Metric System
80 likes | 208 Vues
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the metric system, focusing on base units used to measure length (meter), mass (gram), temperature (kelvin), time (second), and volume (liter). It explains common metric prefixes, such as micro, milli, centi, and kilo, which indicate fractions or multiples of these units. The document also covers conversion factors for unit conversions and density calculations, defined as mass divided by volume. Practice problems are included to reinforce understanding of these key concepts.

Metric System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Metric System The Scientific Way to Measure
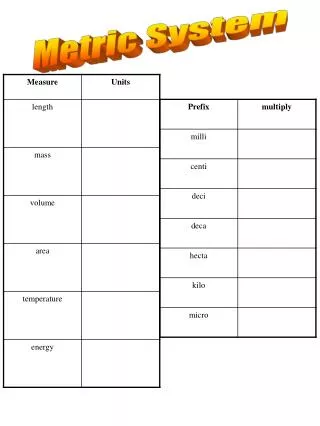
Base units • Meter (m)- measure length • Gram (g)- measures mass • Kelvin (k)- measure heat • Second (s)- measures time • Mole- (mol) measures particles ex, atoms molecules • Liter (L) measures volume or cm3
Metric Prefixes • Micro (μ) 1/1,000,000 or 1.0 X 10-6 • Milli (m) 1/1000 or 1.0 x 10-3 • Centi (c) 1/100 or 1.0 x 10-2 • Deci (d) 1/10 or .1 • Deka (D) 10 • Hekto (H) 100 • Kilo (K) 1000 or 1.0 x 103 • Mega (M) 1,000,000 or 1.0 x 106
Conversion Problem • Use conversion factors to convert from one unit to another • Are expressed as fraction, which represent absolute relationships • For example: • 1 dollar/100 pennies, 1 dollar/4 quarters, 1 dollar/ 10 dimes • 1 foot/12 inches
Practice • 1.0 meters = ? Cm • 12 DL = ? mL • 155 dg = ? Kg
Density • Density is equal to mass divided by volume • D = m/V • Volume= l x w x h or liters • If an object masses 114g and has the volume of 10.0 cm3 what is its density • D=
Density Practice • Mass- 3.1 g, Volume 0.35 cm3 D= ? • Mass- 14 g, Density- 10.5 g/cm3 Volume= ?