Preparing a Cost Analysis
230 likes | 372 Vues
This document outlines the process for preparing a cost analysis for control devices, focusing on both capital and recurring costs. It covers identification and annualization of capital expenses, including procurement, installation, and indirect costs such as engineering and contractor fees. It also discusses annual costs associated with operation, maintenance, and overhead. By the end of the analysis, it provides estimations for various control systems, including fabric filters and electrostatic precipitators (ESPs), ensuring a comprehensive understanding of overall investment requirements.

Preparing a Cost Analysis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Preparing a Cost Analysis March 10, 2009 John Calcagni
Preparing a Cost Analysis Overview • Identify all capital costs necessary to get control device operational • Annualize capital costs • Identify all annually recurring costs associated with control device • Identify and value any recovered product (energy, sulfuric acid, gypsum, etc)
Direct Capital Expenses • Purchased Equipment • Auxiliary Equipment (including instrumentation and ductwork) • Buildings, foundations and supports • Site Preparation • Direct Installation (electrical, piping, insulation, painting) • Sales Tax • DO NOT INCLUDE LAND
Indirect Capital Expenses • Engineering • Contractor fees • Start-up • Performance testing • Contingencies
Direct Cost Factors for Fabric Filters • Purchased Equipment As Estimated, A • Instrumentation 0.10A • Sales Tax 0.03A • Freight 0.05A • Purchased Equipment Cost 1.18A, B
Direct Capital Cost Factors for Fabric Filters (Cont.) Direct Installation Costs • Foundation and Supports 0.04B • Erection 0.50B • Electrical 0.08B • Piping 0.01B • Insulation for auxiliaries 0.07B • Painting 0.04B • Site Prep As estimated • Buildings As Estimated Total Direct Installation Cost 1.74 B + SP + Bldg.
Indirect Capital Cost Factors for Fabric Filters • Engineering 0.10B • Construction and Field 0.20B • Contractor Fees 0.10B • Start-up 0.01B • Performance Tests 0.01B • Contingencies 0.03B Total Indirect Capital Cost 0.45B Total Capital Investment 2.19B + SP + Bldg.
Direct Equipment Cost Factors for ESP • Purchased Equipment As Estimated, A • Instrumentation 0.10A • Sales Tax 0.03A • Freight 0.05A • Total PEC 1.18A, B
Direct Capital Cost Factors for ESP (Cont.) Direct Installation Costs • Foundation and Supports 0.04B • Erection 0.50B • Electrical 0.08B • Piping 0.01B • Insulation for auxiliaries 0.02B • Painting 0.02B • Site Prep As estimated • Buildings As Estimated Total Direct Installation Cost 1.67 B + SP + Bldg.
Indirect Capital Cost Factors for ESP • Engineering 0.20B • Construction and Field 0.20B • Contractor Fees 0.10B • Start-up 0.01B • Performance Tests 0.01B • Model Study 0.02B • Contingencies 0.03B Total Indirect Capital Cost 0.57B Total Capital Investment 2.24B + SP + Bldg.
Adjusting Purchased Equipment Estimates • Sometimes Purchased Equipment Cost estimates for similar projects are used with adjustment for size and/or inflation • Size - 0.6 power rule • PEC1=PEC2[gas flow rate1/gas flow rate2]0.6 • Inflation – Use industrial construction cost inflation index such as CEN, Marshall and Swift, or Vatavuk index Limit adjustments to ~20% or 3-4 years
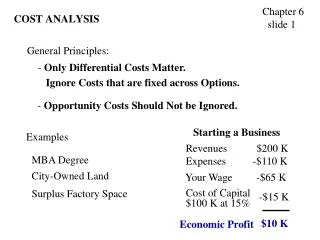
Annualizing Capital Costs • Capital costs need to be annualized to be useful in calculating $/ton • Key Parameters • Useful life ~20 years for most equipment. • DO NOT USE IRS depreciation life for equipment (~10 -15 years) • Cost of Capital ~7% for large firms, slightly higher for smaller firms. • DO NOT USE company internal expected rates of return or hurdle rates (~15-20%)
Annualizing Capital Costs • Applied like mortgage amortization table • Multiply Total Capital Investment by appropriate amortization rate for time and interest rate • Examples: • 15 years @ 7% = 0.1098 @ 9% = 0.1241 • 20 years @ 7% = 0.0944 @ 9% = 0.1096 • 25 years @ 7% = 0.0858 @ 9% = 0.1018 • DO NOT ALLOW: • 10 years @ 15% = 0.1993
Direct Annual Costs • Materials • Operating Labor • Supervisory Labor • Maintenance • Electricity • Water • Fuel • Waste Disposal
Indirect Annual Costs • Property Taxes • Insurance • Overhead • Administrative
Estimating Direct Annual Costs for Fabric Filters • Operating Labor – 2-4 hrs/shift • Supervisory Labor - 15% of Operator • Materials – N/A • Maintenance • Labor – 1-2 hrs/shift • Materials – 100% of Maintenance Labor
Estimating Direct Annual Costs for Fabric Filters (cont.) • Replacement Parts – filter bag cost depends on design • Cost of replacement bags and labor for replacement should be amortized 2-4 yrs • Utilities – local factors based on design and/or experience • Dust Disposal – often reused otherwise local landfill cost
Estimating Indirect Annual Costs for Fabric Filters • Overhead – 60% of labor costs (operating, supervisory, and maintenance) • Administrative – 2% of TCI • Property Tax – 1% of TCI • Insurance – 1% of TCI
Estimating Direct Annual Costs for ESP • Operating Labor – 3 hrs/day + Coordinator time • Supervisory Labor - 15% of Operator • Materials – N/A • Maintenance • Labor – ~15 hr/week • Materials – 1% of PEC
Estimating Direct Annual Costs for ESP (cont.) • Utilities – local factors based on design and/or experience • Dust Disposal – often reused otherwise local landfill cost
Estimating Indirect Annual Costs for ESP • Overhead – 60% of labor costs (operating, supervisory, and maintenance) • Administrative – 2% of TCI • Property Tax – 1% of TCI • Insurance – 1% of TCI
Recovery of Product Recovered products often have value • Ash – Road Bed Aggregate • CaSO4 – Gypsum/Wallboard, kiln feed • Metal fines – reprocessed • H2SO4 – Saleable product Recovered product should be added back at market price
References • EPA Cost Manual: http://www.epa.gov/ttn/catc/products.html#cccinfo • Clean Air Technology Center: • http://www.epa.gov/ttn/catc/products.html