Gram Negative
940 likes | 2.74k Vues
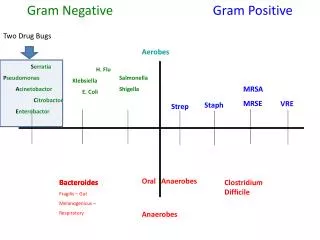
Gram Negative. Bacterial Diseases. Proteobacteria. Alpha: Parasitic bacteria Tick borne diseases Flea vector Beta: GNC Gamma Largest group Enterics Delta Sulfur reducing bacteria in soil/water Predatory (attack other bacteria) Epsilon : GI. Gram Negative Cell Wall. Neisseria.

Gram Negative
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Gram Negative Bacterial Diseases
Proteobacteria • Alpha: Parasitic bacteria • Tick borne diseases • Flea vector • Beta: GNC • Gamma • Largest group • Enterics • Delta • Sulfur reducing bacteria in soil/water • Predatory (attack other bacteria) • Epsilon : GI
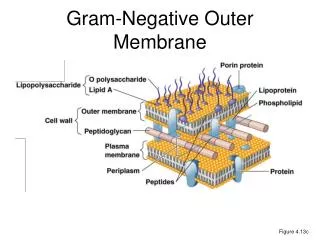
Neisseria • Characteristics • GNC, diplococci • Capnophile • Nonmotile • Oxidase (+) • Pathogenicity • Fimbria • Capsule • Protease (inhibit IgA) • LOS (oligosaccharide) • Lipid A endotoxin
Neisseria meningitidis • Epidemiology • Normal microbiotica (resp) • Pathogenicity • Various strains • Capsule • LOS: lipid A • Disease • meningitis • Septicemia/death • Dx: CNS, Ab • Tx: AB • Prevention • Vaccination • Prophylactic AB to exposed
Neisseria gonorrhoeae • Gonococci • Eye • Pharynx • Uritogenital • Rectum • Pathogenicity • Adhesins • Pili • Protein II • Replicate in WBCs • Disease • STD “Clap” • PID scar tissue • Neonatal conjunctivitis • Inflammation • Urinary • Repro • Oral Cavity
Neisseria gonorrhoeae • Dx • Culture/Isolation • Symptoms • Tx: • AB • Cepha- • quinolones • Iodine/Silver Nitrate (eye) • Prevention: • Screen/Detection • Tx infected individuals • Condom use • Public education
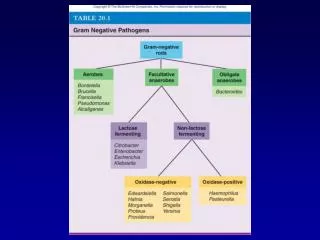
Enterobacteriaceae • Characteristics • GNR • Motile = flagella • Capsule/slime layer • Nitrate reduction • FA • Oxidase (-) • Epidemiology • Source • GI • Water • Soil • Decaying vegetation Gamma Proteobacteria
Enterobacteriaceae • Groups • Gammaproteobacteria: Enterics • Coliforms • Noncoliforms • Pathogens • FA • Oxidase (-) • Reduce nitrate • (cocco)bacilli
Enterobacteriaceae • Pathogenicity • LPS • Core polysaccharide • O polysaccharide • Lipid A endotoxin • Antigens • Capsular (K) • Flagellar (H) • Virulence factors • Immune evasion • Capsule • Fimbriae • Type III secretion system • Adhesins • Exotoxins • Hemolysins • Iron-binding compounds
Enterobacteriaceae • Dx • Culture/Isolation • MAC • EMB • Location • Tx • Supportive • AB • Prevention • Hand washing • Sewage control
Coliforms • Normal GI microbiotica • Groups • Escherichia • Klebsiella • Serratia • Enterobacter • Hafnia • Citrobacter • Biochemical tests • Ferment lactose
Enteric Bacteria • Pathogenicity • Glycocalyx • LPS • Core polysaccharide • O antigen • Lipid A endotoxin • K (capsular) antigens • H (flagellar) antigens • Fimbria • Adhesins • Exotoxins • Hemolysins • Bacteriocins • Iron binding proteins • Sex Pili AB resistance
Enteric Bacteria • Diagnosis • Culture • Biochemical tests • Treatment • AB • Toxin neutralization • Prevention • Hygiene • Clean water supply
Esherichia coli • Coliform • E. coli O157:H7 • Pathogenicity • O, H, K antigens • Plasmids for virulence • Shiga-like Toxin • Type III secretion system • Disrupt PM • Receptors for attachment • Diseases • Gastroenteritis • Food-fecal contamination • UTI • Uremic syndrome • Pyelonephritis • Septicemia • Neonatal meningitis
Klebsiella • Epidemiology • Nosocomial • Reservior • Soil, water • GI • Respiratory tract • Pathogenicity • Polysaccharide capsules • Diseases • UTI • Bacteremia • Meningitis • Pneumonia • Cherry red sputum • Lung abscess • Empyema • Dx: Culture • Tx: AB
