Six Sigma Example
1.09k likes | 1.64k Vues
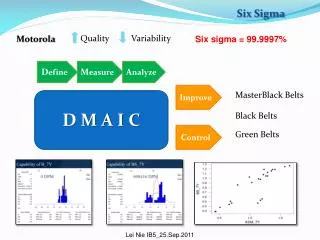
Six Sigma Example. Project Report Presentation. Project Number: ABC-123 Project Name: Company New Business Improvement Project Team Leader: Tom Jones Project Sponsor: Sally Run. Six Sigma Roadmap. Define. Measure. Analyze. Improve. Control. Operational Definitions of Key Terms.

Six Sigma Example
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Six Sigma Example Project Report Presentation Project Number: ABC-123 Project Name: Company New Business Improvement Project Team Leader: Tom Jones Project Sponsor: Sally Run
Six Sigma Roadmap Define Measure Analyze Improve Control Company New Business Improvement 2 .PPT
Operational Definitions of Key Terms • Cat 5: Category 5 proposals • COPQ: Cost of Poor Quality • Delivery SLA: Deliver proposal within agreed time frame, default: 10 business days • IS: Infrastructure support • On Time delivery: Proposal delivery within agreed timeframes, either to agreed service level of 10 business days between requirement confirmation date and first delivery date or as otherwise agreed • RFP: Requirements for Proposal Form, to communicate project • PMO: Proposal Management Office Company New Business Improvement 3 .PPT
Project Goal & Scope • Problem Statement: • The Company Bid & Proposal process requires improvements in the low proposal approval rate (67% overall proposal approval rate), slow delivery speed (only 64.6% of proposals are delivered in the agreed timeframe) and cost (overspend forecasted against FY08 B&P budget). • Goals/Objective(s): • Improve delivery speed to 95% of Cat 5 proposals delivered in agreed timeframe and approval rate to 94% of Cat 5 proposals approved by the end FY08 (Mar 2008). • In Scope: • Company account • Proposal management process for Cat 5 proposals • Items Out of Scope: • Cat 1-4 proposals • Database process • Other accounts Company New Business Improvement 4 .PPT
Financial Impact: Business Case or COPQ Calculation • Calculation of potential Cost reduction and Revenue increase • Assumptions: • Reduction of wasted effort for declined proposals leads to cost savings • Reduction of declined proposals leads to increased revenue • Half the avoided declined proposals can be won • Data: • Cat 5 only, source: Database, P/L cost report • Proposal data for Apr06 – Aug07 • hourly cost only (no allocations, leave pay, …) Potential Cost Reduction of $69,000 and Revenue Increase of $662,582 Company New Business Improvement 5 .PPT
High Level Process Map (SIPOC) Complete Commercial Qualification Complete Technical Qualification Confirm Customer Requirements Design Project/ Solution Conduct Internal Reviews The scope of this project covers the Company steps of the Bid and Proposal process Company New Business Improvement 6 .PPT
Voice of the Customer—CTQ Company New Business Improvement 7 .PPT
Six Sigma Roadmap Define Measure Analyze Improve Control Company New Business Improvement 8 .PPT
Translate Ys From CTQs VOC quotes could be translated into 2 Ys Company New Business Improvement 9 .PPT
Project Y (or Ys) in Y=f(x) • Y1: Proposal Acceptance Rate = accepted Cat 5 proposals / all Cat 5 proposals accepted and declined x 100; calculated monthly • Y2: Delivery in SLA timeframe = Cat 5 proposals delivered in agreed timeframe / total Cat 5 proposals delivered x 100; calculated monthly, as calculated by Database system (see operational definition) Company New Business Improvement 10 .PPT
Detailed Process Map: Proposal Management Cat 5 Commercial Qualification often rushed Requirements often not well understood Handovers often via Database system, not via verbal comms Even small Cat5 proposals are reviewed Often Rework is not captured properly Final Reviews by PM and Architects are often missed Work often delegated to inexperienced Solution Designers Process workshop immediately identified key issues Company New Business Improvement 11 .PPT
Data Collection • Process Measures Defined • Input Measures: • Proposal Requests: Number of proposal requests per month • Process Measures: • Withdrawn Proposals: Number of proposal requests withdrawn per month • Commercial Qualification: Number of proposal requests with completed Commercial Qualification documentation • Customer Requirement Confirmation: Business Days between Proposal Request Date and Confirmation Date • Proposal Reviews: Number of Proposal Reworks • Delivery Time: Days between Customer Requirement Qualification and Proposal delivery • Output Measures: • Approvals: Number of proposals accepted • Declines: Number of Proposals declined • Proposal cost: Labor cost per Proposal • Proposal Revenue: Expected Revenue per Proposal Company New Business Improvement 12 .PPT
