IDEF0 Activity Modeling...
990 likes | 1.7k Vues
IDEF0 Activity Modeling. What are Methods? Why IDEF?. Method: A structured approach to accurately capturing the knowledge about the characteristics of the real-world.

IDEF0 Activity Modeling...
E N D
Presentation Transcript
IDEF0 Activity Modeling... CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
What are Methods? Why IDEF? • Method: A structured approach to accurately capturing the knowledge about the characteristics of the real-world. • IDEF: The IDEF Family of Methods was co-developed by industry and government to provide a comprehensive yet flexible framework for describing, analyzing, and evaluating business practices. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
What is an Activity Model? A representation of the activities and the relationships between and among those activities in an existing or planned system. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Benefits of Activity Modeling • Document current activities for standardization and provide guidelines for new activity users to reduce the learning curve. • Capture and analyze AS-IS activities. • Design/Redesign activities for TO-BE scenarios. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
What is IDEF0? • An activity modeling method. • Supports descriptions at any desired level of detail through Decompositions. • Provides both a process and a language for constructing a model of the activities and their interrelationships. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
What is a Generic Activity Modeling Tool? • Complies with the method standard. • Provides background quality checking and advisory support. • Employs a SmartDraw capability. A generic activity modeling tool automates the IDEF0 method, and . . . CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Why Develop An Activity Model? • To identify, document, and communicate what an enterprise does. • To facilitate the collection of data needed to perform functional analysis. • To identify value added and non-valued added activities. • To identify activities or functions that need to be improved. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
What is represented in IDEF0 • Functions - Decisions, Actions, or Activities of the domain • Objects - Physical or conceptual of the domain • Roles that objects stand-in relative to a functions • Relations between functions formed by objects • Relations between functions formed by the composition relationship CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
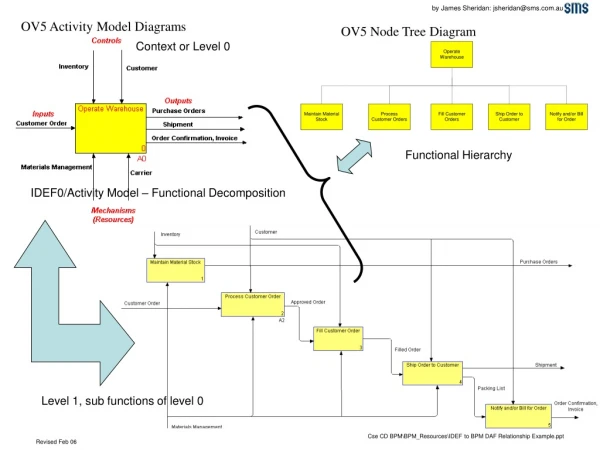
IDEF0: Provides Both a Procedure and a Language for Constructing a Model of the Decisions, Actions, and Activities in an Organization. Customer Expectations Understanding of Customer Requirements Needs Establish Requirements Requirements A1 Design System Alternative Technologies Contract for Tradeoff Decisions Knowledge of Previous Design A2 Design Build System Raw Material Product A3 Analysis Methods Design Methods Fabrication Methods CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Components Model = A collection of diagrams, glossary, and text along with the context, viewpoint, and purpose statements CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Components:Context, Purpose and Viewpoint CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Establishing the ModelObjectives Viewpoint: • Determines what can be seen and from what perspective. Purpose: • Establishes the goal of the communication intended by the model. • Defines why the model is being developed. • Specifies how the model will be used. Context: • Establishes the scope of a model. • Establishes the subject as part of a larger whole. • Creates a boundary with the environment. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Personnel Regulations Department Policy Supervisor Instructions Manning Conditions Applicant Data Perform Personnel Actions Customer Request Personnel Action Employee/Position Data Reports Supplies & Equipment Personnel Office Staff Information System Context, Purpose, and Viewpoint: Context The context defines the boundaries of your model, i.e. what will be included in the model. For example, Employee/ Position Data comes from outside the model. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Context, Purpose, and Viewpoint: Context • Scopes the model and defines the boundaries. • If the scope is too big, the model becomes too complex and resource-intensive. • If the scope is too small, the model becomes trivial. • Determining the context is the most critical step in Activity Modeling. