Macromolecules
220 likes | 391 Vues
Macromolecules. An amazing journey. Carbon!. *All living organisms contain carbon ! Chemistry of Carbon: Carbon can bond with many elements including other Carbons and can make 4 bonds!. Monomer and Polymers.

Macromolecules
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Macromolecules An amazing journey
Carbon! *All living organisms contain carbon! Chemistry of Carbon: • Carbon can bond with many elements including other Carbons and can make 4 bonds!
Monomer and Polymers • Monomers are single units and when you get lots of monomers together, you get a polymer • This process is called polymerization
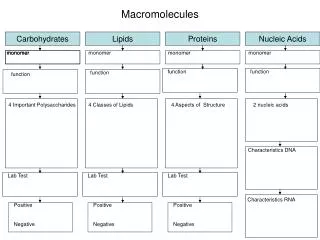
4 Types of Macromolecules • Carbohydrates • Lipids • Proteins • Nucleic acids
carbohydrates • Made up of C, H, and O in a ratio of 1:2:1 • Used by living things as their main source of energy
Composition of polymers • Monomer for carbohydrates: glucose Polymer for carbohydrates: -starch -cellulose -glycogen
Where do we see Glucose in our daily lives? Honey is Glucose with minor things added by the bees. If you put two glucose together (dissaccharides), you can get several different things Sucrose Lactose Fructose C12H22O11 C12H22O11 C12H22O11
If you stick several Glucose Molecules together we get……… Complex carbs also known as polysaccharides Function: long term storage of glucose used for different things Starch: Used by plants to store excess glucose Cellulose: Used by plants as a building material Glycogen: Used by animals to store excess glucose
What can you eat that has more energy than Carbs? FATS! Lipids (fats) can store enough energy that they can even hold a flame! Plants store fat as liquids. Animals store fat as solids
Lipids: -Composed of C and H -Known as fats, oils, waxes, and steroids -At least 1 C=C double bond makes a fat unsaturated
Lipid Composition: A Glycerin Molecule This acts as a connector for: Three Fatty acids The fatty acids contain several carbon groups that store energy in their bonds.
Uses for Lipids: 1. Energy Storage: We use fatty acids for energy when we work out and carbs. have been used up 2. Structure of cells: Every cell has a cell membrane that is made of Phospholipids. 3. Messengers: Steroids are lipids that carry messages through the blood stream
If I am trying to get strong, what do I eat? Proteins! Proteins are found in meat, nuts, beans Monomer: Amino acids:20 different molecules that combine to make all proteins These are just two
Proteins -Contain N, C, H, and O -Have an amino group(-NH2) & a carboxyl group (-COOH)
Protein Uses: • Control the rate of reactions (these are called enzymes) • Regulate cell processes • Form bones and muscle • Transport substances • Fight disease
Nucleic Acids Contain: H, C,O,N, and P Function: Store and transmit genetic information
Monomer • The monomer of a nucleic acid is a nucleotide • A nucleotide is composed of a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base
Thepolymerof a nucleotide is a DNA or RNA strand • DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid • RNA stands for ribonucleic acid