Data Collection
420 likes | 716 Vues
Data Collection. Presented by: Meredith Penner, M.Ed. Rebecca Rotondo, M.Ed. Norristown Area School District Itinerant Autistic Support Teachers 610-630-6000, ext.6025. Agenda. Introductions Data Collection Purposes Data Collection Formats IEP Relevance Data Collection

Data Collection
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Data Collection Presented by: Meredith Penner, M.Ed. Rebecca Rotondo, M.Ed. Norristown Area School District Itinerant Autistic Support Teachers 610-630-6000, ext.6025
Agenda • Introductions • Data Collection Purposes • Data Collection Formats • IEP Relevance • Data Collection • Data Collection Methods • Examples of Data • Audience Input • Keys to Successful Data Collection • Helpful Hints • 8 steps to Determine Methodology • Group Activity
Presenters: • Meredith Penner • 6 years as Full-time AS teacher • 1 year as Itinerant AS teacher • School TSS consultant • mpenner@nasd.k12.pa.us • Beckie Rotondo • 6 years as Full-time AS teacher • 6 years as Itinerant AS teacher • District Assistive Technology Leader and Consultant • rrotondo@nasd.k12.pa.us
Purposes • Directs teaching and instruction (monitoring/adjusting) • Starting point • Determines instructional approach • Assess student mastery
Purposes (cont.) • Memory aid for student performance • Maintain objectivity and consistency (must be measurable) • Verifies eligibility for programs, services and placement
Purposes (cont.) • Lets student know how they are doing • Feedback for improvement • Rewards and success
Data Formats • Standardized tests • Chapter tests, Quarterly Tests • Teacher-Made tests and formats (rubrics, etc.) • Format Structure • Efficient-quick and to the point • Easily understood to those reading • Should not require insight, interpretation, or judgment
IEP Relevance • You are only responsible to collect on IEP goals and objectives • Good idea to also collect data on maladaptive behaviors that may emerge to establish patterns • Collect data in relation to how and when as stated on the IEP (weekly, monthly, quarterly—work samples, checklists, etc.)
IEP Relevance (cont.) • DUE PROCESS!!!!!! • Don’t put anything in the IEP that you are unwilling or unable to do • Restraining students • You must document all times of restraining as per Ch.14 • Eye contact Exception…you should collect data on new behaviors to identify function (FBA)
Where Does it Fit in the IEP? • Measurement of objectives and goals • Present Ed. Levels • Progress Reporting • Due Process
Data Collection in the IEP • The connections • Direct link between: • Expected level of achievement (How well is the student to perform on this objective?) • Evaluation schedule (when and how often) • Method (assessment procedure)
Criteria Examples • % of time • # of times • With # or % of accuracy • With no more than x errors • Words/digits per minute • With X movement on a prompting hierarchy
Criteria Examples • Independently • With a grade of x or better • X or better on a rubric • With no more than x occurrences • With an x or better on a rating scale • With x/x points on an assessment checklist
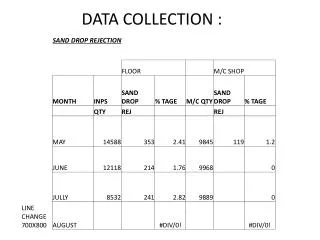
Methods of Evaluation • Teacher-made data collection forms • Work samples • Recording sheets • Anecdotal records • Teacher checklists • Baseline information • Performance data collection • Curriculum-based assessments • Portfolios • Rubrics • Rating scales
Methods of Evaluation • And these… • Charting toileting successes and accidents • Number of independent responses • Teacher checklist of ability to complete a task (task analysis) • Teacher checklist of prompting hierarchy
Types of Behavioral Data • Frequency • How often a behavior occurs over a given period of time • Best used when the goal is to increase or decrease the occurrences of a behavior
Types of Behavioral Data (cont.) • Proportion • What percentage of available opportunities did the behavior occur? • worksheets • Best used when the goal is to increase the quality of a behavior • Episode • Was there an occurrence of the behavior during this period (maladaptive behaviors)
Types of Behavioral Data (cont.) • Duration • for how long did the behavior occur? • Best used for open-ended behaviors that you are trying to increase • The amount of time a student attends to a task
Types of Behavioral Data (cont.) • Latency • How long was the period of time between the discriminative stimulus and the response • Used with the student who “wastes” time between a request and its associated response • Inter-response time • How long was the period between behaviors
Types of Behavioral Data (cont.) • Intensity • To what degree was the behavior present? • BE CAREFUL!!!! Very subjective • Rating scales-often used to describe a behavior • Quality • How well was the behavior performed? • BE CAREFUL!!!! Tough to be objective • Portfolios
Can we help? Audience Input… • Share any ideas • Ask for some help
Keys to Successful Data Collection • Make data useful • Used to shape student’s educational program • Assess the efficacy of the chosen activities and teaching styles • Look for trends in behaviors and learning
Keys to Successful Data Collection • Make the data relevant to your goals • Make sure you are taking data that is appropriate for the documented behavior and goals • Make it as painless as possible • Find a style and method that is comfortable and effective for you
Helpful Hints and Ideas • Use small counters for frequent and countable behaviors • Removable label on leg • Peer tutors for flash cards • Take time at the end of the day to review data • Review and summarize quarterly
Helpful Hints and Ideas • Individual student binders • Subject binders • Tape charts to wall (beware of confidentiality) • Central location to house all data
8 Steps to Determine Methodology • Review existing data • chapter tests, worksheets, work samples • Organize data • Dated, scored, placed in central location • Identify relevancy of data • Related to IEP goals, prerequisite skills
8 Steps to Determine Methodology • Decide relationships among data • Correlation or causation • Decide what new data are needed • In what form? Frequency, duration, latency, etc. • Decide how to collect needed data • Using what tools? Percentage, # correct, # incorrect
8 Steps to Determine Methodology • Decide who will collect the data • Special ed. teacher, therapist, regular ed. teacher • Set the next checkpoint for review • Marking periods, IEP dates, etc.)
Activity • For each goal: • identify one criteria example and one method example • Create, adapt, or select a data form that would be most efficient
Goal #1 • Within the speech room, John will identify spatial concepts (in, on, under, and beside) using manipulatives and pictures by responding verbally to “where” questions 4/5 trials for 3 consecutive weeks.
Goal #2 • In a variety of settings, Tim will use math computation skills needed to keep a personal budgetwith 80% accuracy for 3 consecutive weeks.
Goal #3 • In the regular ed. setting, Melissa will write a 5-7 sentence paragraph, using capitalization, punctuation, and no more than 3 spelling errors on 4/5 trials for 3 consecutive weeks.
Goal #4 • In the vocational setting, George will apply problem-solving techniques independently in the workplace on 4/5 trials for 3 consecutive weeks.
Goal #5 • In the special education classroom, Suzy will utilize eye gaze location in order to identify her name when presented with a choice of 2 words 4/5 trials for 3 consecutive weeks.
Goal #6 • Throughout his school day, Jose will recognize dry/wet pants by verbalizing his need to use the bathroom 4/5 times for 3 consecutive weeks.