Motion
350 likes | 745 Vues
Motion. Chapter 11. Video. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uDP7Pty8Qnw. @ 34 seconds. Distance and Displacement. 11.1. Frame of Reference. System of objects that are not moving with respect to each other Frame of Reference needed to describe motion accurately and completely

Motion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Motion Chapter 11
Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uDP7Pty8Qnw @ 34 seconds
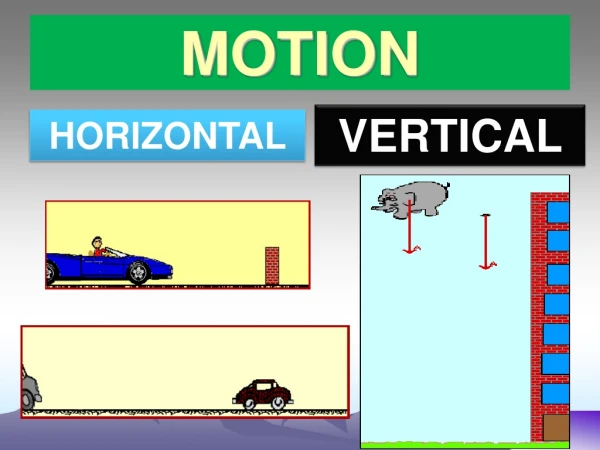
Frame of Reference • System of objects that are not moving with respect to each other • Frame of Reference needed to describe motion accurately and completely • Ex: Moving car and a tree on the side of the road • Relative Motion: movement in relation to frame of reference
Distance And Displacement • Distance: Length of path between 2 points • Displacement: direction and distance in a straight line from the starting point
Combining displacements • Vector: quantity that has magnitude and direction • Add displacements using vector addition • When 2 vectors have same direction add them • When 2 vectors have opposite directions subtract them
Combine Displacements • Resultant Vector: sum of two or more vectors
Section Review Questions • What is a frame of reference, how is it used to measure motion? • How are distance and displacement different? • How are displacements combined?
Horse Head Nebula (interstellar clouds of dust), found in Orion, dark portions are thick dust, pinkish glow is from hydrogen gas
Speed and velocity 11.2
speed • The ratio of the distance and object moves to the amount of time an object moves • How far an object goes in a certain amount of time • S = D/T or V = D/T • Avg. Speed = calculated for the entire trip • Instantaneous speed = calculated at a point in time
Math Triangle S =D/T D = S x T T = D/S • S D T
Math Practice • Nissan GTR 11.2 Sec @ 121.8 miles/hour How long was the race? D=S * T 121.8 miles/hour = .03 miles/second D = .03 miles/second * 11.2 seconds = .38 miles
Velocity • Description of both speed and direction • Velocity is a vector • Why is velocity a vector? • Has both magnitude (size) and direction. • Changes in velocity can be: in speed, direction or in both
Velocity practice • Decide in the scenarios below if there is a change in velocity: • A car is going 45 mph and stops at a stop light. • A driver going down a straight portion of the highway is using cruise control to remain at a constant speed. • A child is riding a merry go round.
Math Triangle V =D/T D = V x T T = D/V • V D T
Combing Velocities • Two or more velocities may be added by vector addition • A boat is heading down river at 20 mph, the river is flowing at 3 miles per hour, what is the combined velocity? • 23 mph
Distance-Time Graphs • Distance time graphs show velocity
0-60 in 3 seconds Reaching speeds in upper 60’s
Acceleration 11.3
Acceleration • Acceleration is a vector • Changes in speed direction or both (change in object’s velocity) • Can be positive change in speed, increasing speed • Can be negative change in speed, decreasing speed • Example: Airplane taking off is positive acceleration, airplane landing is negative acceleration F-16
Acceleration • Changes can be in direction • Merry go round is constant acceleration (constant speed always changing direction) • Changes can be in both direction and speed • Ex: Roller Coaster
Acceleration • Free Fall: movement of an object toward Earth due to gravity • Unit is: m/s2 • Objects on accelerate towards Earth at a rate of 9.8 m/s2 • Constant Acceleration: steady (constant) change in velocity • Instantaneous Acceleration: How fast a velocity is changing at a specific instant http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AvKJ9DcaJ8M&noredirect=1
Calculating Acceleration Vf- Vi t A
Graphing Acceleration • Slope of a speed-time graph is acceleration
Graphing acceleration • Acceleration is a curved line on a distance-time graph