Memory
120 likes | 315 Vues
Memory. Overview. How are memories important? How do memory systems work? How can you improve your memory?. Memory as Information Processing. Encoding Storage Retrieval. Three-Store Model (Atkinson & Shiffrin ). Sensory Register. Response. Short-Term Store. Long-Term Store.

Memory
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Overview • How are memories important? • How do memory systems work? • How can you improve your memory?
Memory as Information Processing • Encoding • Storage • Retrieval
Three-Store Model (Atkinson & Shiffrin) Sensory Register Response Short-Term Store Long-Term Store
Sensory Memory • iconic – visual, about ¼ sec. • echoic – auditory, 1-2 sec • attention needed for further processing
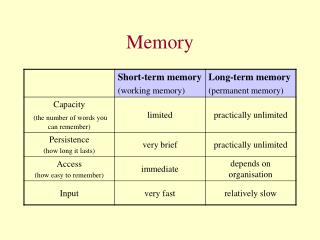
Short-Term Memory • Visual, acoustic, or kinesthetic • Chunking • Rehearsal • Duration of about 20 sec without rehearsal
Working Memory • Modern version of short-term memory • Emphasizes processing while storing • Active part of long-term memory
How do memories become long-term? • Hippocampus • Long-term potentiation (LTP)
Long-Term Memory • Meaning-based • Very high capacity • Long duration
Types of Long-Term Memory • Declarative • Semantic • Episodic • Procedural • Implicit • Priming effects • Deja vu
Construction in Memory • Misinformation effect • Source amnesia • Effects of expectation and bias • Repressed Memory
Improving Your Memory • mnemonics • encoding specificity • avoiding interference • proactive • retroactive • distributed practice/spacing • state-dependent learning