RECEPTORS
120 likes | 337 Vues
RECEPTORS. Cellular component to which the drug binds and through which initiates the effect

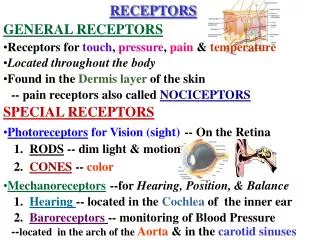
RECEPTORS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
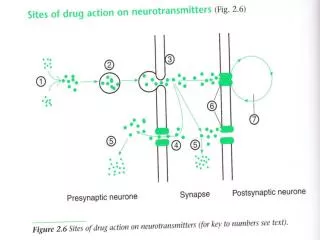
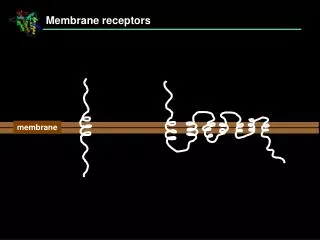
RECEPTORS Cellular component to which the drug binds and through which initiates the effect Ionotropic: ligand gated Ionic Channels, activation leads to rapid and transient increase in membrane permeability. Causes excitation or inhibition of the post synaptic membrane. e.g. GABA A receptors Quick response Metabotropic; Produced slower response involving G protein which bind to the intracellular portion of the receptor and activate a second messenger. This will altered the phosphorylation state of key proteins rendering them active or inactive e.g. antipsychotics, antidepressants
MECHANISM OF ACTION FOR SIDE EFFECTS Agitation ALPHA2 Blockade, 5HT 2A/2C stimulation Akathisia D2 antagonism, 5HT2A stimulation Delirium anticholinergic effect (muscarinics) EPSE D2 blockades Insomnia alpha 1 stimulation, 5HT2A Stimulation (hence SSRIs) Amnesia antimuscarinics and GABA stimulation Hyperprolactinaemia D2 blockade, 5HT1A stimulation Sweating Cholinergic effect and increases with NARIs Anorgasmia Alpha 1 antagonism, 5HT2A/2C stimulation (delayed ejaculation on SSRIs Impotence alpha 2 blockade, 5HT2A/2C stimulation (also low libido)
WEIGHT GAIN Cannot be explained by a single mechanism of action Antihistaminic effect 5HT2A/2C antagonism Insulin resistance (Valproate and Olanzapine are noted) Genetic factors seems to be involved - 5HT2C receptor. Drugs with strong affinity for this receptors will have a greater impact on weight increase.