Efficient Distributed Query Processing with Partitioned Inverted Files and Global Indexing Techniques
100 likes | 231 Vues
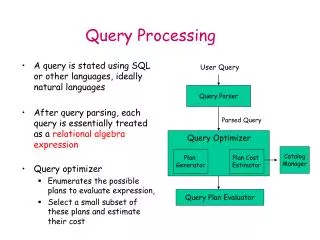
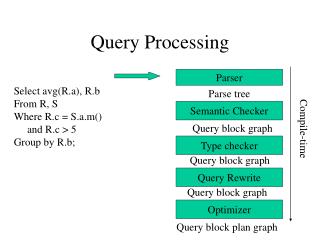
This workshop paper by Claudine Badue discusses innovative strategies for distributed query processing using partitioned inverted files (Local Index - LI) and lexicographical global indices (Global Index - LGI). The paper examines the architecture of various index layouts, focusing on their impact on search costs. It explores trade-offs in efficiency and cost-effectiveness, providing insights into how different indexing strategies can optimize query processing in distributed systems. Through an extensive comparative analysis, this research aims to enhance performance in query execution frameworks.

Efficient Distributed Query Processing with Partitioned Inverted Files and Global Indexing Techniques
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Claudine Badue April 08, 2003 Workshop SIAM Distributed Query Processing Using Partitioned Inverted Files
Local Index (LI) and Lexicographical Global Index (LGI) Documents Documents 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 A A x x x x x x . . . . . . P1 C C x x x x x x x x D D x x x x x x x x Te rms Te rms . . . . . . P2 G G x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x H H . . . . . . P3 N N x x x x x x x x x x x x x x O O . . . . . . P4 Z Z x x x x x x x x P1 P2 P3 P4 • LI • LGI
Random Global Index (RGI) Documents A x x x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 . . . C x x x x P1 D x x x x Te rms . . . G x x x x P2 H x x x x . . . N x x x P3 x x x x O . . . Z x x x x P4
Network of Workstations Model Network Switch Memory 1 Memory 2 Memory 3 Memory p Processor 1 Processor 2 Processor 3 Processor p Disk 3 Disk p Disk 1 Disk 2 . . . . . .
Client-Server Paradigm Client 1 Client 2 Client 3 Client c Proc 1 Proc r Proc 1 Proc 2 Proc d . . . Ranking Server . . . I/O Server . . .
Query Processing (LI) Processor 1 Processor 2 Processor 3 Processor 4 d1, d3, d7, d5, d8, d2 a, b, c Ranking Server a, b, c a, b, c a, b, c a, b, c d1, d2 d3 d5 d7, d8
Query Processing (LGI) Processor 1 Processor 2 Processor 3 Processor 4 aaa, d, f d8, d2, d1, d3 a d5, d1, d3 aa, b, c Ranking Server aaa a aa b, c d, f d8, d2 d1, d2, d8, d3 d2, d5, d6 d5, d1,d3
Query Processing (RGI) Processor 1 Processor 2 Processor 3 Processor 4 aaa, d, f d8, d1, d3, d2 a d5, d1, d3 aa, b, c d2, d5, d6 Ranking Server d, f aaa b, c aa a d8, d2 d5, d1,d3 d2 d1, d2, d8, d3 d2, d5, d6
Issues to Explore • Identify and explore the tradeoffs of the distinct index layouts on disk • Identify the most cost effective layouts • Evaluate how the architecture of the system impact the final searching costs