Exploring Colonial Motivations: Why People Became Colonists
220 likes | 352 Vues
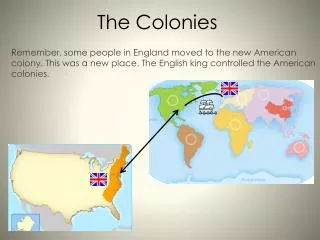
This study delves into the key motivations behind colonization in America during the 17th century. It contrastingly examines the opportunities, mobility, and freedoms sought by European settlers against the hardships they left behind. The motivations for colonization from three main countries—England, France, and Spain—are highlighted, with a focus on influential settlements such as Jamestown and Plymouth. The analysis also encompasses the different regions of English colonies, their economies, social structures, and everyday life, offering insights into the complexities of early colonial life.

Exploring Colonial Motivations: Why People Became Colonists
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Notes on the Colonies… Miss Springborn Team 6 Social Studies
Why be a Colonist? • What would make you want to leave your homeland and travel across the unknown ocean to a strange land??
America: What was here… • Opportunity • Mobility • Freedom • Liberty
Europe: What they are leaving behind… • Hard Times • Rigidity • Restraint • Persecution
Define Motive… • A reason for doing something
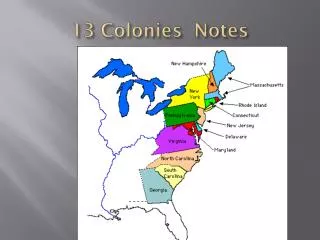
Three Countries France Spain England Three new settlements…
New Spain • All of Southwest United States, Central America, and the Caribbean Islands • MOTIVE- Wanted to get GOLD, slaves for plantations, and sugar plantations • King of Spain in charge of the Spanish lands • Conquistadors (Spanish Soldiers) and Missionaries main group that comes to settle in Americas.
All of Canada, St. Lawrence River, Great Lakes, and west of the Mississippiriver. Capitol city was Quebec MOTIVE: Main source of money was through the fur trade Worked with the Natives to make money, partners King of France in charge of these settlements Traders, trappers, and Missionaries were the groups that came to settle in the Americas New France
England: Two Settlements • Jamestown in Virginia and Plymouth in Massachusetts
Jamestown… • Jamestown was created by a Joint Stock Companyand wanted to make money • They farmed rice, indigo, and tobacco. • Had a ruling body called the House of Burgessesthat would make laws for the community • Jamestown populated by soldiers, indentured servants, strong men, and a few women and children
Plymouth was created as a religious haven for the Pilgrimswho were not allowed to worship in England Plymouth was populated by families trying to start a new life Plymouth was not founded to make a profit, they ruled themselves using the Mayflower Compactas a guide to make laws: SELF-GOVERNING Plymouth
Three Types of English Colonies • Corporate Colonies-A group in charge to make money • Proprietary Colonies-Individuals in charge • Royal Colonies-King in charge
The English Colonies… • The new world for the English could be split into four distinct regions… • New England • Middle • Southern • Frontier
New England Colonies… • Cold climate, shortgrowing season, bad for farming • Thick forests • Subsistent Farming-when you grow enough to eat • Mostly turned to sea for fish and whales • Grew cornand wheat as crops
Everyday life in New England… • Jobs included fishermen, traders, shipbuilders, and forest workers • Education very important, public schools, students could read the bible • Religionwas very important • Mostly English immigrants • Very passionate about democracy • Pilgrims created the Mayflower Compact
Middle Region… • Winter lessharsh than New England • Longergrowing season • Fertile valleys • Soil great for grains • Nickname the breadbasket colonies because their main crop was GRAINS: including wheat, oats, barley, rye, and corn • Farmers could grow surplus of food
Everyday life in the Middle Region • Jobs included farming, shipbuilding, furtrade, and small businesses • Trade school and apprenticeships main source of education • Skilled workers made things like hardware, clocks, glass, nails, and paper • Many different cultures, very different from New England and South • Groups like English, Dutch, German, Scottish, Irish, Swedish and Finns immigrated to this region • More of an emphasis on equality • Early peace with the Native Americans
Southern Region… • Long growing season, fertile soil, warm summers, mild winters • CASH CROPS: tobacco, rice, cotton andindigo • Wealthy: Needed slaves to run their large plantations, cheap labor • Small farmers: grew things like corn, grains, and enough for their families
Everyday life in the South… • Jobs mainly farming, some lumbering and shipping/trading on the shore • Only the rich were educated, used tutors • Illegal to educate slaves • Mostly Protestant but Maryland had a large number of Catholics • Most immigrants were English, slaves were mostly African • These colonies existed to serve the king, he appointed a governorthat ruled in his place
South continued… • Slavery was major part of the south • Import: products brought into the area • Export: products brought out of an area
Frontier Region… • Soil was best in the valleys • Subsistent Farming • Grew wheat and corn • Raised hogs(pigs) • Made moon shine (whiskey)
Everyday life in the Frontier • Jobs included farming and trapping in the fur trade • Self-educated, learned from the Bible • Mostly Protestant, very religious • Immigrants included Scottish, Germans, Irish, and a few English • Very Independent, Strongly Democratic and believed in equality(ready for a rebellion)