Shakedown! - Interactive Wildlife Education Game
540 likes | 563 Vues
Test your knowledge of wildlife with this PowerPoint game. Choose a difficulty level, answer questions, and compete against other groups. Learn about light pollution, animal classifications, and more. Suitable for classroom use.

Shakedown! - Interactive Wildlife Education Game
E N D
Presentation Transcript
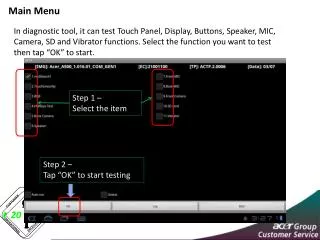
Main Menu Shakedown! Instructions Play Game Quit Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
How To Play Main Menu General Rules: 1) You must have Microsoft PowerPoint and run it in slide show mode in order for this game to work properly 2) Break class into groups. Suggested group size is 5-6 students per group. 3)Group one will choose a difficulty level and point value. Click on that square to read the question. Group one will have approximately 30 seconds to discuss the question and attempt to answer it correctly. 4) If group one does not know the answer to the question, they can choose to pass it to group two. If group two answers the question correctly, they get the points added to their score. It then becomes group two’s normal turn to choose a question. If group two answers the question incorrectly, they receive no points and it becomes group three’s normal turn. 5) If group one chooses to answer the question, then click on the question to reveal the answer. If they answered the question correctly, they receive the points for the question and it is group two’s turn. If they answer the question incorrectly, they receive no points and it is group two’s turn. 6) If group two answers the question incorrectly, they get no points, and the turn moves to group three. 7)Continue in this pattern until all of the questions have been answered. Score board: Students can keep score on paper or on the board. As each group receives points, add them together. At the end, the group with the most points wins. There are three double-plays on the board. When these come up, students receive double points for getting the correct answer. PowerPoint does not keep track of which squares students have already picked. It is recommended to print slide three from PowerPoint before playing the game and cross off the squares as students choose them. See notes for printer instructions. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/Charles Smith
Shakedown! LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3 LEVEL 4 LEVEL 5 50 150 250 350 600 100 200 300 400 700 150 250 350 450 800 200 300 400 500 900 250 350 500 600 1000 Main Menu Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Which is a cause of light pollution? A)Home Lights B) Hotels C)Street Lights D) All of the above Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
D) All of the above Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
True or False: Amphibians can live in water and on land. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
True Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Which is not a reptile: • Lizard • Frog • Turtle • Snake Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
B) Frog Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Which one do birds NOT have? A) Beaks B) Feathers C) Live Young D) Two legs only Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
C) Live Young Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
True or False: There are more types of insects than any other animal on the planet. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
True Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Do mammals lay eggs or have live young? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Live Young Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Insects have: • Six Legs • An outer skeleton • Body segments • All of the above Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
D) All of the above Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Are birds warm-blooded or cold-blooded? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Warm-blooded Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
What is this a picture of? Credit: International Dark-Sky Association Double Points! Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Light Pollution Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
True or False: Moths get fixated by streetlights and have problems mating. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
False Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
True or False: No amphibians can breathe through their skin. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
False Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Name three examples of a mammal. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Any animal that has: • Hair • Warm-blooded • Produce milk • Sweat glands • Live young Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
What does migration mean? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
When a species of animal Travels from environment To another for feeding Or breeding. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
What animal is facing extinction because it is lured away from its home and into the cities by bright lights. Double Points! Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Sea Turtles Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Name two examples of an amphibian. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
An amphibian is an animal • That: • Lives on land and water • Cold-blooded • Lays eggs in water • Moist smooth skin Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Which continent has no reptiles? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Antarctica Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
What does nocturnal mean? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Animals that Function at night Instead of during The day are nocturnal. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Name a way you can stop light pollution. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Turn out unused lights. • Use motion sensors. • Use timers. • Use energy efficient lights. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Who do mammals usually learn from? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Their Parents Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Name a disorder that light pollution can cause in mammals. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Sleeplessness • Unable to breed • Blindness • Grumpiness • Cancer Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
What is the difference between amphibians and reptiles? Double Points! Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Amphibians: • Smooth skin • Wet skin • Can swim • Breath through • skin • 5) Fertilize egg • outside of body • 6) Live first part of • life in water • Reptiles: • Scales • Crawls on belly • Lives on land • Fertilize egg • inside body Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
How are bright lights used by fishing boats harming the fish population? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Bright lights lure fish toward fishing boats causing them to be overfished. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
Why do insects have such complex coloring? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby
Insects use colors to camouflage and warn predators. Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/ Gordon H. Rhodda
What is this a picture of? Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service/James Appleby