Understanding Limiting Reactants in Chemical Reactions
120 likes | 232 Vues
This educational resource from the Highland Science Department explores the concept of limiting reactants in chemical solutions. It defines a limiting reactant as the substance that gets consumed first in a reaction, while the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete. The guide also illustrates how to identify the limiting reactant by comparing mole ratios from a balanced chemical equation. A practical example involving the reaction of aluminum sulfate and calcium hydroxide is provided to calculate the mass of precipitated aluminum hydroxide, enhancing comprehension through real-world application.

Understanding Limiting Reactants in Chemical Reactions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution
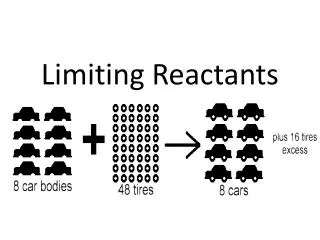
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution Limiting Reactant: the reactant that is used up first in a chemical reaction. Excess Reactant: the reactant that will still be left over when the reaction is complete
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution Limiting Reactant: the reactant that is used up first in a chemical reaction. Excess Reactant: the reactant that will still be left over when the reaction is complete Finding Limiting Reactant: compare mole ratios to those needed in the balanced chemical reaction to see which one is present in lower numbers
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.0150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide.
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.0150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide. G: Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3Ca(OH)2(aq) 2Al(OH)3(s) + 3CaSO4(aq)
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.0150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide. G: Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3Ca(OH)2(aq) 2Al(OH)3(s) + 3CaSO4(aq) volume = 20.0 mL concentration = 0.0150 mol/L Al2(SO4)3(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) = 0.0200 L volume = 30.0 mL concentration = 0.0185 mol/L Ca(OH)2(aq)Ca(OH)2(aq) = 0.0300 L M.M. Al(OH)3(s) = 78.0 g/mol
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.0150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide. U: mass of aluminum hydroxide
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.0150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide. U: mass of aluminum hydroxide S: 1. limiting reactant = volume x concentration ÷ lowest # moles n V M.R. M.M. 2. concentration moles moles mass L.R. L.R. Al(OH)3 Al(OH)3
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.00150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide. S: 1. moles = 0.0200 L = 3.0 x 10-4 mol Al2(SO4)3 moles = 0.0300 L = 5.55 x 10-4 mol Ca(OH)2
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.00150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide. S: 1. moles = 0.0200 L = 3.0 x 10-4 mol Al2(SO4)3 3.0 x 10-4 mol = 1 equal to 1 mole moles = 0.0300 L = 5.55 x 10-4 mol Ca(OH)2 3.0 x 10-4 mol = 1.85 less than 3 moles
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.00150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide. S: 1. moles = 0.0200 L = 3.0 x 10-4 mol Al2(SO4)3 3.0 x 10-4 mol = 1 equal to 1 mole Excess moles = 0.0300 L = 5.55 x 10-4 mol Ca(OH)2 3.0 x 10-4 mol = 1.85 less than 3 moles Limiting
Highland Science Department Limiting Reactants in Solution e.g. 1: Find the mass of aluminum hydroxide that precipitates when 20.0 mL of 0.00150 mol/L aqueous aluminum sulfate is mixed with 30.0 mL of 0.0185 mol/L aqueous calcium hydroxide. S: 2. mass = 0.0300 L Ca(OH)2 Al(OH)3 = 0.0289 g