Serratia • Characteristics • Red pigment • coliform • Agent: S. marcescens • Epidemiology • Nosocomial • Opportunistic • Fomites (catheters, saline solutions) • GI • Soil, water • Pathogenicity • AB resistance • Endotoxin • Diseases • UTI • URTI
Enterobacter • Agents • E. aerogenes • E. cloacae • Location • Coliform • Water, sewage • Soil • Epidemiology • Opportunistic • Blood • Wounds/incisions • Nosocomial • Pathogenicity • Endotoxin • AB resistance • Disease • Dairy contaminant • UTI • Pneumonia
Characteristics GNR, FA motile Agent: H. alvei (2 biogroups) Epidemiology GI micorbiotica (HARF) Opportunistic, nosocomial Pathogenesis Attach and efface enterocyte mucosa (LEE) Disease Diarrhea Gastroenteritis Peritinitis Septecemia Liver Abscesses UTI Endocarditis Meningitis Pneumonia Dx: Culture fluids Tx: AB Hafnia (formerly Enterobacter sp)
Characteristics GNR, FA Ferment lactose Agent: C. freundii Epidemiology GI microbiotica (HARF) Soil, water Decaying vegetation Pathogenesis Opportunistic Lipid A endotoxin Disease UTI Cholecystitis Meningitis OM Dx: Culture fluids Tx: AB Citrobacter
Noncoliform • Opportunistic • Nosocomial • Diseases • UTI • Kidney stones • Groups • Proteus • Morganella • Providencia • Edwardsiella • Biochemical • Non lactose fomenters
Proteus • Characteristics • GNR, FA • Flagella (polar), swarms • Urease (+) • Agent • P. mirabilis • P. vulgaris • Epidemiology • Colon, soil & water • Opportunistic • Pathogenicity • Urease • Motility • Endotoxin • Disease • UTI (catheter) • Kidney stones • Dx: Culture • Tx: AB, resistance is developing
Characteristics GNR, FA, motile Only glucose fermentation Agents M. morganii Epidemiology GI microbiotica (HAR) Nosocomial Pathogenesis: Lipid A endotoxin Disease UTI GI diarrhea CNS infection Ear and Sinus infections Dx: Culture Tx: AB Morganella (formerly Proteus sp.)
Characteristics GNR Motile FA Agents: P. stuartii P. rettgeri P. alcalifaciens Epidemiology Normal GI microbiotica animals humans Nosocomial Catheter Endotracheal tubes Pathogenesis: plasmid codes for urease Disease GU: UTI, prostatitis, kidney stones Pneumonia Bacteremia Dx: Culture fluids, feces Tx: AB, but developing resistance Providencia
Characteristics GNR, FA +/- motility Agents E. hoshinae E. tarda Epidemiology Opportunistic GI tract (HARF) Pathogenesis Disease Gastroenteritis UTI Wound infections Dx: Culture fluids Tx: AB Edwardsiella
Pathogenic Enteric Bacteria • Characteristics • NLF • Virulence • Type III secretion • Toxins • Groups • Salmonella • Shigella • Yersinia
Salmonella • Characteristic • GNR • Motile (peritrichous) • Gas production • H2S production • Urease (-) • Oxidase (-) • Location • GI (S. enterica) • 2,000 serovars • Examples • S. typhi • S. paratyphi • S. typhimurium
Salmonella pathogenicity • Epidemiology • Fecal contamination • Poultry products • Milk • Pathogenicity • Many serotypes • Proteins endocytosis • Invade intestinal mucosa • Toxins • Enterotoxin • Cytotoxin • Diseases • Salmonellosis • N/V/D • Bacteremia • Typhoid fever • Gastroenteritis • Bacteremia • Peritonitis
Salmonella • Dx • Culture • Isolation • Symptoms • Tx • Supportive • AB • Cholecystectomy • Prevention • Hygiene • Proper food handling • Cooking • Refrigeration • Vaccination
