Hypothesis Helper
170 likes | 357 Vues
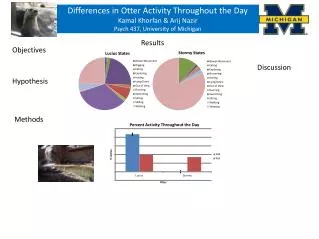
Hypothesis Helper. An important process interconnected with Earth’s climate history is …. PLATE TECTONICS. Pangaea. Modern Continents. Animation courtesy of U.S. Geological Survey. EARLY SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESIS - “CONTINENTAL DRIFT”. Glossopteris Fossil.

Hypothesis Helper
E N D
Presentation Transcript
An important process interconnected with Earth’s climate history is …
PLATE TECTONICS Pangaea Modern Continents Animation courtesy of U.S. Geological Survey
EARLY SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESIS - “CONTINENTAL DRIFT” Glossopteris Fossil Photo courtesy of U.S. Geological Survey
Hypothesis : Glossopteris areas were once close together but then broke apart & moved to the continents’ current positions. Distribution of Glossopteris plant fossils in Permian (250-299 mybp) rocks(mybp = million years before present) Illustration credit: Peter Bockman
But how do we know this is true? Are there other possible explanations and hypothesesfor finding this fossil plant on widely separated continents?
ACTIVITY 1: Hypothesis Helper Let’s think about this …
Which species could have spread between Africa & South America only if those continents were once connected? Which of the five species (if any) might provide the best evidence for tectonic plate movement?
NOPE! Not the species that could have reproduced across the ocean …
… but the species that could have spread only on continuous land which later broke apart
A - Large triangular leaves; berries commonly eaten by migratory animals • B - Short, narrow, oval leaves; produces few seeds, reproduces mainly by stolons • C - Small thin feathery leaves; large seeds have spongy outer cover, allowing seeds to float and travel easily in either fresh or salt water • D - Thrives in swampy or watery environments; very large, heavy seeds sink and lodge in bottom sediments • E - Long thin leaves; small fluffy seeds easily carried by wind stolons
WOOHOO!You have used ancient plants’ adaptations for reproduction & seed dispersal (seed transport) to test a hypothesis about tectonic plate movements!
HOW DO THE SCIENTISTS KNOW SO MUCH ABOUT THEM? IF THOSE PLANTS ARE FOSSILS & ANCIENT & PROBABLY EVEN EXTINCT … I HAVE A QUESTION! WHOA! JUST A SECOND!
PRINCIPLE OF UNIFORMITARIANISM (UNIFORMITY) Earth processes that operated in the past are similar to those operating today. “The present is the key to the past.”
So earth scientists study modern volcanoes to understand ancient volcanic rocks … • And modern rivers, glaciers, deserts, & coastlines and their sediments to understand how ancient sedimentary rocks formed … • And modern plants & their adaptations to understand similar ancient plants & their adaptations.
FOR GLOSSOPTERIS, WHICH HAS NO MODERN REPRESENTATIVES Tree shape & roots like modern bald cypress Warm, very wet environments Seeds too fragile to survive a long sea trip • Based on its fossil remains and on certain similarities to modern Bald Cypress, scientists have interpreted: GLOSSOPTERIS BALD CYPRESS Illustration credits: Glossopteris, Rose Prevec, Rhodes University (South Africa); bald cypress, NRCS