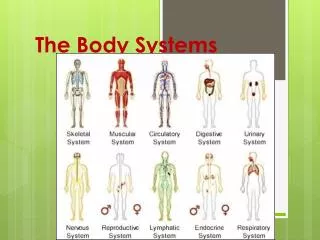
This guide explores the organization of the human body, highlighting the major systems, including the lymphatic, immune, endocrine, nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and muscular systems. Each system has specific cells and organs performing vital functions essential for maintaining homeostasis and health. We delve into how these systems cooperate with one another, exemplified by how the cardiovascular system supports multiple systems. Additionally, common diseases affecting each system are discussed to emphasize their importance in overall well-being.

The Body Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Organization of Life • Levels of organization • Cells, tissues, _______, ______, _______ • Division of labor • Each body system has a specific job
Lymphatic System • Organs • Function- a transport system for lymph and white blood cells
Lymphatic System • Cooperation- Transports white blood cells for the immune system. Transports fluids for the cardiovascular system. • Diseases • Tonsillectomies • Swollen nodes
Immune System • Parts- • Bone Marrow • Spleen • Thymus • Special cells- WBCs, T-Cells, macrophages, antibodies
Immune System • Function- protects the body against foreign invaders, • Cooperation- Uses the ________ system for transportation. The skin is apart of the integumentary system. • Invaders- bacteria, viruses
Endocrine System • Organs • Function- makes hormones which regulates your body • Regulates- growth, sugar, reproduction, sleep, mood
Endocrine System • Cooperation- • uses cardiovascular system for transport • Gets help from kidney, and liver • Diseases • Diabetes • Hormone disorders
Nervous System • Parts • Brain, spinal cord, neurons (nerve cells) • Function • Transmit messages between the brain and rest of the body using chemicals and electricity
Nervous System • Cooperation • Control movements of the muscular and skeletal body systems • Diseases • Epilepsy • Alzheimer’s • Parkinson’s • Multiple sclerosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cNaFnRKwpFk
Common Themes • Organization of Life • Division of Labor • Homeostasis • Checks and Balances
Cardiovascular System • Cardio- heart • Vascular – blood vessels • Also called circulatory system • Parts (anatomy) • Cardiac cell, cardiac tissue, heart, vein, artery, blood • Function • Pumps blood through the body • Transport system
Cardiovascular System • Cooperation • Receives oxygen from the respiratory system • Transports hormones for the endocrine system • Transports nutrients from the digestive system • Diseases • Heart attacks • High blood pressure • strokes
Respiratory System • Respire- breathe • Parts ( anatomy) • Lung cell, lung tissue, lungs, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tube, bronchiole, alveoli • Function • Take in oxygen (O2) and release carbon dioxide (CO2)
Respiratory system • Cooperation • Cardiovascular system • Diseases • Pneumonia • Emphysema • Lung cancer
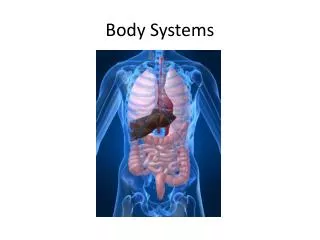
Digestive System • Anatomy (Parts) • Stomach cell • Stomach tissue • stomach, mouth, esophagus, small intestines, large intestines, gull bladder, liver • Function • Breaks down food so your body can absorb nutrients
Digestive System • Cooperation • Cardiovascular system • Diseases • Obesity • High blood pressure
Urinary System • Anatomy • Cell- kidney cell • Tissue- kidney tissue • Organs- Kidneys, Bladder • Function • Filters and eliminates liquid wastes
Urinary System • Cooperation • Receives waste from the Digestive System • Returns water and nutrients with the Cardiovascular System • Diseases • Urinary tract infection
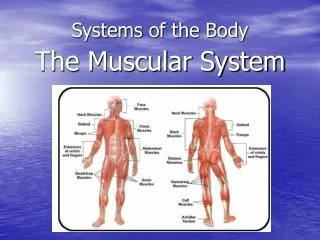
Muscular System • Anatomy • Cell- muscle cell • Tissue- muscle tissue • Organs-muscles • Function • Moves your body
Muscular System • Cooperation • Works with the skeletal system and nervous system to move your body. • Diseases • Muscular dystrophy • Parkinson's