Fig 3-1
280 likes | 622 Vues
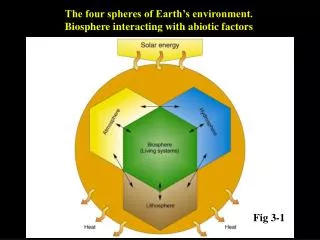
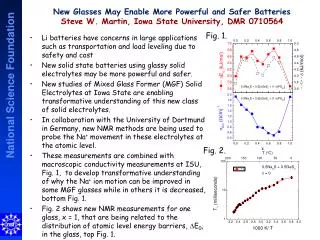
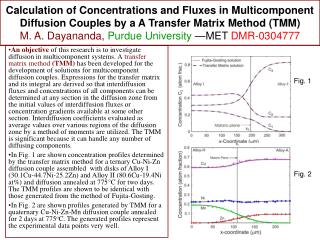
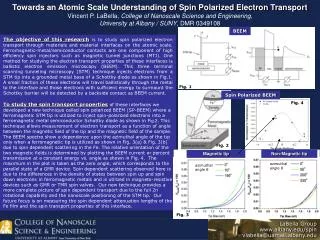
The four spheres of Earth’s environment. Biosphere interacting with abiotic factors. Fig 3-1. Periodic Chart of Elements John Wiley — Resource Manager CD-ROM. N-CHOPS. Law of the Minimum/Law of limiting factors - Liebig's Law. Justus von Liebig "father of the fertilizer industry”

Fig 3-1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The four spheres of Earth’s environment. Biosphere interacting with abiotic factors Fig 3-1
Periodic Chart of ElementsJohn Wiley — Resource Manager CD-ROM N-CHOPS
Law of the Minimum/Law of limiting factors - Liebig's Law Justus von Liebig "father of the fertilizer industry” law of the minimum If one crop nutrient is missing or deficient, plant growth will be poor, even if the other elements are abundant. like a barrel with unequal boards One nutrient becomes the limiting factor
Energy changes in organisms and ecosystems (Fig 3-12) Light energy chemical energy Many calories of light energy to produce a few calories of carbohydrate
Primary production GPP= NPP + energy used by the plants
Productivity of different ecosystems Fig 3-15
Basic Principles of Ecosystem Sustainability • For sustainability, ecosystems use sunlight as their source of energy. • For sustainability, ecosystems dispose of wastes and replenish nutrients by recycling all elements.
Continuous input Recycling
The Carbon Cycle • How and in what form does carbon enter and leave the cycle? • How do the roles of autotrophs and heterotrophs differ? • What are the human impacts on the cycle?
The Phosphorus Cycle • How and in what form(s) does phosphorus enter and leave the cycle? • How do the roles of autotrophs and heterotrophs differ? • What are the human impacts on the cycle?
The Nitrogen Cycle • How and in what form(s) does nitrogen enter and leave the cycle? • How do the roles of autotrophs and heterotrophs differ? • What are the human impacts on the cycle?
Nitrogen fixation: Bacteria in root nodules of legumes An example of mutualism Fig 3-19
Microcystis Anabaena Cyanobacteria
Quick Quiz Nitrogen and Phosphorus are 2 of the main components in fertilizer for agriculture and your garden. How does the source of these materials for human use differ? How does the difference in source affect their potential availability? What happens to excess Nitrogen and Phosphorus that is put on farm fields? What happens to the N & P not used by crops?
There is much talk in the news about carbon emissions and high CO2 causing global warming. Plants take up CO2 during photosynthesis. Why don’t plant just take up all the extra CO2 and get it out of the atmosphere?
Hydrologic cycle Fig 9-3
What limits production? Low N & P Low rain
Nutrient cycling and energy flow through an ecosystem Fig 3-20
Fig 3-23. Flow of nutrients in human society The Human System: How can we make it sustainable?