A Crash Course in Electric Fields
60 likes | 293 Vues
A Crash Course in Electric Fields. By Leah Chernoff. What are Electric Fields? What do they do?. An E-field (E) exerts a force on charged particles in space. F=qE, when F is force and q is a charged particle.

A Crash Course in Electric Fields
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A Crash Course in Electric Fields By Leah Chernoff
What are Electric Fields? What do they do? • An E-field (E) exerts a force on charged particles in space. F=qE, when F is force and q is a charged particle. • E-fields are created by voltage differentials between points in space. E= -∆V/R, when ∆V is the voltage difference over a certain distance R.
Why Does Voltage Affect the E-Field? • For a point charge Q, V= kQ/R • For a point charge Q, E= kQ/R2 • So, E= -dV/dr (the negative accounts for the fact that electric fields are directed in the direction opposite to the direction of increasing voltage; that is, fields go from high voltage to low voltage.)
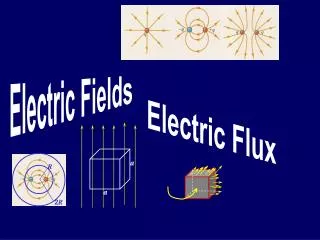
Field Lines • THEY CAN NEVER CROSS (like in Ghostbusters) • Negative charges always feel force opposite of the electric field • Double the field lines means twice as strong • Positive E-field --> lines go out; lines go in for negative E-field • Confused? Check out this cool simulation! http://www.vias.org/simulations/simusoft_efield.html
Example Problems There is a 10V voltage difference over 25 m. What is the magnitude of the electric field? ANSWER: E = ∆V/R; 10/25 = .4 V/m What is the force on a particle with charge -3 C in this field? ANSWER: F = qE F = -3(.4) = 1.2 N in the opposite direction of the field
Useful Equations and Facts • Units: N/C or V/m • E = -dV/dr = kQ/R2 • F = qE • Another cool simulation website: http://www.its.caltech.edu/~phys1/java/phys1/EField/EField.html