Changes of State
160 likes | 431 Vues
Changes of State. Going from one state of matter to another. Change of state. A change of state is the conversion of a substance from one state to another All changes of state are physical changes The identity of a substance does not change. Energy and changes of state.

Changes of State
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Changes of State Going from one state of matter to another
Change of state • A change of state is the conversion of a substance from one state to another • All changes of state are physical changes • The identity of a substance does not change
Energy and changes of state • During a change of state, the energy of a substance changes • The energy of a substance is related to the motion of its particles • If energy is added to a substance, its particles move faster • If energy is removed from a substance, its particles move slower
Energy and changes of state • The temperature of a substance is a measure of the speed of its particles • This means temperature is a measure of the energy of a substance • A transfer of energy, known as heat, causes the temperature of a substance to change and can lead to a change of state
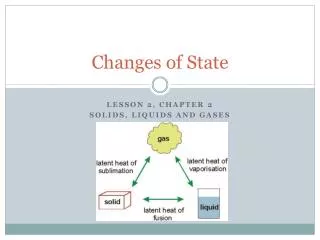
Melting • Melting is the change of state fro a solid to a liquid • The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which the substance changes fro a soli to a liquid • Most substances have a unique melting point that can be used with other data to identify them • Melting point is a characteristic property of a substance
Melting • For a solid to melt, particles must overcome some of their attraction to each other • When a solid is at its melting point, any energy it absorbs increases the motion of its atoms or molecules • Melting is an endothermic change because energy is absorbed
Freezing • Freezing is the change of state from a liquid to a solid • The temperature at which a liquid changes from a liquid to a solid is it freezing point • Freezing and melting occur at the same temperature • Freezing is an exothermic change because energy is removed from the substance
Vaporization • Vaporization is the change of state from a liquid to a gas • Boiling is vaporization that occurs throughout a substance • The temperature at which a substance boils is called its boiling point • Boiling point is a characteristic property of a substance
Vaporization • Evaporation is vaporization that occurs at the surface of a liquid below its boiling point • When you perspire, your body is cooled by the process of evaporation • Evaporation also explains why water in a glass on a table will disappear after a few days
Condensation • Condensation is the change of state from a gas to a liquid • The condensation point of a substance is the temperature at which the gas becomes a liquid and is the same temperature as the boiling point at a given pressure • Condensation is an exothermic change
Sublimation • Sublimation is the change of state from a solid directly into a gas • Frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice) will change from a solid directly to a gas • The molecules must go from being very tightly packed to being very spread apart • Sublimation is an endothermic change