Atomic Structure Review
600 likes | 805 Vues
Atomic Structure Review. Have a Periodic Table & a calculator per group!. The number 14 in the name Carbon-14 represents:. The mass number. True or False: The nucleus of the atom is very dense. true. convert 2.75g Al to moles of Al. 2.75 g Al 1 mol Al

Atomic Structure Review
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Atomic Structure Review Have a Periodic Table & a calculator per group!
The number 14 in the name Carbon-14 represents: • The mass number
convert 2.75g Al to moles of Al 2.75 g Al 1 mol Al 27 g Al = 0.102 mol Al
How many Al atoms are in 26.982 g of Al? • 6.02X1023 Al atoms
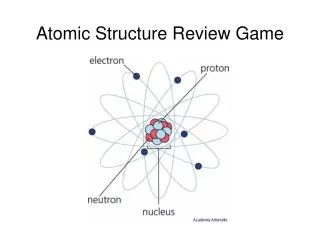
What subatomic particles are located in the nucleus? • Protons & neutrons
What is the name of Rutherford’s Model? • The Nuclear Model
Alpha particles have a _________ charge. • positive
What model is pictured below? • The Plum Pudding Model
convert 0.75 mols Na to atoms of Na 0.75 mol Na 6.02x1023 atoms Na 1 mol Na = 4.5x1023mol Na
Molar mass is measured in ________. Hint: what is the unit? • grams
atomic mass is measured in ________. Hint: what is the unit? • amu (atomic mass unit)
convert 2.5x1015 atoms of Au to moles of Au 2.5x1015atoms of Au 1 mol Au 6.02x1023atoms Au = 4.0x10-9mol Au
What subatomic particles are different in isotopes? • Neutrons
Who used a cathode ray during his experiments? • J.J. Thomson
Who used gold foil & alpha particles during his experiment? • Ernest Rutherford
Who is known as the Father of the Modern atomic theory? • John Dalton
What is the name of Thomson’s model of the atom? • Plum Pudding Model
List 2 of the 5 statements that sum up Dalton’s atomic theory. • All matter is composed of atoms • Atoms can’t be divided, created or destroyed • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds • Atoms are identical in mass • Atoms can be combined, separated or rearranged
Is modern atomic theory the same as Dalton’s atomic theory? • NO!!
List 1 modification to Dalton’s atomic theory. • Atoms of the same element can have different masses –isotopes • Atoms are divisible – Nuclear chem. • Atoms can be changed from one element to another- Nuclear chem.
Who discovered the neutron? • James Chadwick
Who discovered electrons? • J.J. Thomson
A _________explains observations and predicts new observations • Theory
What did Thomson use to discover electrons? • Cathode Ray Tube
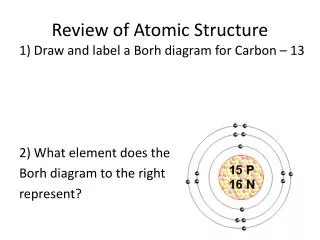
The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom equals the ____________ • Mass Number
Describe Thomson’s model of the atom? • Consisted of a cloud of evenly distributed positive charge with the negative electrons embedded randomly in it.
What is the conversion factor between moles and grams? • one mole = molar mass
What is the name of Thomson’s model of the atom? • The Plum Pudding Model
What is the nuclear symbol notation for the following?: atomic number = 26; mass number = 56 • 56 Fe 26
convert 0.25 moles of Pb to grams of Pb 0.25 molPb 207 g Pb 1 molPb = 51.75 g Pb
How did cathode rays behave near positively charged objects? • Cathode rays were attracted to the positive charge
What did these observations suggest about cathode rays: Cathode rays were attracted to the positively charged end of a magnet? • Cathode rays have a NEGATIVE charge
What are cathode rays? • beam of electrons
Who was the first person to come up with the idea of an atom? • Democritus
During the gold foil experiment some alpha particles (positively charged) passed through the gold foil. What did this suggest? • Atoms are mostly empty space
During the gold foil experiment some alpha particles (positively charged) bounced back toward the main source. What did this suggest? • the atom has a small dense positive region that caused the positive particles to bounce back…..the nucleus
What is the difference between an atom and an element? • An atom makes up an element. • An element can’t be broken down.
Protons have a ______ charge • positive
What is the conversion factor between moles and atoms? • one mole = 6.02 X 1023 atoms
Neutrons have a ______charge • neutral
The si unit for an amount of a substance is the _____ • MOLE!!
A _________ makes generalizations and does not explain observations • Scientific Law
What did Ernest Rutherford discover? • NUCLEUS
Rutherford’s model of the atom is called the “Nuclear Model”. Describe this model. • Suggested that the electrons travel around the positively charged nucleus. • Difference is that the positive charges are NOT spread out like in Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of _________ • NEUTRONS!
How are Atoms electrically neutral? • The number of protons and electrons are the same!