Piezoelectric crystals
460 likes | 848 Vues
This comprehensive guide explores piezoelectric crystals, their mechanical and electrical axes, and various vibration types in applications like microphones. It covers materials such as Seignette salt and PZT, types of piezoelectric plates, and configurations of piezoelectric bimorphs. A special focus is given to the classification of microphones including pressure, velocity, and mixed types. Additionally, it describes microphone sensitivity, directivity, and the impact of diffraction on performance characteristics, making it an essential resource for understanding electroacoustics.

Piezoelectric crystals
E N D
Presentation Transcript
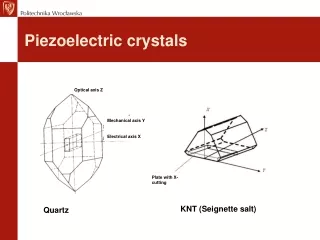
Piezoelectric crystals Optical axis Z Mechanical axis Y Electrical axis X Plate with X-cutting KNT (Seignette salt) Quartz
Vibration types of piezoelectric plates Compressional – longitudinal Compressional – thickness Shear – longitudinal Shear - thickness
Piezoelectric materials • acid amonium phosphate (ADP) • Seignette-Rochelle’s salt (KNT) • barian titanete (BAT) • lead titanete zirconato (PZT) • polymers • vinylidene polyfluoride
Piezoelectric bimorphs Bending bimorph Torsional (twisting) bimorph
Piezoresistive transducer Housing Membrane Beam Piezoresistor
Carbon (coal) transducer Membrane Semispherical electrode Coal pulver chamber Fixed electrode
Microphones – the general classification • Pressure mics – the electrical response is caused by variations in pressure of actuating sound wave • Velocity mics – the electrical response corresponds to particle velocity resulting from the propagation of sound wave through acoustic medium the difference in pressure between two points in space pressure gradient • Pressure-velocity mics – a combination of the above
Microphones • Pressure microphones • carbon mics • condenser mics • piezoelectric mics • moving conductor mics (dynamic – moving coil)
Microphones • Velocity mics • ribbon dynamic mics (with both sides of membrane actuated by the sound wave) • condenser mics (with both sides of membrane actuated by the sound wave)
Microphones – kind of transducer • Dynamic microphones (moving coil, ribbon) • Condenser microphones („real” condenser, electret)
Sensitivity of microphone • Sensitivity in free field • Sensitivity in diffused field • Pressure sensitivity
Other parameters • Output impedance • Frequency response • Directivity (polar pattern) • Noise level
Ce Equivalent circuit
Frequency responses Diffractional effects diaphragm The aperture for pressures equalization
The schematic action of condenser cardioid microphone w. 2 diaphragms