Ancient India
540 likes | 564 Vues
Explore the ancient civilization of India, with its rich diversity in languages, geography, and religions like Hinduism and Buddhism. Discover the achievements of the Indus Valley Civilization and the influence of the Aryans. Learn about the caste system, family structure, and economy of ancient India. Delve into the fundamental beliefs of Hinduism, including reincarnation and karma. Follow the Hindu life cycle, and understand the practice of yoga for spiritual enlightenment.

Ancient India
E N D
Presentation Transcript
India Land of Diversity - Major Religions 1. Hinduism and Buddhism - Diverse Languages 2. 18 Different Languages a. Hundreds of Dialects
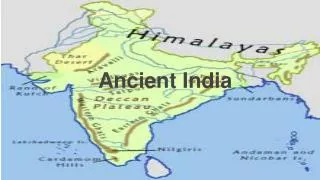
Indian Geography Geography (much diversity) 1. subcontinent 2. shaped like a diamond 3. a number of core regions a. Himalayas and Karakoram mountains (far north) b. Ganges Valley (just south of Himalayas) c. Indus River Valley (west of the Ganges)
By 2500 B.C.E. the entire region was dominated by two cities called; Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro
Harappa: Traded with Iran and neighboring regions in India to the east.
Mohenjo-Daro Traded with the Persia Gulf and Sumer to the west.
Indus Valley Achievements: • Writing system
Trading Seals Writing developed from earlier trading seals, which had the merchants name and symbols of trade items.
Peaceful items like toys jewelry.(Terracotta toy cow with Moveable head.)
The first civilization to cultivate cotton and make cotton clothing.
Cities had sewer systems; because bathing was an essential part of their religion.
Religious beliefs: • Great Bath Tanks were used for the purification of the body & soul.
Religion beliefs were centered on the idea of an afterlife, thus bodies were buried with personal items.
Hump-back bull; • Symbolized leader, whose strength protects the people
Priest meditated in yogi style to become connected with the gods.
The Aryans The Aryans 1. 2000 B.C. 2. Indo-European speaking 3. nomadic people a. Siberia - moved west (Europe) b. moved south (India) 4. eventually controlled all of India 5. ancient culture of the Aryans a. strong warrior people b. organized into tribes c. earlier Aryans had no written language d. start farming (1500 – 1000 BC)
The Aryans 6. Sandskrit (1,000 BC) a. written language * Vedas
Organization of Society The Caste System 1. invading peoples over conquered subjects a. skin color b. society Aryans took over more advanced c. decided by caste * skin color * economic advantages * position in society
Top Caste Brahmins * ruling elites in Aryan society * priests and warriors Second Caste Kshatriyas * were warriors Third Caste Vaisyas * commoners * usually engaged in commerce Forth Caste Sudras * not Aryan * great part of the Indian population * peasants artisans / manual labor The Untouchables
Reasons for the caste system: - It was an attempt by the upper class to freeze the economic system. • It was imposed by a coalition of priests and warrior-kings to maintain control over the local population. • It was created as an alternative to open slavery.
Family in Ancient India • Primary Unit of Society • - extended family • 1. three generations • Patriarchal • Superiority of men • 1. no women priests • 2. men only ones educated • Education • 1. Guru
Family in Ancient India Marriage - marriages arranged - women considered a minor - divorce 1. women almost never 2. take second wife (if first wife could not have children) - children important Sati (STOPPED IN 1800s)
Ancient Indian Economy Subsistence Farming - Indian civilization moves to around Ganges River 1. Sharecroppers 2. Environmental Dangers a. flooding b. food shortages
Hinduism Originated - Aryan Religious Beliefs - Vedas 1. hymns and ceremonies 2. oral tradition Beliefs - single force of the universe 1. Brahman - Atman (individual self) to seek ultimate reality 1. reunite with Brahman after Death
Fundamental Beliefs of Hinduism: - There is no set dogma (unquestionable truth) to Hinduism. - Therefore Hinduism is a religion with a variety of beliefs.
