Integumentary: Burns
650 likes | 1.59k Vues
Integumentary: Burns. Marnie Quick, RN, MSN, CNRN. Skin layers. Types of burns. Thermal Chemical Thermal Radiation . Thermal burn. Cool burn with cold water until pain is relieved- Do not apply to more than 20% body surface- hypothermia may occur. Chemical burn from sulfuric acid.

Integumentary: Burns
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Integumentary: Burns Marnie Quick, RN, MSN, CNRN
Types of burns • Thermal • Chemical • Thermal • Radiation
Cool burn with cold water until pain is relieved- Do not apply to more than 20% body surface- hypothermia may occur
Electrical burns: top picture- toe Leg bottom picture- mouth
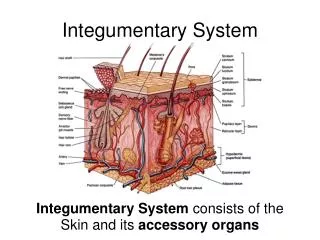
Full thickness third degree burn • All layers skin
Full thickness • Involves past the 3 layers down to the bone and/or organs
Extent of Burn: Rule of Nines Lund & Browder- age
What are the Priorities in this patient??? • Is this patient a candidate for a major burn center?
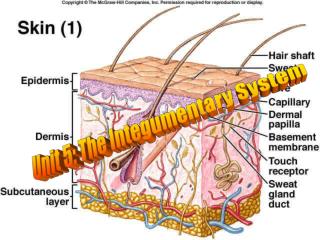
Common manifestations/complications of Major Burn • 1. Integumentary system • eschar formation • necrotic tissue • hard, leathery • must be removed for healing to take place
Common manifestations/complications Major Burn • 2. Cardiovascular • Burn shock- third spacing (hypovolemic) 24-36 hrs • Blood vess damaged> inc cap permeability • H2O, Na & serum albumin> intestial space(3rd space) • HCT and blood viscosity increases • > 40% burn causes dec cardiac contractibility & CO • Electrical burn can cause arrhythmias/cardiac arrest • Compartment syndrome of extremities/torso as edema compresses blood vessels and nerves- may need escharotomy
Before the escharotomy, how would this eschar affected his respirations?
Common Manifestations Complications Major Burn • 3. Respiratory • Direct inhalation injury/systemic response (ARDS) • Upper airway thermal injury- esp if burned in enclosed space (room) & breaths in hot air. May be no outward sign of burn- look for soot, nasal hairs • Laryngeal spasms as edema peaks in 34-48 hrs • Bronchial congestion and infection • Intersitial pulmonary edema; alveolar collapse • CO poisoning- 200 X’s greater affinity for hemoglobin- hypoxia> headache to coma sym
What are your #1 priorities in this patient? Patient #1 Patient #2
Common Manifestations Complications Gastrointestional • Paralytic ileus > increased risk for aspiration • Stress ulcer (Curling’s ulcer) ck pH • Ischemia of intestine increases intestinal mucosal permeability> bacteria can cause systemic sepsis, ARDS and multiple organ failure
Common Manifestations/Complications Urinary • Urinary- • Renal blood flow/GFR decrease causing release ADH • Myoglobinurea- dark urine may block renal tubules
Common Manifestations/complications Immune system and metabolism • Immune system • Capillary leak- serum levels immunogloblin decreased • Opportunistic infections can be fatal • Most common source infection/septicemia- clients own GI track • Metabolism • BMR increases 2X’s, more if complications • Hypermetabolism continues until wound closure • Body weight and temperature drop- shivering inc met
Common Manifestations/Complications- Pain • Where are nerve ending? • Morphine/Fentanyl • Give IV in acute stage due to fluid shift---No IM’s
Therapeutic Interventions Major Burns Stage one: Emergent/resuscitative Stage • Onset injury to successful fluid resuscitation • Major concern- Fluid Resuscitation- prevent hypovolemic shock • 2 large bore IV’s in unburned area to restore bl vol due to inc capillary permeability> 3rd spacing • Guidelines burns >20% TBSA- Parkland formula or Modified Brooke formula • Need Weight and % TBSA burned to calculate
Lactated Ringers solution 1st 24 hrs then add 5% Dextrose to crystalloid fluid • 50% of formula volume in first 8 hrs; rest over next 16 hrs; then maintain urinary output • Hourly output 30-50 cc/hr (foley); heart rate less than 120/min; hemodynamic monitoring • Elevate edematous part; escharotomy
Elevate arms to decrease swelling also note escarotomy of arms and chest- assess CMS
Other therapeutic interventions during Stage one: emergent/resucitative stage • First aide treatment to limit severity of burn • Prevent heat loss through burn- warm envir • Respiratory involved- • intubation/ventilation with PEEP/humidified O2 • bronchodilators • mucolytic agents to liquefy secretions • TCDB • HOB 30 • GI- Pepcid; NG tube when gut ready- antacids
Therapeutic Interventions Major Burns Stage 2: Acute Stage • Start of diuresis and ends with closure of burn • Major concern in this stage- infection • Most common cause infection- pts own GI track • Wound management- • hydrotherapy, debridement of eschar • topical antimicrobial creams (open/closed method) • splints/exercise prevent contractures; • Excision/grafting of 3rd degree (temporary cover 2nd )
Hydrotherapy: Hubbard Tank
Topical broad spectrum antimicrobials (p.425) • Silvadene • Silver Nitrate • Sulfamylon
Wound Care • Open Method • Apply topical chemotherapy
Wound Care- Closed method • Apply topical chemo and wrap with gauze, fluffs, kerlix • Assess for constriction; circulation checks
Elevate burned arms on pillows • Give pain meds 30 minutes prior to treatments
Several patients utilizing closed method Who is that nurse with white stockings& cap?
Excision & Grafting • Removal of necrotic tissue • Eschar is removed until viable tissue is reached
Acute Phase • Autograft- • on right- donor site • Permanent if no infection • Temporary grafts • Homograft- cadaver • Heterograft- animal • Synthetic
Interventions • Assist with positioning • ROM exercises • Support O.T. & P.T. efforts