Data Collection (continued) • CTQs and Specifications • CTQ #1: Proposals delivered in individually agreed timeframe • Specification: Proposals are delivered to the customer before or on the agreed delivery date (SLA or individually agreed delivery time) • Defect: Proposal delivery date later than agreed delivery date • Upper barrier: 100%, LSL: 85% • CTQ #2: Customer Requirements confirmed • Specification: Proposals are confirmed with the customer on the agreed Customer Requirements Confirmation date • Defect: Proposals are not confirmed with the customer on the agreed Customer Requirements confirmation Date • Upper barrier: 100%, LSL: 95% • CTQ #3: Commercial Qualification • Specification: Proposals are fully commercially qualified • Defect: Proposals are not fully commercially qualified • Upper barrier: 100%, LSL: 95% • CTQ #4: Proposal Reviews • Specification: Proposals are reviewed by the required people • Defect: Proposals are reviewed too often or not by the right people • Upper barrier: 100%, LSL: 95% Company New Business Improvement 13 .PPT
Plan for Data Collection • Questions to be answered: • Y1: Withdrawn proposals • How often is a proposal withdrawn before delivery to the customer? • What are the reasons for the withdrawals? • How much effort/cost is wasted on withdrawn proposals? • Y1: Declined proposals • How often are proposals declined? • What are the reasons a customer declines a proposal? • How much effort/cost is wasted on declined proposals? • Y2: Delivery timeframe • How long does the delivery of a proposal take? • How long does it take to deliver a proposal after the requirements are confirmed with the customer? • How often is a proposal late, eg delivered after the agreed delivery date? • Y2: Proposal rework • How often are proposals rejected by the customer and need to be reworked? Company New Business Improvement 14 .PPT
Plan for Data Collection (continued) Company New Business Improvement 15 .PPT
Measure Process Capability Proposal 123984: confirmed outlier Proposal 124286: confirmed outlier • Y2 Proposal Delivery Time Proposal Delivery Time displays two outliers Company New Business Improvement 16 .PPT
Measure Process Capability (continued) Plots of Proposal Delivery Time (2 outliers removed) Company New Business Improvement 18 .PPT
Measure Process Capability (continued) Process Capability (12 mth average) Total Proposals Delivered: 230 Delivery SLA met: 130 On Time Ratio: 57% DPMO: 435,000 Y2 Sigma: 1.66 Proposal Delivery Service Level: 10 days from Requirements confirmation or as agreed The Proposal Delivery to an Agreed Date is getting worse Company New Business Improvement 19 .PPT
Measure Process Capability (continued) Qualification Proposal Development Reviews Commercial Qualification Technical Qualification Customer Requirement Confirmation Project/ Solution Design Internal Reviews Delivery to Customer • Process Cycle Time Analysis • Analysis of a sample of 26 proposals: 13 accepted, 13 declined • 3 key process steps: Request Qualification, Proposal Development, Reviews • Rework analysis • 46% (12 or 26 proposals) of the sampled proposals had at least 1 rework step (data not shown) Many handovers in the Request Qualification and the Review phases as well as the Rework amount appear to be a cause for delay Company New Business Improvement 20 .PPT
Measure Process Capability (continued) Process CapabilityProposal Acceptance Proposals Accepted 189 Proposals Declined: 33 Acceptance Ratio: 85% DPMO: 150,000 Y1 Sigma: 2.54 • Y1 Acceptance Rate The high number of declined proposals over the last 12 months indicates lost efforts Company New Business Improvement 21 .PPT
Measurement System Analysis • Risk of poor Data • Data Generation: Low risk: All data is entered into Database, workflow is automated and all Entries are time stamped. • Data extraction: All data extracts are carried out via automated Database and SAP reports • Data manipulation: All manipulation of data is carried out in EXCEL • MSA • Incorrect count of delivered Proposals (calculate business days, exclude ‘on hold’ days): based on Extract from Database (801 line items), remove Requests for Change, Budget advices, proposals delivered before Jan 07 or after Aug 07, Cat 1-4 proposals) • Error in Database functionality: 2 proposals didn’t have a delivery date, even though they were delivered MSA failed due to wide variance in the calculated number of proposals. Work instructions were created to remove variance. Calculations were not re-tested, due to a changed procedure and staff changes. Company New Business Improvement 22 .PPT
Potential Xs: XY Prioritization Matrix The team agreed on seven potential causes to be analyzed further Company New Business Improvement 26 .PPT
Potential Xs: Selection of Xs Seven potential causes will be analyzed further Company New Business Improvement 27 .PPT
Potential Xs—Theories To Be Tested Seven potential causes will be analyzed to identify the Root Causes (vital few Xs) Company New Business Improvement 28 .PPT
Six Sigma Roadmap Define Measure Analyze Improve Control Company New Business Improvement 29 .PPT
