Cell Processes
150 likes | 313 Vues
Cell Processes. (water). What is Diffusion?????. The movement of molecules from areas where there are many (high concentration) to areas where there are few (low concentration) Solute: The particles that are in the least amount in a solution. (usually a solid)

Cell Processes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
(water) What is Diffusion????? • The movement of molecules from areas where there are many (high concentration) to areas where there are few (low concentration) • Solute: The particles that are in the least amount in a solution. (usually a solid) • Solvent: The particles in the greatest amount in a solution. (usually a liquid) • Equilibrium: When molecules are spread evenly throughout a space.
Osmosis Diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane (usually a cell membrane) • Semi-permeable: permeable to solvents (WATER), but not to large molecules • Molecules move from high [water] to low [water] Hypertonic Solution: has a higher concentration of solutes than in cytoplasm (less solvent outside cell) -cell shrinks Hypotonic Solution: has a lower concentration of solutes than in the cytoplasm (more solvent outside cell) -cell swells, may burst Isotonic Solution: has an equal concentration of solutes to that of the cytoplasm (same amount of solvent outside) -cell remains the same size
Active Transport • http://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/activetransport/ • Definition- the movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy • Materials are moved from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration • Active transport REQUIRES energy!
What is the Cell Cycle? • The cell cycle is an orderly cycle of growth & division of a cell. • The cell cycle has three major phases: interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis.
What is Mitosis? • Mitosis is process in which the nucleus of a cell divides into two nuclei and the formation of two identical daughter cells begins. • Each daughter cell has the same numberandkindof chromosomes as theparentcell.
REMEMBER: • IInterphase • Peeled Prophase • My Metaphase • Apple Anaphase • Today Telophase • Class Cytokinesis.
Meiosisis the production of gametes (sex cells) Sperm (male sex cell) Egg (female sex cell) Meiosis reduces the chromosome number in sex cells by 1/2. Egg: 23 chromosomes (humans) Sperm: 23 chromosomes (humans) Fertilization: Union of egg and sperm (sexual reproduction) Zygote: baby produced from the union of the egg and sperm (46 chromosomes, human)
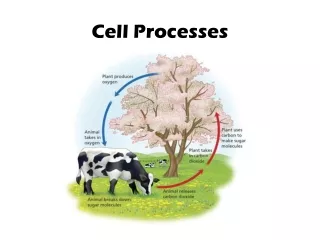
Photosynthesis & Respiration: Do you remember these processes?
Photosynthesis: • The process of changing light energy to chemical energy • Energy stored as sugar • Occurs in plants and some algae • Plants need light energy, CO2, and H2O • Takes place in the chloroplasts, using chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants
What is the equation for the chemical reaction of photosynthesis? 6CO2 + 6H2O + SUNLIGHTC6H12O6 + 6O2 (Reactants) (Products) Six molecules of carbon dioxide react with six molecules of water to form 1 molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen.
Cellular Respiration: Once the energy that was in sunlight is changed into chemical energy by photosynthesis, an organism has to transform the chemical energy into a form that can be used by the organism. This process takes place in the mitochondria! C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy (reactants) (products)
Compare and contrast the two formulas! 6CO2 + 6H2O + SUNLIGHT C6H12O6 + 6O2 (reactants) (products) VS. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy (ATP) (reactants) (products)
Last Slide!Terms to know:Passive TransportDiffusionOsmosisActive TransportCell CycleMitosisMeiosisPhotosynthesisCellular Respiration