Salmonella typhi • Epidemiology • Source • Carrier’s feces • Transmission • Contaminated food/H2O • Pathogenesis • Invade GI spread to LN, Liver, GB • Shed bacteria in feces: 3mos • Abdominal pain, anorexia • Disease • Typhoid fever • Dx: Culture blood, feces; Serology • Tx: AB • Prevention: • Food handling • Isolation of infected individuals • Vaccine for high risk individuals
Shigella • Characteristics • GNR • Nonmotile • FA • (-): urease, oxidase • Examples • S. dysenteriae • S. flexneri • S. boydii • S. sonnei
Shigella • Location • GI pathogen • Epidemiology • Source: food/water contamination with feces • Transmission • Fecal-oral • 4 F’s • food • fingers • feces • flies
Shigella • Pathogenesis • Multiply in colon mucosa • Disrupt phagosome membrane and invade • Toxins • Exotoxin: Shiga Toxin • Endotoxin • Disease • Diarrhea: • water, blood, mucus • Shigellosis dysentery • Ulcerate colon • Dx: Isolates, biochemical tests, serology • Tx: fluid support, AB • Prevention • Hygiene • Sewage treatment
Yersinia • Characteristics • GNR • Location • GI of animals • Endemic (in West Texas) • Epidemiology • Food/H20 contamination with feces • Direct contact • Indirect: inhalation • Vector: flea bite • Agents • Y. enterocolitica • Y. pseudotuberculosis • Y. pestis
Yersinia • Pathogenicity • Pathogen • YOPS • outer membrane proteins • Prevent phagocytosis • Plasmid virulence factors • Adhesins • Type III secretion systems • Trigger apoptosis • PMN • MO
Yersinia • Diseases • Gastroenteritis (Y. enterocolitica) • SI • Mesenteric LN • Plague (Y. pestis) • Bubonic (LN) • Pneumonic (Lungs) • Dx: Blood ID, culture, PCR • Tx: AB • Prevention: control • Rodent • Flea • Vaccination • Isolation of infected persons
Plague life cycle • Reservoir • Rats • Mice • Voles • Vector: Flea • Hosts • Amplify • Prairie dogs • Rabbits • Deer • Dogs/Cats • Cycle • Flea bite • Exposure to infected animals
Bubonic Plague • Lymphadenopathy • Bacteremia • DIC • S.C. Hemorrhage • Gangrene • “Black” Death
Pneumonic Plague • Lungs • Bloody sputum • Dyspnea • Respiratory droplet
Alpha, Beta, & other Gamma proteobacteria • Aerobic • GNR • Groups • Alpha • Bartonella • Brucella • Beta • Bordetella • Burkholderia • Gamma • Pseudomonads • Pseudomonas • Moraxella • Acinetobacter • Francisella • Legionella • Coxiella
Bartonella • Characteristics • Aerobic • Location: animals • Vectors: insects • Examples • B. bacilliformis • B. quintana • B. henselae
Bartonella Diseases • Bartonellosis • Sand flies • RBCs invaded • Trench fever • Lice • Bone pain • Bacillary • Angiomatosis • Peliosis hepatitis • Cat-Scratch fever • fleas • Cat nails, teeth • LN and abscesses
Brucella • Characteristics • coccobacillus • Location • Intracellular parasite • Animal hosts • Pathogenicity • Prevent phagolysosome • Examples • B. melitensis • B. abortus • B. suis • B. canis
Brucella • Epidemiology • Unpasteurized dairy • Animal blood / urine • Reproductive organs • Disease • Undulant fever (Bangs) • Tx: AB • Prevention • Animal vaccination
Bordetella • Characteristics • Aerobic • GN coccobacillus • Location • Examples • B. pertussis • B. parapertussis • B. bronchiseptica
Bordetella • Epidemiology • Inhaled aerosols • Inhibit ciliary action • Pathogenicity • Adhesins • Toxins • Pertussis • Adenylate cyclase • Dermonecrotic • Tracheal • Disease: whooping cough • Prevention • Hygiene • Vaccination (DPT)
Burkholderia • Characteristics • Aerobic • Flagella • Location • environmental • Opportunistic: • Lungs • Joints • Skin • Diseases • Meliodosis • Glanders • Example • Burk. cepacia • Burk. mallei • Burk. pseuodomallei