Theories To Be Tested X1 Poorly understood requirements X2 Poor Commercial Qualification X6 Lack of Proposal Ownership Y1 Poor Proposal Acceptance X3 Missing Communication in Company A survey was considered but not used due to political and timing reasons X5 Not enough contact with the customer Y2 Proposals are delivered late X4 Too much Rework X7 Financial & Comm. Reviews not needed • Theories for Causal Relationships to be Analyzed Seven potential causes leading to nine theories to be tested. The team decided against using X6 for further analysis (covered in X1, X2, X3, x5). Company New Business Improvement 30 .PPT
Data Collection Plan for Analyze Phase Company New Business Improvement 31 .PPT
Test of Theories • Y1 Acceptance Rate=f(X1 Understanding of Customer Requirements) • Theory:No difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate after introduction of customer requirement confirmation date • Ho: No difference in Proposal Acceptance rate due to customer requirement date • Ha: Significant difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate due to customer requirement date • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: -0.0793651 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.284933, 0.126203) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = -0.76 • P-Value = 0.449 • NOTE * The normal approximation may be • Inaccurate for small samples. • Fisher's exact test: P-Value = 0.683 • Statistical Conclusion: alpha = 0.05. P is greater than 0.05 fail to reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: The Proposal Acceptance rate does not change due to customer requirement date. Company New Business Improvement 32 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y2 Delivery SLA=f(X1 Understanding of Customer Requirements) • Theory:No difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to customer requirement date • Ho: No difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to customer requirement date • Ha: Significant difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to customer requirement date • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: 0.211640 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.0667272, 0.490008) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = 1.49 • P-Value = 0.136 • Statistical Conclusion: alpha = 0.05. P is greater than 0.05 fail to reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: There is no difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to customer requirement date. Company New Business Improvement 33 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y1 Acceptance Rate=f(X2 Commercial Qualification) • Theory:No difference in the Proposal Acceptance Rate after introduction of Commercial Qualification meetings (Commercial Qualification meetings were introduced Sept 2007) • Ho: No difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate after introduction of CQ meetings • Ha: Significant difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate after introduction of CQ meetings • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: 0.0638985 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.0522402, 0.180037) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = 1.08 • P-Value = 0.281 • Statistical Conclusion: alpha = 0.05. P is greater than 0.05 fail to reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: There is no difference in the Proposal Acceptance rate after the introduction of Commercial Qualification meetings. Company New Business Improvement 34 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y1 Acceptance Rate=f(X3 Missing Communication Within Company) • Theory:No difference in the Proposal Acceptance Rate due to RFP document usage. • Ho: No difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate due to RFP document usage • Ha: Significant difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate due to RFP document usage • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: -0.268775 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.509869, -0.0276799) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = -2.18 • P-Value = 0.029 • Statistical Conclusion: alpha = 0.05. P is smaller than 0.05 reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: There is significant difference in the Proposal Acceptance rate after introduction of good documentation of requirements in RFP documents. Company New Business Improvement 35 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y2 Delivery SLA=f(X3 Missing Communication Within Company) • Theory:No difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to RFP document usage. • Ho: No difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to RFP document usage • Ha: Significant difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to RFP document usage • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: 0.0135135 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.258433, 0.285460) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = 0.10 • P-Value = 0.922 • Statistical Conclusion: 0.05. P is greater than 0.05 fail to reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: There is no difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to the use of RFP document for requirement documentation. Company New Business