Cell Processes
220 likes | 373 Vues
Cell Processes. The following are cell process That you are required to know: Mitosis Cytokinesis Photosynthesis Respiration Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport. Mitosis - The process by which the cell’s nucleus divides into two nuclei. Mitosis is a four step process that

Cell Processes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The following are cell process That you are required to know: Mitosis Cytokinesis Photosynthesis Respiration Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport
Mitosis - The process by which the cell’s nucleus divides into two nuclei. Mitosis is a four step process that gets the cell ready for cell division. Way to remember the phases of mitosis Please Make Anna Tell!
INTERPHASE: 1. The period between cell divisions is known as interphase. During interphase all normal cell functions are taking place. The cell is not dividing. 3. Chromosomes are duplicated during this phase. (but you can’t see them!)
Step 1: Prophase - nuclear membrane begins to disappear. Chromosomes become visible.
Also in prophase, the centrioles begin to move to opposite sides of the cell. The centriolesbegin to form the spindle (that will eventually pull the chromatids apart.
Step 2: Metaphase - Pairs line up in the middle of the cell. Actual Cell Photo of a cel going through metaphase
Also in metaphase, the spindle is completely formed and is pulling on the chromosomes causing them to line up down The middle of the cell.
Step 3: Anaphase -chromosomes split apart and move to opposite poles. Actual cell in anaphase
Step 4: Telophase - Last stage of mitosis. Chromosomes begin to lengthen and nuclear membrane reappears. Results in two new nuclei Animal cell in telophase Plant cell in telophase
Cytokinesis: Cell division The cell cytoplasm divides and Cells return to Interphase.
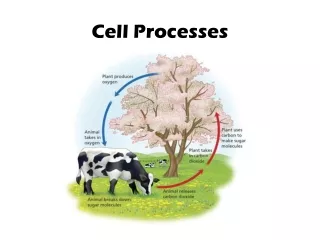
Metabolism -All controlled chemical reactions by which cells gain and use energy.
Questions? 1. Can cells make energy? 2. Where do cells get energy?
Answers! 1. No, energy cannot be created or destroyed . However, cells can change energy from one form to another. In order to get the energy needed for life processes, plants cells convert sunlight into food (glucose) and then break the glucose down to release the energy. Animals break down injested food to release the energy stored within it.
The sum of these reactions, which involve the building up and breaking down of molecules, is called metabolism.
Photosynthesis 6CO2+6H2O+ sunlight (Carbon Dioxide) + (Water)+ (sunlight) Yields C6H12O6 + 6O2 (glucose) + (oxygen)
Photosynthesis Defined Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants use CO2 , H2O and light energy and give off Glucose (sugar) and Oxygen. **Chlorophyll traps light energy which is needed to make the plants food (glucose).
Two Major steps for Photosynthesis 1. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy. When this occurs the water molecules split (Oxygen and Hydrogen.) 2. Hydrogen quickly combines with Carbon Dioxide (CO2) forming glucose (C6H12O6).
Respiration -The process by which cells release energy from food. 1. Aerobic Respiration aerobic - containing oxygen C6 H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O +energy 2. Anaerobic Respiration - Energy released without Oxygen
Diffusion - process by which food molecules, oxygen, water and other materials enter and leave the cell through the cell membrane. Substances move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lesser concentration. Cell Energy is not needed for diffusion.
Osmosis - the diffusion of water into or out of a cell. Energy not needed for osmosis. Water travels from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Active Transport: Cells use energy to obtain or remove materials within the cell. Substances are “pulled” or “pushed” out off the cell.