Understanding the Periodic Table: Properties and Patterns of Elements
90 likes | 219 Vues
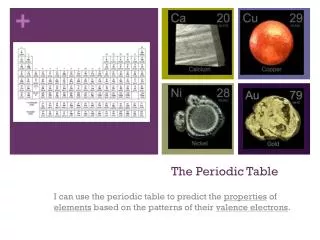
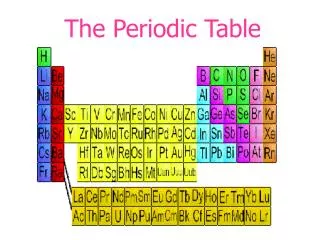
The periodic table allows us to predict element properties based on their valence electrons. Elements are arranged in increasing atomic number, revealing a repeating pattern of chemical and physical properties. Horizontal rows are called periods, while vertical columns are groups or families. Each group shares similar characteristics due to having the same number of valence electrons. Metals, non-metals, and metalloids are categorized by their properties. Understanding these concepts helps us grasp the behavior and reactions of elements within different groups.

Understanding the Periodic Table: Properties and Patterns of Elements
E N D
Presentation Transcript
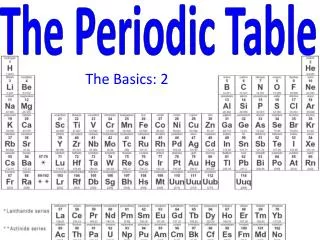
The Periodic Table I can use the periodic table to predict the properties of elements based on the patterns of their valence electrons.
The Periodic Table- Cracking the Code • The Periodic Law- __________ and __________ properties repeat in a predictable way, when elements are arranged in order of increasing ___________ ______________. • physical property- a characteristic of matter than can be ______________or measured without changing the sample’s composition. (density, color, melting point) • chemical property- the ability or inability of a substance to _______________with or change into one or more new substances (reaction with water)
The Periodic Table- Cracking the Code Each horizontal row is called a __________. Elements in the same period have their valence electrons in the same energy level Ex: Na, Mg, P, Ar have their valence electrons in the ____________ principal energy level
The Periodic Table- Cracking the Code Elements in the same column are called __________ or families, numbered 1-18. Elements in the same group have the same number of___________ __________, (in red)
The Periodic Table- Cracking the Code • Elements are divided by a “____________” line into metals, non-metals and metalloids • Elements to the ________ of the “stair step” line are ____________ • Can be _________ (brittle/powdery), _________ or ___________ • _________ conductors of electricity • Elements to the _______ of the line are _________, except for ______________, which is a non-metal • Usually _________- Mercury (Hg) is the exception, which is a __________ at room temperature • _________(shiny), _________ (bendable) • __________ conductor of electricity
The Periodic Table- Cracking the Code • Elements that _______ the line are called ________________. • Share properties with _______ metals and non-metals • ___________ is a common metalloid, used in ___________ ______
The Periodic Table- Cracking the Code • The Periodic Table can be split into regions that show the _________ that contain the elements’ highest energy valence electrons. • s block- group ___ and ____ • All elements in this block have their valence electrons in an s sublevel • Li has 1 valence electron in the 2s sublevel, Be has 2 electrons in the 2s sublevel • p block- groups ____-_____ • All elements in this block have an either partially or fully filled p sublevel. • Group 18 elements, the ________ ________are unique because they have completely filled s and p sublevels. This makes them very stable. • d block- groups ________(transition metals) • f block- lanthanides and actinides
The Periodic Table- Cracking the Code • Elements that have the same number of ________ _________tend to ______ in the same way. • Group I: ________ __________(excluding hydrogen) • ____ valence electron in___ sublevel • Very reactive with ______ and _____ • Combine easily with __________ to make _______ • Group 2:____________ _________ ____________ • ___ valence electrons in ____ sublevel • Reactive with air and water
The Periodic Table- Cracking the Code • Group 3- Group 12: _________________ _________________ • Number of valence electrons varies • React with many elements to make______________ _________ • Group 17: _________________ • _____ valence electrons • Highly reactive with alkali metals and alkaline earth metals to produce_______ • Group 18: _________ ____________ • _____ valence electrons • __________________