Assessing Hydroelectricity: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Brazil's Case Study
110 likes | 213 Vues
This overview highlights the advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric power generation, focusing on the construction and maintenance of dams. Key advantages include consistent electricity production, long lifespan, renewable energy status, low pollution, recreational opportunities, and controllable energy output. Conversely, challenges such as high construction costs, potential flooding, ecological impacts, drought vulnerability, and investment risks are discussed. Additionally, a case study on Brazil illustrates the impact of reliance on hydropower amid water supply variability and its economic ramifications during droughts.

Assessing Hydroelectricity: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Brazil's Case Study
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Hydroelectricity Group 5: Chow Hanqi (6) Looi Han Liong (16) Marcus Lai (8)
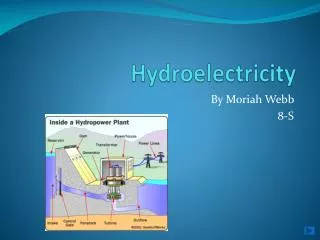
Advantages • Electricity can be produced at a constant rate by building a dam for water to flow through. • Long lasting electricity productions as dams are designed to last for many years. • It is a renewable energy source. • Cheaper than other energy sources such as uranium or oil fuel. • Minimum pollution is produced as it does not produce waste. • Energy can be created the whole day unlike solar energy. • Other than producing energy, can also be used as recreational areas such as canoeing and fishing. • Amount of energy produced is controllable.
Advantages • Electricity can be produced at a constant rate by building a dam for water to flow through. • Long lasting electricity productions as dams are designed to last for many years. • It is a renewable energy source. • Cheaper than other energy sources such as uranium or oil fuel. • Minimum pollution is produced as it does not produce waste. • Energy can be created the whole day unlike solar energy. • Other than producing energy, can also be used as recreational areas such as canoeing and fishing. • Amount of energy produced is controllable.
Disadvantages • The costs to build dams are extremely expensive. • May cause floods and lead to people around the area evacuating the area. • Building of large dams can cause earthquakes around the area such as the Hoover Dam causing some earthquakes in USA. • May kill the fishes in the water being used for the turbines and cause some of the fish species to be exterminated.
Disadvantages • Droughts may cause the dams to stop working as the water will be dried out. • As it is expensive to build a dam, long term investment will be required in order to earn back the money spent. • If the builders are unaware that two dams are built on a single water source, both will gain nothing for it as both dams will try to change the current of the water to flow through their dam.
Case Study • The connection between water and energy production is not always appreciated. Areas with a lack of diversity in their energy sources can expose themselves to risks if water supplies are unreliable Brazil has the Western Hemisphere’s third-largest electricity sector, but it also illustrates the risks inherent with water unreliability. • Hydropower accounts for over 90% of Brazil’s electricity – and this abundant hydroelectric power is a mixed blessing.
Case Study • On the positive side, hydroelectric power reduces Brazil’s overall generation costs, compared to countries with more diverse sources of supply. And compared to most thermal generation, it is also more sustainable for the environment. However, this dependence makes the country more vulnerable to supply shortages in years with low precipitation, especially given sustained and increasing consumer and industrial demand.
Case Study • Consider what happened in 2000 and 2001, when Brazil faced a severe drought. In order to prevent blackouts, the government imposed energy quotas that aimed to reduce consumption by 10 to 35%, according to a report by environmental advocacy group Ceres. Many industries in Brazil’s south-eastern region – which accounts for almost 60% of the country’s GDP – were negatively impacted by reductions in operational capacity, production delays and increased production costs. • Overall, the drought is estimated to have reduced the country’s GDP by 2%, or roughly $20 billion (US) – proving that, especially in countries that depend on hydroelectric power, the impact of water management touches every part of the economy, and can force real drawbacks when resources are unexpectedly diminished.
Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rnPEtwQtmGQ
Bibliography • http://growingblue.com/case-studies/brazils-reliance-on-hydropower/ • http://www-wds.worldbank.org/external/default/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2007/05/23/000090341_20070523152800/Rendered/PDF/397410Electricity0gap01PUBLIC1.pdf • http://www.pacinst.org/reports/remaining_drops/CLSA_U_remaining_drops.pdf • http://growingblue.com/case-studies/brazils-reliance-on-hydropower/ • http://www-wds.worldbank.org/external/default/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2007/05/23/000090341_20070523152800/Rendered/PDF/397410Electricity0gap01PUBLIC1.pdf • http://www.pacinst.org/reports/remaining_drops/CLSA_U_remaining_drops.pdf