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Personnel Regulations Department Policy Supervisor Instructions Manning Conditions Applicant Data Perform Personnel Actions Customer Request Personnel Action Employee/Position Data Reports Supplies & Equipment Personnel Office Staff Information System Context, Purpose, and Viewpoint: Purpose Purpose = the reason to develop this particular activity model Purpose: To document the activities associated with managing Personnel Actions and identify non-value added activities that might be eliminated CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Personnel Regulations Department Policy Supervisor Instructions Manning Conditions Applicant Data Perform Personnel Actions Customer Request Personnel Action Employee/Position Data Reports Supplies & Equipment Personnel Office Staff Information System Context, Purpose, and Viewpoint: Viewpoint Viewpoint = the perspective of the person/group developing the model Purpose: To document the activities associated with managing Personnel Actions and identify non-value added activities that might be eliminated Viewpoint: Personnel Officer CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Components of the IDEF0 Graphical Modeling Language CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Diagram Syntax Controls Outputs Inputs Function or Activity (Verb Phase) Mechanisms CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Activity (Verb Phase) Activity Represents an action, function, or operation. Represented by a box and labeled as a verb phrase. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Learn IDEF0 Methodology Components A function/activity = a labeled box... e.g., ... that represents an action, process, or operation. It is always labeled with a verb phrase CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Learn IDEF0 Methodology Components A concept/constraint = an arrow... ... that bounds or constrains the function/activity. They are always labeled with a noun or noun phrase. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Activity (Verb Phase) Input Input An input is any real object or data needed to perform an activity. An input is transformed through the completion of the activity. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Learn IDEF0 Methodology Components Inputs are real or conceptual objects or data transformed by an activity... New Student ...they undergo some form of change or transformation to form an output when the activity is accomplished CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Activity (Verb Phase) Output Output Input An output results from the completion of the activity. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Learn IDEF0 Methodology Components Outputs result from the accomplishment of the activity... New Student Trained Student ...although inputs are transformed into outputs, there is not a one-to-one relationship (e.g. several inputs become a single output) CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Activity (Verb Phase) Control Control Output Input A control directs, guides, or initiates the activity. They may also be combined in some way with input(s) to result in an output. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Learn IDEF0 Methodology Components Controls direct, guide, or initiate the activity... Training Regulations New Student Trained Student ...they may also be combined in some way with inputs to result in an output. Their primary function is to “trigger” “regulate” or otherwise influence the execution of the activity. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Activity (Verb Phase) Mechanism Control Output Input Mechanism A mechanism indicates how the activity is accomplished. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Training Regulations Learn IDEF0 Methodology New Student Trained Student Instructor & Textbooks Components Mechanisms are used to accomplish the activity... ...they represent the means by which the activity is accomplished. They may be consumed in the process of accomplishing the activity. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Minimally, we must have... Control Output Activity CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Functional Decomposition CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Functional Decomposition • Used to further define an activity by dividing it into its sub-activities. • Decomposition insures the gradual, systematic exposition of detail required to understand and communicate what activities are being performed. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
3 Decomposition More General (Parent) A0 A-O A1 A2 A3 A4 More Detailed (Child) A0 A-O 2 A41 4 A42 A43 A4 CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Functional Decomposition • Each activity is composed of distinguishable sub-activities • A “parent” activity is decomposed into three to six “child” activities • Each child can become a parent and be further sub-divided CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Decomposition Example Company guidelines Budget guidelines Maintain Accounts Payable Correct ledger Purchase request Payment A0 Accounting staff CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Company guidelines Process guidelines Order Process request Purchase request Invoice guidelines A1 Process invoice Invoice Payment A2 Ledger guidelines Apply purchase to books Correct ledger A3 Accounting staff Decomposition Example CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Activity Hierarchy • Each activity in a model is uniquely identified with an Activity Number (i.e., A0, A1, A12, etc.). • Each activity can be uniquely placed within a model according to its relative decomposition number. • An activity is depicted only once in an activity model. