Enhancing Electronic Patient Records in Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview of Project Strategies
190 likes | 324 Vues
This document provides a detailed examination of the Electronic Patient Records (EPR) project initiated at St. Olav Hospital. It highlights the evolution of the project from the MEDINA and MEDAKIS initiatives, collaboration with Siemens, and adaptation to organizational changes. Key components include user access management, documentation protocols, and e-learning strategies for effective training of healthcare professionals. By creating a comprehensive digital environment, the project aims to improve efficiency, reduce paper usage, and enhance patient care while navigating the challenges of integration and user adaptation.

Enhancing Electronic Patient Records in Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview of Project Strategies
E N D
Presentation Transcript
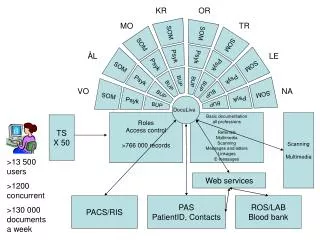
KR OR MO TR ÅL LE VO NA SOM SOM SOM SOM SOM SOM SOM SOM Psyk Psyk Psyk Psyk Psyk Psyk Psyk Psyk BUP BUP BUP BUP BUP BUP BUP BUP Roles Access control >766 000 records Basic documentation all professions Referrals Multimedia Scanning Messages and letters Linkages E-messages DocuLive Scanning Multimedia TS X 50 >13 500 users >1200 concurrent >130 000 documents a week Web services PACS/RIS PAS PatientID, Contacts ROS/LAB Blood bank
Patient overview Integration LAB Integration RTG/X-ray Digital discharge notes PAS LAB RTG Prim. lege Content in today’s DocuLive Users and access control Documentation all professions Scanning Multimedia Messages, letters Documentation logistics Internal referrals Prescriptions RTV forms
Electronic patient records- history, status and challenges Guest lecture Health informatics 1. september 2005 project manager Rut Naversen Project introduction EPR St. Olav Hospital
Some background • MEDINA project from 1996 • MEDAKIS project from 1998 • Joint development project for the 5 regional hospitals • Industrial partner: Siemens • Regional EPR project from 2000 • Reorganization due to State takeover of hospitals • Wish for common EPR and solutions in Helse Midt-Norge (Central Norway Regional Health Authority) • Another reorganization in 2003 • HEMIT 1. juli 2003 • New regional project manager HEMIT: Terje Dale • New project manager St. Olav: Rut Naversen R Naversen
Project owner: Helse Midt-Norge RHF Steering committee: Regional steering committee for PACS/RIS and EPR Project manager: Terje Dale, HEMIT Reference group Product development. Introduction Scanning Prj. Mng. Workflow Prj. Mng. Introduction NT: Ingunn Bjørkli Introduction XX: ?? Reference group Reference group Reference group Reference group Project group Project group Project group Project group Project organization R Naversen
Organization St. Olav • IT steering committee • Stein Sundmoen (finance director/manager) • Ola Bergslien (chief medical officer/system owner) • Gudmund Marhaug (director Children and youth) • Arild Faxvaag (senior physician Department of rheumatology/NTNU) • Liv Sjøvold (divisional manager Psychiatric health care) • Ragnhild Brå Vardehaug (Spec.cons./nurse) • Ida Lise Salberg (General manager/Orkdal hospital) • Thore Smevik (IT strategist/secretary) R Naversen
Departmental EPR groups • Multidisciplinary • Doctor, nurse, secretary • Plan introduction in coordination with line management • Introduce new software components • Routine adaptation • Organizational adaptation • Work on record content quality • Requests for changes to production functionality R Naversen
Superusers – new in 2005 • 25 secretaries and 76 nurses • teach new employees, temps and students from own occupational group within own department • Secretary superusers are also responsible for educating doctors • responsible for follow-up/guidance of new and existing EPR users • train colleagues when introducing new software modules • follow up on document flow and work lists R Naversen
Introductory activities • When new functionality is to be introduced • Assess need for pilot • Prepare user documentation • Prepare paramount procedures and guidelines • Disseminate information (meetings, “Kilden” etc.) • Educate superusers • Pre and post planning and follow-up on department/clinic • Evaluate the delivered product and project introductory activities • Provide feedback to the regional project on eventual required changes R Naversen
eLearning • www.helse-midt.no/elaring • Practice module • Theory module • Certification module (intranet) • Regional project manager Jane Wik R Naversen
Progress • The new university hospital • Comprehensive use of IT tools is a design prerequisite for area dimensioning • An total efficiency gain of 30 % is assumed – the use of a complete EPR by all record users is presumed to be the most important efficiency improvement measure • No areas for paper archives • Patient records • Case files • Patient areas are not dimensioned for temporary paper storage R Naversen
Paperless patient record within 1. Januar 2007 …although not a paperless hospital…
Status from user database, June 2005 • Today, all departments except Psychiatric healthcare are using DocuLive • Somatic: a total of ca. 5000 users • Assistant nurses – ca. 590 • 40 % are users - divided on 75 % authors 25 % readers • Nurses – ca. 3000 • Roughly 80 % authors, 100 % with access rights • Doctors – ca. 800 • Other occupational groups ca. 800 R Naversen
Towards the paperless hospital R Naversen
Towards the paperless hospital R Naversen
Challenges • Relocation determines deadline/progress rate and sequencing of training • Lab center relocates Sep/Oct 2005 • Women-children relocates Oct/Nov 2005 • Scanning – paperless patient record • Dermatology department pilot spring 2004 • Lab center • Medical genetics • Women-children • Children and youth department • Gynecological department • Access to EPR not stable – backup paper solution still required for the following months R Naversen
Challenges • Training – capacity for basic training has increased over the last year • Diversified offerings • E-learning • Decentralized guidance for super user follow-up • Phasing out of introductory project course room classes • Remaining author training • Somatic: ca. 500 nurses + 200 assistant nurses • Psychiatric health care ca. 800 in total • Distributed on 350 caregivers and 450 environment therapists • Maintenance training – ca. 1300 a year! • Equipment • The XP project has lead to a hospital-wide renewal of machinery equipment by June 2005 • There will also be an increase of PCs in the old hospital as units relocate to the new hospital R Naversen
Minister of Health and Care Services, Ansgar Gabrielsen • S@mspill 2007 shall secure • Strengthened and efficient cooperation • between different disciplines and administrative areas • Improved user contact • Quality improvements • Inquiry into investment effects… • Changing work processes and routines might be the biggest challenge. Up to 90 percent of the resource allocation in the wake of a successful IT implementation will often be in skills development and organizational development R Naversen