lecture 8. Epistasis and Pathways
240 likes | 484 Vues
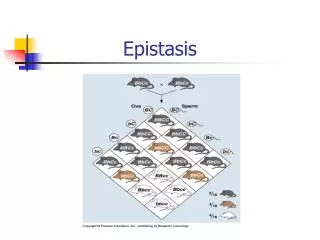
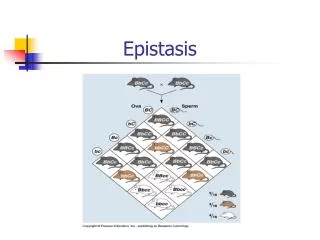
lecture 8. Epistasis and Pathways. Interactions of null alleles Additivity of nulls implies distinct pathways. Epistasis of nulls implies common pathway. Synergism of null alleles implies parallel pathways with a common target. Additivity of hypomorphs is consistent with anything. 1. 3.

lecture 8. Epistasis and Pathways
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Interactions of null alleles Additivity of nulls implies distinct pathways Epistasis of nulls implies common pathway Synergism of null alleles implies parallel pathways with a common target Additivity of hypomorphs is consistent with anything
1 3 Y X Z 1 2 Z X Y 1 2 3 X Y Z
Switch Regulation Pathway outcome 1 A B condition outcome 2 Yes ON ON outcome 1 outcome 2 No OFF OFF
Switch Regulation Pathway outcome 1 A B condition outcome 2 Yes OFF ON outcome 1 outcome 2 No ON OFF
Some C. elegans sexual specializations Male tail sensory structures that locate the vulval opening spicules Hermaphrodite vulva 2° 1°: the opening vulval muscle-1 insertion cues to male 2°: vulval muscle-2 insertion cues to male 1°
somatic sex determination in C. elegans • genotype XX XO • +fm • tra-1(lf)m m • tra-1(gf)ff • her-1(lf) ff • her-1(gf)~m m • f, female somatic tissues; • m, male somatic tissues. • lf, loss-of-function; • gf, gain-of-function
somatic sex determination in C. elegans • genotype XX XO • +fm • tra-1(lf)m m • tra-1(gf)ff • her-1(lf) ff • her-1(gf)~m m • tra-1(lf); her-1(lf)m m • tra-1(gf); her-1(gf)ff
OFF ON ON OFF
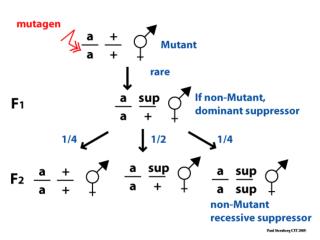
Intragenic revertant of a dominant mutagen • egl-1(sd)+ +ced-9(gf) • egl-1(sd) + + ced-9(gf) • egl-1(sd) ced-9(gf) • + + • egl-1(sd) ced-9(gf+lf) • + + x Common Non-Egl OR Rare Egl In egl-1(sd) mutants, the HSN dies, and hence the hemaphrodites cannot lay eggs
ced-3(lf) NO cell death ced-4(lf) NO cell death ced-1(lf), 2, etc No engulfment ced-9(gf) NO cell death ced-9(gf+lf) EXTRA cell death nuc-1 No DNA degradation ced-3(lf) ced-9(lf) NO cell death ced-3 (lf) nuc-1(lf) NO cell death