The city Harappa was rebuilt 6 times due to flooding The game chess began in India Ancient Indians invented the number system and zero They used anesthesia No slavery was known of They were the first ones to calculate pi It held the worlds first university They came up with navigation Hinduism Reincarnation - the individuals soul is reborn in a different form after death 1. unite with Brahman Karma (law of moral cause and effect) - force of a person’s actions determining his rebirth in a next life a. consequences b. Caste System Dharma 1. divine law 2. demands different actions by different members of society
- Atman – the soul of each individual - Samsara – reincarnation, the soul passes through a series of bodies - Nirvana (Moksha)– release from worldly life and unification with the universal spirit (called Brahman)
Hindu Life Cycle: - Youth; being educated by a Hindu Guru (teacher). - Householder; leading your family in the ways of Hinduism. - Reflection; using the teachings in order to break the cycle of bad karma. • Meditation; the atman seeking communion with the universal spirit. • Nirvana; breaking the cycle of life and becoming one with the universal spirit.
Hinduism Yoga 1. a method to develop a oneness with god 2. four types of Yoga for different needs of different people a. path of knowledge b. path of love c. path of work d. path of meditation * still the mind to create oneness with God
Hinduism Hinduism Polytheistic ? - Concrete Symbols 1. 33,000 Deities a. Brahma the creator b. Vishnu the preserver c. Shiva the destroyer 2. Gods a. different expressions of the one ultimate reality
Holy Writings • Vedas • Ramayana • Story of Rama (Vishnu’s Avatar and wife Sita) • Mahabharata • Story of two families warring in the Indus Valley • Bhagavad Gita • Part of the Mahabharata • Conversation between Krishna (Vishnu’s Avatar) and Arjuna • Life, philosophy, and trusting God are the topics
Shiva – The Destroyer and Transformer • Often depicted as slaying demons • Brings about life through destruction and rebirth • Often shown as terrifying; but sometimes as meditative • The Cosmic Dancer
Vishnu – The Preserver of Life • At constant peace • Is the foil of Shiva, but they work together • Wants humanity to find people with all living things • Avatar (human form) is Krishna
Devi – the Mother Goddess • Protector of the people • Reincarnates as an Aviator constantly to protect • Seen as the female balance in the universe
Surya – the God of Light • Name means “supreme light” • Depicted as being dawn by seven horses or one horse with seven heads • Brought light to the Earth and thus life
Ganesh – Remover of Obstacles • The Child God • Elephant headed • Born that way? • Beheaded by Shiva? • Son of Shiva • One of the most popular • Worshiped in Jainism • Believed to get people through tough times
Trimurti – the Holy Trinity • A popular sect worships the Trimurti • These three gods are seen to be the most important • Brahma • Vishnu • Shiva • Together they represent creation, preservation, and destruction
Kali – Goddess of Time and Change • Consort of Shiva • Revered as the protector of her people and bringer of death and change • Often depicted as dark-skinned and wild • Wears a necklace of human skulls and a belt made of arms • Often depicted with fangs and wielding a sword
Jainism • Sect of Hindus that formed their own sect in 500 BCE • Founded by Mahavira who believed that Hindus put too much into rituals • Believe in ahimsa (nonviolence towards all living things)
Jainism • Extreme Jains give away all of their possessions and live as monks and nuns • Some even sweep the ground as they walk so they won’t step on insects • Promise never to lie or steal • Non-monks fast for spiritual enlightenment
Buddhism Siddhartha Guatama (6th century BC) 1. Born 563 BC a. ruling princely family b. Southern Nepal (today) 2. Raised in the lap of luxury a. trained to be a warrior 3. Married at 16 a. had everything 4. Dismayed by the troubles of the world a. spend his life trying to find a cure for human suffering
Buddhism 5. Followed Ascetics a. did not help and almost killed him 6. Followed Deep Meditation a. one day sitting under a tree * Bodhi Tree (wisdom) * Nirvana (annihilation of the ego) * finds the meaning of life and enlightenment b. Spent the rest of his life preaching what he had learned
Four Noble Truths 1. Ordinary life is full of suffering 2. Suffering is caused by desire to satisfy ourselves 3. The way to end suffering is to end desire for selfish goals 4. The way to end desire is to follow the Middle Path Middle Path (Eightfold Path) 1. Right View 2. Right Intention 3. Right Speech 4. Right Action 5. Right Livelihood 6. Right Effort 7. Right Mindfulness 8. Right Concentration