Discrete Random Variables
270 likes | 1.52k Vues
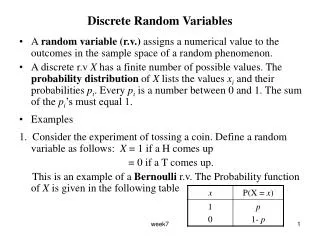
Discrete Random Variables. Presentation 6.1 Overview and Examples. Random Variables. A random variable X is simply a variable whose value is a numerical outcome from a random event. Examples Number of videos rented by a random customer at a video store. Height of a randomly selected person.

Discrete Random Variables
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Discrete Random Variables Presentation 6.1 Overview and Examples
Random Variables • A random variable X is simply a variable whose value is a numerical outcome from a random event. • Examples • Number of videos rented by a random customer at a video store. • Height of a randomly selected person. • The number rolled on a die. • Number of fans attending a Gonzaga basketball game. • Amount of soda in a can.
Discrete Random Variables • In order for a random variable to be discrete, there must be a countable number of outcomes. • From the previous examples, the following were countable, or discrete: • Number of videos rented by a random customer at a video store (X = 1, 2, 3, …videos). • The number rolled on a die (x = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6). • Number of fans attending a Gonzaga basketball game (X = 1, 2, 3, …people).
Probability Distributions of Discrete Random Variables • Consider the number of videos a customer rents when visiting a rental store. • The customer may rent 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or more videos. • Let X = the number of videos the customer rents. • The probability distribution shows the probability that the random variable takes on each of the above values.
Probability Distributions of Discrete Random Variables • The table below shows the probability distribution for the number of videos rented. • Notice the notation of X and P(X).
Properties of Discrete Probability Distributions • Each probability is a number between 0 and 1. • The sum of all the probabilities is 1. • Each event (or value of X) is disjoint.
Working with Discrete Probability Distributions • Verify that this is a legitimate probability distribution. • Confirm that the sum of the probabilities is 1. • 0.1+ 0.4+ 0.35 + 0.1+ 0.05 = 1 • What is the probability that a customer does not rent any videos? • This is P (X=0) = 0.1 or 10% of customers do not rent any videos. Please notice the notation.
Working with Discrete Probability Distributions • What is the probability that a customer rents more than 2 videos? • This is P (X>2) = 0.1 + 0.05 = 0.15. • What is the probability that a customer rents 2 or more videos? • This is P (X≥2) = 0.35 + 0.1 + 0.05 = 0.5.
Working with Discrete Probability Distributions • What is the probability that a customer rents 1 or 2 videos? • This is P (X=1 or X=2) = P (X=1) + P (X=2) = 0.4 + 0.35 = 0.75. • The addition of the probabilities is valid as the events (renting 1 video and renting 2 videos) are disjoint.
Discrete Random Variables • This concludes this presentation.