Macromolecules
280 likes | 399 Vues
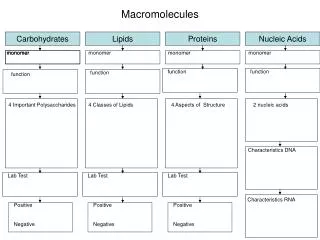
This guide provides an overview of macromolecules, which are essential organic compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen. There are four main types: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates act as short-term energy sources, while lipids serve for long-term energy storage and structural support. Proteins are crucial for body structures and enzymes assist in chemical reactions. Nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. Gain insights into how these macromolecules interact, form, and contribute to life processes.

Macromolecules
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction • Organic Compounds – contain carbon and hydrogen atoms • Inorganic Compounds – contain one or the other, but not both. • Most of your body’s molecules are organic.
Macromolecules • Built from small organic compounds by linking a lot of chains
Monomers • Large carbon compounds are built up from smaller simpler molecules. Mono = One
Polymers • When monomers bind to one another to form a complex molecule. • Poly = many • Consists of repeated linked units which bind forming Macromolecules. • Macro = large
Chemical reactions • Monomers link to form polymers through a chemical reaction called condensationreaction or dehydration synthesis. • Water is released or is a byproduct of the reaction.
Hydrolysis • Break down of some complex molecules • Hydrolysis is the reverse of a condensation reaction.
4 main types of macromolecules • 1. Carbohydrates • 2. Lipids • 3. Proteins • 4. Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates • Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in the proportion of 1:2:1 • Glucose formula: C6H12O6 • SHORT TERM ENERGY • MAIN Source of Energy
Monosaccharide's • Simple sugars Examples • Glucose: found in blood of animals • Galactose: found in milk • Fructose: found in fruit Isomers – same formula, but different structure
Disaccharides • Contain 2 monosaccharide's joined by dehydration synthesis. Examples • Lactose: found in milk • Sucrose: transported in plants
Polysaccharides • Carbohydrates formed from linking individual sugars into long chains. Examples • Starch: storage of glucose in in plants • Cellulose: contained in cell walls of plants • Glycogen: storage of glucose in animals (stored in the muscles and liver)
Lipids • Do not dissolve in water 3 Functions • Energy storage – LONG TERM ENERGY • Structural support for cell membranes • Serve as a reactant (starting material) for metabolic reactions
Lipids Cont. • Phospholipids make up the cell membrane.
Fatty Acids • Building blocks that make up most lipids • Classified as either saturated or unsaturated
Saturated Fatty Acids • Have the maximum number of bonds possible • They are full • Usually solid at room temp • Most come from animal products
Unsaturated Fatty Acids • Have double bonds in the carbon chain • Most are liquid at room temp • Usually referred to as oils
Triglycerides • Tri = 3 • Common lipid that contains fatty acids • Glycerol linked to 3 fatty acids in the shape of an E by condensation reaction.
Proteins • Composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen atoms • Construction materials for body part like hair, skin, nails, and blood
Amino Acids • The building blocks that make up most proteins. • 20 different kinds of amino acids
Enzymes • Important group of proteins • Help control chemical reactions by acting as catalysts. • Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy. • Enzyme rates are affected by Ph, hot and cold temperatures.
Enzymes - Add • Substrates – reactants of enzyme – catalyzed reactions. • Reduces the energy needed for the reaction. • Works like a lock and key.
VERY IMPORTANT • Proteins DO NOT produce, store, transmit, or have anything to do with ENERGY. • Do not get confused with protein bars!!!
Nucleic Acids • Complex organic molecules that store genetic information in the cell.
Nucleotides • Nucleotides are the building blocks that make up most nucleic acids • Consist of sugar, base, phosphate
3 main types of Nucleic Acids • 1. DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid • Genetic info inside the nucleus of cells 2. RNA – Ribonucleic acid - code for protein synthesis 3. ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate - Contains a base, sugar, and 3 phosphates - ATP is used as energy for the cell