Cell Division
320 likes | 540 Vues
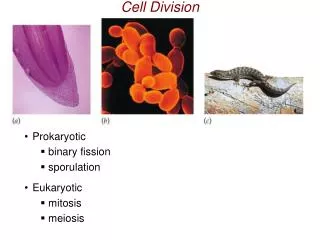
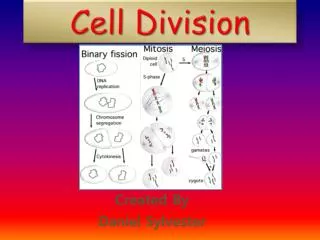
Cell Division. Prokaryotic binary fission sporulation Eukaryotic mitosis meiosis. Prokaryotic Cell Division - Binary Fission. Eukaryotic DNA is Packaged into Chromosomes. Chromosomes, Chromatids, and Chromatin. Karyotypes. spectral karyotype.

Cell Division
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cell Division Prokaryotic binary fission sporulation Eukaryotic mitosis meiosis
Karyotypes spectral karyotype
Numbers of Chromosomes in Some Plant and Animal Species Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae 16
Checkpoints in Cell Cycle Progression G1 to S and G2 to M transitions are regulated by proteins called cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and cyclins
Cyclin proteins and Cdk activity Cyclin proteins are made and destroyed in a cyclic pattern during the cell cycle Cdks are activated by binding to one of several different cyclin proteins
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases and Cyclins Regulate Transitions in the Cell Cycle Cdk-cyclin complexes each phosphorylate different target proteins to regulate progression ofthe cell cycle MPF p53
Disruption of Cell Cycle Control Cyclin-Cdk complexes act as checkpoints. When functioning properly, they allow or prevent passage to the next stage of the cell cycle In cancer cells, these checkpoints are often disrupted Rb/p105 (retinoblastoma) Loss of Rb permits unregulated cell division p53 Loss of p53 prevents synthesis of p21 which allows production of cyclin D
Meiosis and Alternation of Generations in Sexual Reproduction
Crossing Over Forms Genetically Diverse Chromosomes Meiotic Recombination