VASCULAR PLANTS
150 likes | 1.6k Vues
VASCULAR PLANTS. Vascular Plants. plants that have tube-like cells in their roots, stems, & leaves that carry water and nutrients. Vascular Plants-. An adaptation that allows plants to grow very tall. Vascular comes from the Latin word “ vasculum ” which means “ vessel ”.

VASCULAR PLANTS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
VASCULAR PLANTS
Vascular Plants plants that have tube-like cells in their roots, stems, & leaves that carry water and nutrients Vascular Plants- An adaptation that allows plants to grow very tall • Vascular comes from the Latin word “vasculum” which means “vessel”
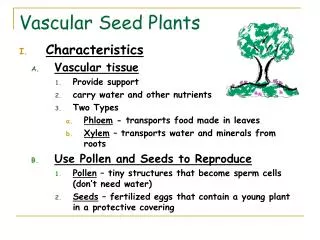
Vascular Plants: 2 Types of Tubes • vascular plants have 2 different types of tube-like structures inside them a) xylem b) phloem • each one has a specific function (job) • think of tiny pipes...like a plumbing system tube-like cells that carry water & dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves Xylem - tube-likecells that carry food, which is made in the leaves, to all parts of the plant Phloem-
Turn & Talk Time • Turn to your elbow partner and talk about what you notice about Phloem and Xylem. How are they alike and different. • Together create a way to remember these differences or similarities. Be prepared to share it with the class 10 minute timer
L k Xylem & Phloem: Phloem Take another xylem
Seedless Vascular Plants • Characteristics: • Have vascular tissue • Reproduce by spores • First appeared on earth 400 million years ago • Over 12,000 species alive today • Popular house plants and used to grow other house plants Types: FERNS
Seedless Vascular Plants (Ferns continued) • usually grow in moist shady areas typical fern • they have adapted to grow in other environments: -aquatic (water) -dry climates -tropical regions water horn fern • stem stores the food & water tropical fern
Vascular Plants: Seedless (ferns) 4 Parts of a Fern: an underground stem that anchored by the roots rhizoid- anchor the fern roots- Frond- full grown leaves that stand vertically tightly coiled new leaves Fiddlehead-
Vascular Plants: Seedless (ferns) 4 Parts of a Fern: roots- rhizoid- Frond- Fiddlehead-
Vascular Plants: Seedless (ferns) The Fern Reproduction • reproduce by spores formed on the underside of the leaf • the cases that hold the spores look like brown and orange spots
Seedless Vascular Plants CLUB MOSSES • Very Small • Grows in moist woodlands and near streams
Seedless Vascular Plants HORSETAILS • Only 30 species alive today • Stems are jointed and long, coarse, needle-like • Small leaves grow flat against stem