Improvement 36 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y1 Acceptance Rate=f(X4 Rework) • Theory:No difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate because of Proposal Rework • Ho: No difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate due to the occurrence of rework • Ha: Significant difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate due to the occurrence of rework • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: -0.0755556 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.343644, 0.192533) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = -0.55 • P-Value = 0.581 • Statistical Conclusion: 0.05. P is greater than 0.05 fail to reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: There is no difference in the Proposal Acceptance rate due to the occurrence of Proposal rework. Company New Business Improvement 37 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y2 Delivery SLA=f(X4 Rework) • Theory:There is no difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance because of Rework • Ho: No difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to Rework • Ha: Significant difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to Rework • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: -0.175556 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.441630, 0.0905194) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = -1.29 • P-Value = 0.196 • Statistical Conclusion: 0.05. P is greater than 0.05 fail to reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: There is no difference in the Proposal Delivery SLA performance because of the occurrence of Rework. Company New Business Improvement 38 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y1 Acceptance Rate=f(X5 Missing Customer Contact Before Proposal Delivery) • Theory:No difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate due to customer contact before proposal delivery. • Ho: No difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate due to customer contact before proposal delivery • Ha: Significant difference in Proposal Acceptance Rate due to customer contact before proposal delivery • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: -0.0204082 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.250612, 0.209796) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = -0.17 • P-Value = 0.862 • Statistical Conclusion: 0.05. P is greater than 0.05 fail to reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: There is no difference in the Proposal Acceptance rate due to customer contact before the delivery of the proposal. Company New Business Improvement 39 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y2 Delivery SLA=f(X5 Missing Customer Contact Before Proposal Delivery) • Theory:No difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to customer contact before proposal delivery. • Ho: No difference in Delivery SLA performance due to customer contact before proposal delivery • Ha: Significant difference in Delivery SLA performance due to customer contact before proposal delivery • Analysis: • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: -0.539683 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.662759, -0.416606) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = -8.59 • P-Value = 0.000 • Statistical Conclusion: alpha = 0.05. P is smaller than 0.05 reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: Customer contact before the delivery of the proposal does significantly improve the Delivery SLA performance. Company New Business Improvement 40 .PPT
Test of Theories (continued) • Y2 Delivery SLA=f(X7 Financial/Commercial Reviews) • Theory:No difference in Proposal Delivery SLA performance due to Financial and Commercial review (F&C review) steps • Ho: No difference in Delivery SLA performance due to F&C Review steps • Ha: Significant difference in Delivery SLA performance due to F&C Review steps • Analysis: • Sampled proposals: 53 • Average Duration of Financial and Commercial reviews: • 0.98 business days • Test and CI for Two Proportions • Difference = p (1) - p (2) • Estimate for difference: 0.132075 • 95% CI for difference: (-0.0498017, 0.313953) • Test for difference = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = 1.42 • P-Value = 0.155 • Statistical Conclusion: alpha = 0.05. P is greater than 0.05 fail to reject Ho • Practical Conclusion: There is no difference in the SLA performance because of the Financial and Commercial Review steps. Company New Business Improvement 41 .PPT
Summary of Testing Results The team decided to continue looking for solutions for the proven causes X3, X5, and also for causes X1, X2, X4, and X7. Company New Business Improvement 42 .PPT
Vital Few Xs • Y=f(X1,……Xn) • Vital Few Xs are: • X1: Confirmation of Customer Requirements • X2: Commercial Qualification • X3: Missing Communication Within Company (proven cause) • X4: Rework • X5: Missing customer contact before delivery (proven cause) • X7: Too many reviews Company New Business Improvement 43 .PPT
