Analyzing Fractional Diffusion Equations: Cauchy and Signaling Problems Explained
230 likes | 353 Vues
This document explores fractional diffusion equations, focusing on the time-fractional and symmetric space-fractional cases. It covers fundamental solutions for Cauchy and signaling problems, utilizing Fourier and Laplace transforms for analysis. Key concepts include the Caputo fractional derivative, Gaussian and Levy probability distributions, and the properties of fractional diffusion phenomena like sub-diffusion and super-diffusion. The findings are presented with mathematical rigor and graphical representations of probability density functions, highlighting advancements in understanding diffusion processes in physics and engineering.

Analyzing Fractional Diffusion Equations: Cauchy and Signaling Problems Explained
E N D
Presentation Transcript
FOC Reading GroupProbability Distributions Generated by Fractional Diffusion Equations Prepared by: Yiding Han CSIOS Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Utah State University E: yiding.h@aggiemail.usu.edu 4/9/2008
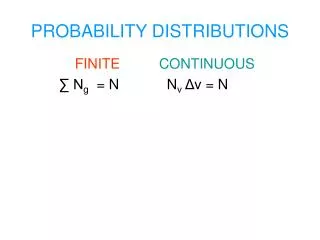
Outline • Standard Diffusion Equation • Fundamental solution for Cauchy problem. • Fundamental solution for Signalling problem. • Time-fractional Diffusion Equation. • The Cauchy problem for the time-fractional diffusion equation. • The Signallingproblem of the time-fractional diffusion equation. • Symmetric, space-fractional diffusion equation. • Conclusions FOC reading group
Standard diffusion equation • Linear partial differential equation where denotes a positive constant with dimensions x and t are space-time variables, is the field variable, which is a causal function of time. • The typical physical phenomenon related to such an equation is heat conduction in a thin solid rod extended along x, and u is the temperature. FOC reading group
Boundary conditions • Cauchy problem • Space-time domain • Data are assigned at t=0+ on the whole space axis. • Signalling problem • Space-time domain • Data are assigned both at t=0+ on semi-infinite space x>0 and x=0+on semi-infinite space t>0 FOC reading group
Initial values for both problems • Cauchy problem • Signalling problem FOC reading group
Cauchy problem • Denote then the Fourier transform of the initial condition is: • The Fourier transform of the standard diffusion equation: • Solving the above ODE, we have, FOC reading group
Continued… • Letting , then , therefore • is the Fourier transform of the fundamental solution or Green function • Thus, This interprets the Gaussian pdf. FOC reading group
Continued… • Furthermore, the moments of even order of the Gaussian pdf turns out to be: or FOC reading group
Signalling problem • Using Laplace transform, we have • The transformed solution of standard diffusion equation satisfies FOC reading group
Continued… • The fundamental solution (or Green function) of the Signalling problem: • It can be interpreted as: This is the pdf of one-sided Levy pdf. FOC reading group
Time-Fractional Diffusion Equation • By replacing the first-order time derivative by a fractional derivative of order 0<α≤2 (in Caputo sense), it reads: where denotes a positive constant with dimensions • The definition of the Caputo fractional derivative of order α>0 for a causal function is given as: where m=1,2,… and 0 ≤m-1<α≤m FOC reading group
Continued… • Thus we need to distinguish the cases and • Then the time-fractional diffusion equation reads: FOC reading group
Cauchy Problem for the time-fractionalDiffusion equation • Cauchy problem • For the time-fractional diffusion equation subject to the above condition, the Fourier transformation leads to the ODE of order • The transformed solution is Where denotes the Mittag-Leffler function of order 2v FOC reading group
Continued… • The Fourier transformation of Green function • The inverse Fourier transformation cannot be obtained but by turning it to be Laplace transform pair, the inverse can be obtained: FOC reading group
The pdf plots FOC reading group
Continued • Furthermore, the pdf can be written as: which is a symmetric pdf in space. • The absolute moments of positive order of the Green function are finite, in particular: • Which can be regarded as a generalization of the moments of order function. • the anomalous diffusion is said to be sub-diffusion when v<1/2, and super-diffusion when v>1/2. FOC reading group
The signalling Problem for the Time-Fractional diffusion Equation • Signalling problem • For the time-fractional diffusion equation subject to the above condition, the application of the Laplace transform leads to 2nd order ODE: • The transformed solution reads: FOC reading group
Continued … • The Laplace transform of Green function • Using the same method, we have: Which is a one-sided stable distribution in time FOC reading group
Pdf plots FOC reading group
Cauchy Problem for symmetric space-fractional diffusion equation • The symmetric space-fractional diffusion equation is obtained by replacing the 2nd order space derivative with order α. where denotes a positive constant with dimensions • The Fourier transformation of Green function reads: FOC reading group
Continued … • Therefore, we have pα (x;0,γ,0) is the pdf of Symmetric (β=0) α-stable distribution with placement variable a=0 and scaling factor • For α=1 and α=2, we can easily obtain the corresponding Green functions by inverse Fourior transformation: Cauchy Distribution Gaussian Distribution FOC reading group
PDfs The fundamental solutions against x of the Cauchy problem for the symmetric space-fractional diffusion equation. a) α=1/2 (bold line), α=1(dashed line) b) α=3/4 (bold line), α=2(dashed line) FOC reading group
Thanks FOC reading group