Polymer Parameters
170 likes | 283 Vues
Explore the intricate details of polymer parameters including structure, composition, morphology, and additives, impacting properties like glass transition temperature, boiling point, and mechanical behavior. Discover the significance of cost, topology, and sequence distribution in polymer applications.

Polymer Parameters
E N D
Presentation Transcript
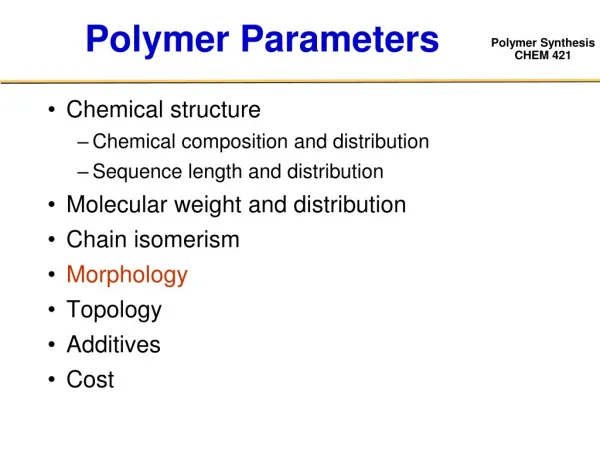
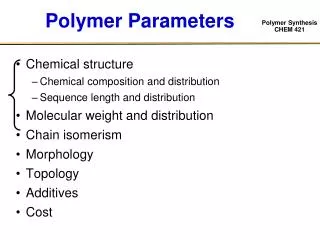
Polymer Parameters • Chemical structure • Chemical composition and distribution • Sequence length and distribution • Molecular weight and distribution • Chain isomerism • Morphology • Topology • Additives • Cost
Amorphous Morphology Glass Transition Temperature • - 80 °C • - 20 °C • 105 °C • 290 °C
Structure-Property Relationships Boiling Point Formula Weight • 46 g/mol • 46 g/mol Boiling Point Formula Weight • 86 g/mol • 188 g/mol
Structure-Property Relationships Tm (°C) ΔG = ΔH — T ΔS
Structure-Property Relationships Tg (°C) Tm (°C) Tm (°C)
Polymer Parameters • Chemical structure • Chemical composition and distribution • Sequence length and distribution • Molecular weight and distribution • Chain isomerism • Morphology • Topology • Additives • Cost
Topology • Soluble and melt processable • Linear • Branched • Long chain • Short chain
Topology • Network • Insoluble • Intractable • No flow with heat and pressure • aka • Gel, cured, vulcanizate, thermoset, crosslinked • Examples • Rubber, epoxy glue, etc
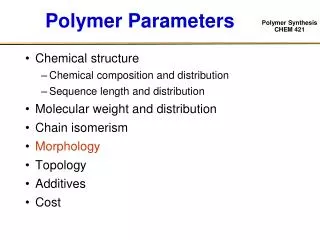
Polymer Parameters • Chemical structure • Chemical composition and distribution • Sequence length and distribution • Molecular weight and distribution • Chain isomerism • Topology • Morphology • Additives • Cost
Additives • Plasticizers • PVC • Tg ≈ 80 °C • Tg ≈ ? °C w/ 2% DOP • Stabilizers • Processing temperature • Operating temperature • Properties • MW • Brittleness • Discoloration • Cross-linking
Additives • Anti-oxidants • Flame retardants • Colorants • Dyes • Fillers • Carbon black: UV screen, enhance modulus • Fibrous reinforcers: glass, carbon, polymeric, ceramics • Economic performance fillers: Saw dust, dirt, etc! • Blowing agents • Lubricants
Polymer Parameters • Chemical structure • Chemical composition and distribution • Sequence length and distribution • Molecular weight and distribution • Chain isomerism • Topology • Morphology • Additives • Cost
Cost • Application dependent • Feedstock dependence • Raw materials cost • Recycle vs new • GDP independence? • Process improvements • COO • Environmental issues • Catalysts • Automation/sensors