Six Sigma Roadmap Define Measure Analyze Improve Control Company New Business Improvement 44 .PPT
Improvement Strategies for Proven Xs The team decided to continue looking for solutions for the proven causes X3, X5, and also for causes X1, X2, and X7. Company New Business Improvement 45 .PPT
Solution Alternatives The team workshopped alternative solutions for the various causes X Company New Business Improvement 46 .PPT
Possible Solutions Matrix (vs. Proven Xs) Company New Business Improvement 47 .PPT
Selection Criteria • The team felt that alternatives selected should fulfill the following criteria’s: Company New Business Improvement 48 .PPT
Selected Solution and Selection Process • Selected Solution • All solution alternatives proposed by the team have been accepted by the Champion. • Selection Process • Tools Considered: • Pugh Concept Selection matrix (shown on next slide) • Criteria Based Selection matrix • Given that all “must” criteria were met, the Pugh matrix was the preferred tool. The team felt that all solution alternatives satisfy the Must criteria, and a Pugh matrix process was chosen to select the strongest solutions. Company New Business Improvement 49 .PPT
Evaluation Using Pugh Concept Selection Matrix Quick Win Phase 2 Solution Phase 1 solutions The team selected five improvement alternatives based on the Pugh matrix process and one other improvement as a quick win. Five improvements will be implemented in the first project phase and one in a separate project. Company New Business Improvement 50 .PPT
Pay-off Matrix of Selected Solutions Key: Brown Solutions are Phase II High The high cost/ high effort solutions involve significant customer negotiations. One of them will be implemented in Phase 2. Benefit Low All low cost solutions were identified as suitable for quick implementation Low High Cost/Effort Company New Business Improvement 51 .PPT
Refine Solutions • Testing and Validation • X1 Confirmation of Customer requirements: It was agreed that multiple changes were required to ensure better understanding of the customer’s needs: Involve staff in planning processes, requesting better documentation, confirmation of requirements after Company started working on the proposals. These changes were validated with the PMO prior to implementation as valid to improve customer requirements understanding. • X2 Commercial Qualification: PMO confirmed the need to have a strong qualification process in place. The new qualification process is closer to the model used on other accounts. • X3 Missing communication within Company: Other accounts provided the model that was used for the new qualification review meeting on this account. Its validity is proven by the successes of other accounts. • X4 Rework: A separate green belt project investigates the occurrence of proposal rework in the IS part of Company. It was assumed that this green belt project will drive further changes in the New Business area or proposal management.. • X5 Missing customer contact before delivery: This cause was debated in length, as it was felt by some that customers don’t want to be ‘pestered’ with the vendor’s calls. A cultural and attitude change is required and the implementation of this change will require a longer time to complete. Its validity was confirmed by other Company accounts. • X7 Too many reviews: Company’s E2E model doesn’t request financial and commercial reviews for Cat 5 proposals. These were implemented on request of Fin and Comm teams, who now agreed that the reviews can be removed. Company New Business Improvement 52 .PPT
Refine Solutions (continued) • Pilot Options • A pilot was not required as a Risk assessment was carried out for each solution. • Most of the solutions were piloted by other Company accounts in some way. The risk of damage because of failure was eliminated and hence “Piloting” was not required. • Cost/Benefit Analysis • Since the estimated cost of these solutions was not very significant, implementation proceeded without detailed cost/benefit analysis. • The benefits were viewed as significant savings (based on COPQ analysis). All solution alternatives proposed by the team were accepted by the Champion Company New Business Improvement 53 .PPT
Solution Details • Solution 1: Rotate staff on site at Company • A roster that allows 2 Company staff to be on site every day in the computer center will involve Company sufficiently in the planning processes and ensure more well documented proposal requests. • Cost: Wireless network cards for all staff on the roster • Risks: Small risk: If on site, Company staff might miss out on Company internal communication • Solution 2: Confirm proposal requests within 48 hours • As practiced on other Company accounts, for each proposal request, a Company person confirms the receipt, delivery and high level requirements with the customer • Detailed requirements are confirmed later if required. • Cost: none • Risks: Small risk: Delay, if customer is not available for discussion Company New Business Improvement 54 .PPT