Evolution
650 likes | 906 Vues
Evolution. Fixed Species Concept. The creator had designed each and every species for a particular purpose. Result. No evolution. Created the viewpoint that all species could be identified and named (Taxonomy). A major factor in the Linnaeus classification system. Theory.

Evolution
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fixed Species Concept • The creator had designed each and every species for a particular purpose.
Result • No evolution. • Created the viewpoint that all species could be identified and named (Taxonomy). A major factor in the Linnaeus classification system.
Theory • Fossils were the remains of species lost due to catastrophe. • No new species originated; species could only be lost over time. • Result - No evolution.
James Hutton • 1795 - Gradualism • Profound change is the cumulative product of slow, but continuous processes.
Result • Changes on the earth were gradual, not catastrophic.
1797 - 1875. Incorporated Hutton’s gradualism into a theory called Uniformitarianism. Charles Lyell
Uniformitarianism • Geological processes have operated at the same rate over the Earth’s history.
Result • The Earth must be VERY old. (much older than 6000 years of the fixed species concept). • Idea that slow and subtle processes can cause substantial change.
Published theory in 1809. Theory - Life changed from simple to complex over time. Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Lamarck • Fossils were the remains of past life forms. • Evolution did occur.
Lamarck’s Mechanisms 1. Use and Disuse - • Body parts used to survive become larger and stronger. • Body parts not used to survive deteriorate.
Lamarck’s Mechanisms 2. Acquired Characteristics • Modifications acquired by use/disuse were passed on to offspring.
Lamarck’s Mechanisms 3. Natural Transformation of Species ….species changed with every generation… extinction never occurred, organisms simply changed overtime.
Problems with Lamarck’s Theory • No knowledge of genetics. • Acquired traits are not transmitted offspring.
To Lamarck’s Credits • Did suggest correctly the role of fossils in evolution. • Did suggest that adaptation to the environment is a primary product of evolution.
Father of the modern theory of evolution. Theory - Descent with Modification. Charles Darwin
Darwin's Background • Trained as a Naturalist (after trying religion and medicine).
Result • Darwin's training and travel opportunities allowed him to formulate and support his ideas on Natural Selection.
Marine Iguana Tortise Unique animals
Paper on Natural Selection identical to Darwin's ideas. Alfred Wallace - 1858
Result - July 1, 1858 • Dual presentation of the Wallace-Darwin ideas to the Linnaean Society of London.
Publication of "The Origin of Species” Darwin - 1859
Comment • Darwin best remembered for the theory because of his overwhelming evidence and because he published.
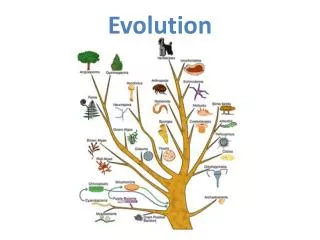
Darwinian View • History of life is like a tree with branches over time from a common source. • Current diversity of life is caused by the forks from common ancestors.
“The Origin of Species” • Documented the occurrence of evolution. • Suggested that the mechanism for evolution was Natural Selection.
Fact 1 - All species reproduce themselves exponentially. The Facts:
Fact 2 - Most populations are normally stable in size. Fact 3 - Natural Resources are limited (finite).
Inference 1 • The large number of offspring must compete for the finite resources. • Result - Most offspring die.
More Facts Fact 4 - No two individuals in a population are exactly alike. Fact 5 - Variation is inheritable.
Inference 2 • Those individuals whose inherited characteristics fit them best to their environment survive and reproduce.
Inference 3 • Offspring inherit the favorable characteristics. Populations shift over time as the favorable characteristics accumulate.
Nature • Determines which characteristics are favorable. • Determines who survives. • Result - “Natural Selection”
Artificial Selection • When man determines the characteristics that survive and reproduce. • Result - the various breeds of animals and plants we’ve developed.
Original Cultivars Ex - Mustard Plant
Evolution Success Measured By • Survival • Reproduction • Whoever lives long enough and has kids is the “winner” in evolution.
Requirements • In order for Natural Selection to work, you must have: • Long periods of time. • Variations within a population.
Subtleties of Natural Selection 1. Populations are the units of Evolution. 2. Only inherited characteristics can evolve.
Comment • Acquired characteristics may allow a species to evolve "outside" of Natural Selection. • Ex: culture, learning
Evidences of Evolution 1. Biogeography 2. Fossils 3. Taxonomy 4. Comparative Anatomy 5. Comparative Embryology 6. Molecular Biology
Biogeography • The geographical distribution of species. • Problem: • Species mixtures on islands • Marsupials in Australia