Ch. 17-1 Electric Charge
140 likes | 325 Vues
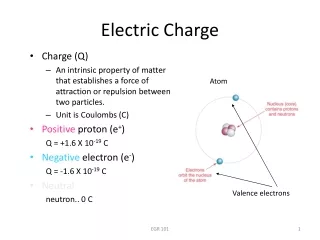
Ch. 17-1 Electric Charge. PreAP Physics Allen High School. How do you acquire charge?. Conservation of Charge Bad Hair Day? Permanent? Grounding—giving or taking an infinite number of electrons. What is Charge?. Proton Neutron Electron Variable: q Unit: Coulomb (C)

Ch. 17-1 Electric Charge
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ch. 17-1Electric Charge PreAP Physics Allen High School
How do you acquire charge? • Conservation of Charge • Bad Hair Day? • Permanent? • Grounding—giving or takingan infinite number of electrons.
What is Charge? • Proton • Neutron • Electron • Variable: qUnit: Coulomb (C) • Another common unit: μC
Charged Objects • Positive object = • Negative object = • Neutral object = • Equilibrium • Not necessarily zero. • The only charges that can move are ____________.
Electron Flow • Conductors • Insulators
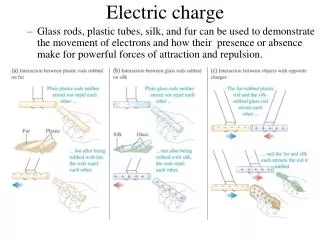
Separating Charge • Conduction (not the heat transfer) Contact between certain materials will separate charge. • Dragging/rubbing speeds up the transfer of electrons.
Separating Charge • Polarization • Electrons shift within the object, but are not transferred. • Think of water’s polar nature.
Separating Charge • Induction • Forcing a set charge on an object by giving an alternate path for charges to flow. • Only works for conductors. • Induces a charge opposite the first charged object.
Who is Robert Millikan? • Millikan’s Oil Drop Experiment proved that charges are quantized, which means they are whole multiples of the fundamental charge. • “Discrete amounts in nature.” • He also found that a proton has a charge equal and opposite to an electron. • qp = + 1.6 x 10-19 C
Electric Charge • Electrons are the only charges that can move, or flow from one material to another. • When you scuff your feet, you borrow electrons—can be a little or a lot. • 1e = 1.6 x 10-19 C (smallest amount) • Charged objects are in multiples of e.
Example 1 • You rub a balloon on your head and acquire a charge of 4.6 μC. How many electrons did you borrow? • Which object is positive? • Which object is negative?
Example 2 • What is the charge of an object that gains 1.2 x 108 electrons?