Plant Classification and Groups: Seedless, Nonvascular to Seed-Producing Vascular Plants
200 likes | 771 Vues
Explore the diverse world of plant taxonomy, from seedless nonvascular mosses to seed-producing vascular gymnosperms and angiosperms. Understand the characteristics and lifecycle stages of these plant groups.

Plant Classification and Groups: Seedless, Nonvascular to Seed-Producing Vascular Plants
E N D
Presentation Transcript
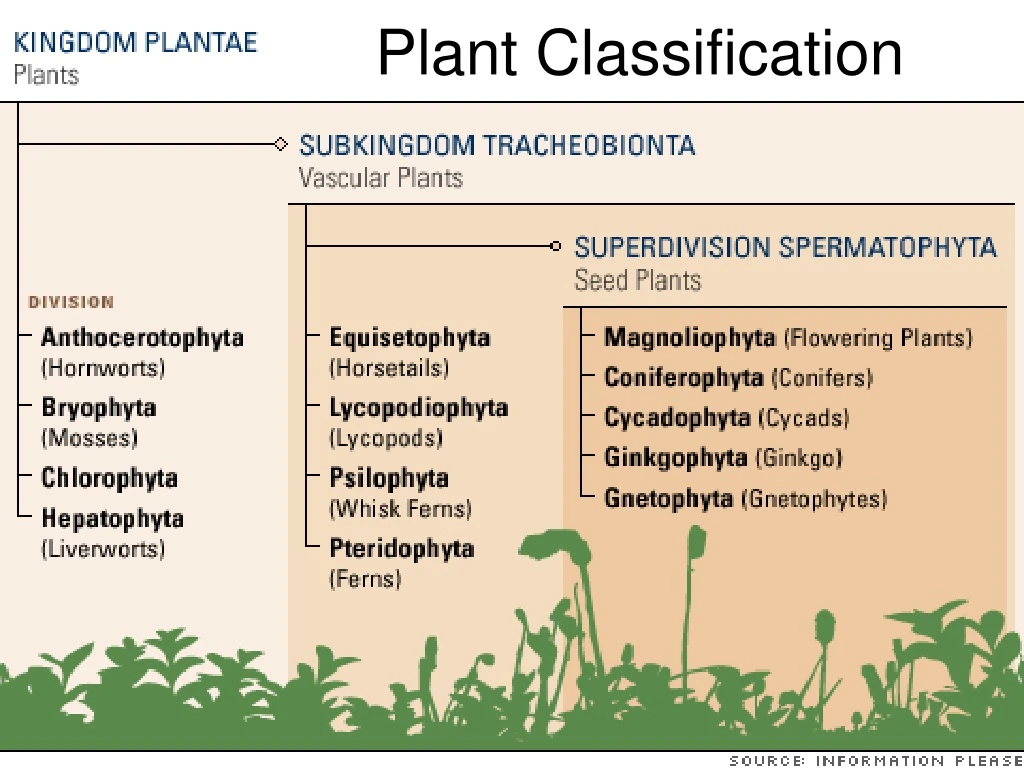
Group 1: Seedless, Nonvascular Plants • Live in moist environments • Liverworts • Hornworts • Mosses
Mosses • Nonvascular, seedless • Grow low to ground to retain moisture • Lack true leaves • Leaf-like structures only 1 cell thick • Rhizoids anchor into soil • Early inhabitant of new ecosystems (succession)
Group 2: Seedless, Vascular Plants • Vascular system allows nutrient transport to greater heights • Club mosses • Horsetails • Ferns
Ferns • Seedless, vascular plants • Vascular: allows taller growth • Rhizoids: underground stems draw nutrients • Fronds: leaves uncurl • sporangia on underside • Sori: clusters of sporangia
Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants • Gymnosperms • Cycads • Ginko • Conifers • Angiosperms
Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants • 1) Seed plants don’t depend on water to reproduce • Pollen (contains sperm) combines with egg • Egg hardens into a seed • 2) Nourishment and protection • Nourish: Nutrients inside seed for the embryo • Protection: Hard shell • 3) Allow dispersal • Carried by wind, water, animals
Type 1: Gymnosperms Seeds not enclosed in a fruit produced inside cones Cone = reproductive structure Male cones: produce pollen Female cones: produce eggs and seeds Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants
Gymosperm example: Conifers Cone plants Needle-like leaves Common to lumber industry Evergreen, Pine, Redwood, Cedar Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants
Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants • Type 2: Angiosperms (flowering plants) • Flower = reproductive structure • Protects gamete and fertilized eggs • Seeds enclosed in a fruit • Fruit: Plant ovary • Often attract animals to disperse the seeds inside
Fruit Production • In the seed • Embryo • Food supply • Surrounding ovary grows into a fruit • Fruit attracts animals to eat and spread the seeds Fruit seeds in fox droppings
Angiosperm types(flowering plants) • 2 groups: Monocots and Dicots (based on seed type) • Cotyledon: embryonic leaf • Monocots: embryo with 1 seed leaf • Dicots: embryo with 2 seed leaves
Angiosperm Life Spans • Three Life Span Types: • Annuals • 1 year: Mature…produce seeds…die • Biennials • 1st year: produces short stem, low growth leaves, food reserves • 2nd year: taller stem, leaves, flowers, seeds • Perennials • Live for more than 2 years
Flowers • Reproductive structure of flowering plants • Sepals • outer ring of leaves • protection • Petals • Inner ring of leaves • Brightly colored to attract pollinators • Open petals & sepals reveal male and female structures
Flowers • Female Carpel • Inner most part • Ovary: within the base (female gametophyte) • Style: long stalk • Stigma: sticky tip, collects pollen • Male Stamen • Surrounds carpel • Filaments: long stalks • Anther: produces pollen (male gametophyte)