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A11 A21 A31 A41 A51 A42 A52 A12 A22 A32 A13 A43 A53 A23 A33 A54 A44 A24 Activity Hierarchy within a Model A0 Perform Personnel Actions A1 Hire People A11 Review Applicant Information A12 Verify Past Employment A13 Interview Applicant A2 Fire People A21 Review Work History A22 Create Dismissal Documents A23 Counsel Employee A3 Promote People A31 Create Awards Package A32 Arrange Ceremony A33 Submit Paperwork A34 Insure Raise Action Completed Indented List Node Tree An activity is depicted only once in an activity model. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
A0 A - 0 3 3 3 DiagramNumbering A-O 2 4 A1 4 A2 A3 A0 A-O 2 4 A-O A31 2 4 A0 4 A11 A32 4 A12 A33 A13 A3 A1 CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Concept Hierarchy within a Model • Concepts (inputs, controls, outputs, and mechanisms) are not uniquely identified within a model, but are identified between parent and child activities. • Each concept is identified by a letter and number combination that specifies the concept’s relative position on the parent diagram. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
C1 Company guidelines Process guidelines Purchase request Order Process request I1 Invoice guidelines A1 Process invoice Invoice Payment O2 A2 Ledger guidelines Apply purchase to books Correct ledger O1 A3 Accounting staff M1 Concept Hierarchy within a Model These designations are called ICOM codes CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Tunneling Tunneled concepts... • Are intended to simplify a diagram. • Communicate functional relationships between activities without cluttering every diagram in-between. • Are not intended to be used as a means of “eliminating” unnecessary concepts from a model. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Tunneling • A concepts tunneled at the unconnected end indicates that the concept is not (will not be) shown at a higher level • A concepts tunneled at the connected end indicates that the concept is not (will not be) shown at a lower level CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Company guidelines Process guidelines Order Process request Purchase request Invoice guidelines A1 Process invoice Invoice Payment A2 Ledger guidelines Apply purchase to books Correct ledger A3 Accounting staff Company guidelines Tunneling Example Budget guidelines ( ) Correct ledger Purchase request Maintain Accounts Payable C1 Payment A0 Accounting staff ( ) I1 ( ) O2 O1 CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design M1
Bundling & Unbundling • Bundling allows us to group several concepts into a larger “set” of concepts. • Unbundling allows us to decompose a general concept into its component concepts. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Company guidelines Process guidelines Process request Invoice guidelines A1 Process invoice A2 Ledger guidelines Apply purchase to books A3 Company guidelines Bundling Example Budget guidelines ( ) Correct ledger Maintain Accounts Payable Purchase request Payment A0 Accounting staff CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Components New Student: An employee of the company that has been directed, or volunteered, to participate in training Glossary ... Instructor & Textbooks: The person responsible for teaching students and the documents, books, or other printed material used during the class ...documents the definition or characterization of one of the IDEF0 components of your effort. Each component in your model must have a glossary! What exactly do you mean by New Student? It’s defined in the glossary. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Components The input “personnel folder” is not an input to the A134 activity “Monitor Supply Consumption” because this group of information is not transformed in any way, or needed by these activities. Text Elaboration... ...is associated with a “diagram”. It describes the things that may not be apparent, but are necessary, to know to understand a diagram. - Why are these inputs only on boxes 1 and 2, but not 3? CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
Some Basic Rules • Excluding the A-0 diagram, which has only one activity box, all other diagrams should have no less than three and no more than six Activity boxes. • Each activity box must have at least one control and one output, but no more than six of each type of concept. • Every diagram in a model must comply with the model’s overall viewpoint, purpose, and context. CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design
IDEF0 Model Development Process CS133340 - Structural & Functional Design