Physics 7C SS1 Lecture 5: Ray Optics
240 likes | 431 Vues
Physics 7C SS1 Lecture 5: Ray Optics. Images Lens Types & Ray Tracing. Review: Light at an Interface. Activity 8.6.3 & FNT 1. Incoming Ray. Air n = 1. Plastic prism n = 1.5. On entering the prism (first boundary), which way will the light bend? a) Up b) Down c) No bend.

Physics 7C SS1 Lecture 5: Ray Optics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Physics 7C SS1Lecture 5: Ray Optics Images Lens Types & Ray Tracing
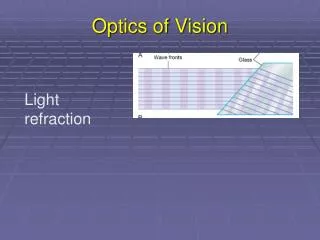
Review: Light at an Interface • Activity 8.6.3 & FNT 1 Incoming Ray Air n = 1 Plastic prism n = 1.5 On entering the prism (first boundary), which way will the light bend? a) Up b) Down c) No bend
Review: Light at an Interface • Activity 8.6.3 & FNT 1 Which Ray? Incoming Ray (a) (b) Air n = 1 Plastic prism n = 1.5 (c)
Review: Light at an Interface • Activity 8.6.3 & FNT 1 Incoming Ray Plastic prism n = 1.5 On leaving the prism, which way will the light bend? a) Up b) Down c) No bend
What phenomenon most completely describes what you are seeing? • Refraction • Convergence • Divergence • Total Internal Reflection • Snell’s Law
What phenomenon most completely describes what you are seeing? • Refraction • Convergence • Divergence • Total Internal Reflection • Snell’s Law
Concepts: Object Image Real Virtual Upright Inverted Magnification Focus Ways to locate Image: Thin Lens Equation Image distance Object distance Sign of lens Ray Tracing Principal Rays Lens Types: Converging Diverging Convex Concave Terms in Optics
How will light emerge from the prism below? • Up • Down • Parallel • Bent inward (converge) • Bent outward (diverge) Incoming Rays
How will light emerge from the prism below? • Up • Down • Parallel • Bent inward (converge) • Bent outward (diverge) Incoming Rays
How will light emerge from the prism below? • Up • Down • Parallel • Bent inward (converge) • Bent outward (diverge) Incoming Rays
How will light emerge from the prism below? • Up • Down • Parallel • Bent inward (converge) • Bent outward (diverge) Incoming Rays
Parallel rays are uncommon…how do lenses work on regular objects?
Diffuse reflection: rough surface reflects light in many directions. Still obeys law of reflection, just scatters at many different angles. Paper Even flat surfaces like paper are not smooth to visible light. A flashlight beam shining on paper can be seen from most angles, not just the one complimentary to the incident.
Every part of the tree reflects light, scattering it all directions. A ray diagram is used to simplify this picture.
What type of image does Ernie make? • Real • Virtual • Upright • Inverted • Bigger • Smaller
What type of image does Ernie make? • Real • Virtual • Upright • Inverted • Bigger • Smaller Lens far away: He was inverted and real Lens close to him: He was upright and virtual
Focal point, f Image plane Image plane c Object plane o i
Focal point, f c Where’s Ernie? o Object plane
Focal point, f c Image plane i o Object plane