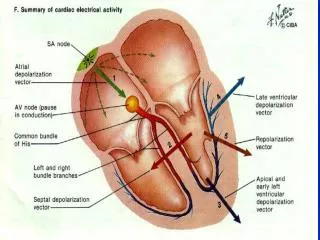
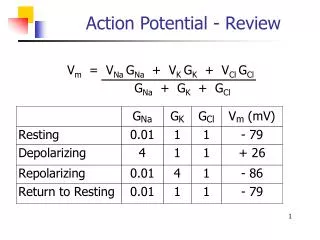
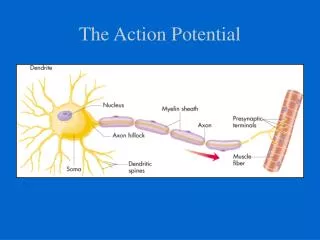
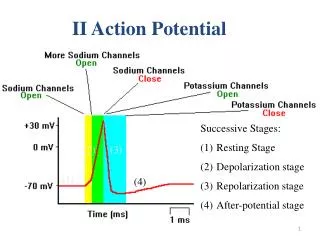
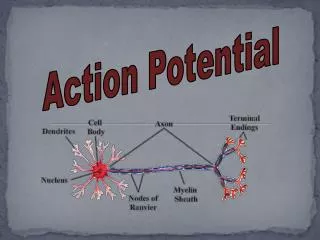
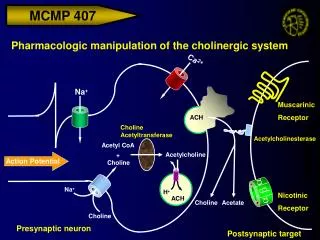
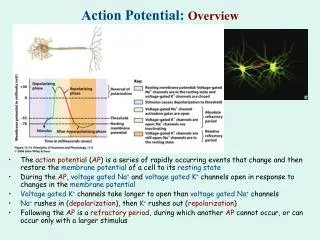
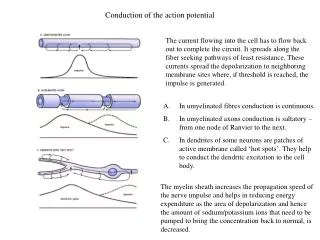
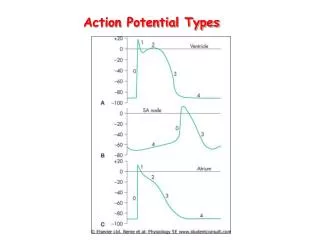
Generation of action potential
1k likes | 1.3k Vues
Generation of action potential. ECG Graph paper. Unipolar precordial leads. Normal ECG. Guide in Reading ECG. Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave

Generation of action potential
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
Standardization Heart rate 60 - 100 beats/min bradycardia < 60 tachycardia > 100 PR interval 0.12 – 0.20 sec QRS < 0.12 sec QRS axis - 30º to + 110º QTc < 0.47 sec males < 0.48 sec females
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
Rhythm SA node – sinus AV node – junctional Ventricular rhythm
Rhythm Are there p waves? sinus, atrial fibrillation Do they look similar? MFAT, wandering pacemaker Are they regular? AF Does a QRS complex follow each p wave? SVT, junctional rhythm, ventricular rhythm
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
Determination of Heart Rate Heart rate assessment by “rule of 300”
Measurement of Rate Formula 1: 300 # big squares between R-R Formula 2: 1500 # small squares between R-R
Determination of Heart Rate Is the atrial rate same as ventricular rate? PVC’s, PAC’s, 3rd degree AV block Is there normal-looking QRS complex after each p wave? What if there are no p waves? Six second strip heart rate
RATE • Sinus Bradycardia • Sinus Tachycardia • AV junctional rhythm • Inherent rate of 40-60/min • No p waves • Normal looking QRS complex • Ventricular rhythm • Inherent rate of 20-40/min • No p waves • Bizaare-looking QRS complex
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
Determination of Axis Hexaxial System
Determination of Axis Axis = 90 x QRS in AVF QRS in [ I] + QRS in [AVF] Special cases: negative QRS deflection in I Add 90 to result
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
P wave morphology and duration No p waves Atrial fibrillation Multiple p waves Multifocal atrial tachycardia Wandering pacemaker Notched p wave Left atrial enlargement Peaked p wave Right atrial enlargement
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
P-R interval Prolongation Hypokalemia 1st degree AV block Shortening Wolff-Parkinson White
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
QRS morphology and duration Normal looking Supraventricular origin Bizarre looking Ventricular in origin Paced rhythm
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
ST segment Elevation Infarction >1mm in limb leads >2 mm in chest leads depression Ischemia >1 mm in all leads from the J point
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
T and U waves T wave Hypokalemia 1st degree AV block Shortening Wolff-Parkinson White
Guide in Reading ECG Standardization & technique Rhythm Rate: atrial & ventricular Axis P wave morphology & duration P-R interval QRS complex morphology & duration ST segment T-wave U wave Q-T interval Hypertrophy and enlargement arrhythmias
Determination of QT interval Corrected QT interval = QT (actual) R-R
QT interval prolongation hypocalcemia shortening hypercalcemia
Atrial Enlargement (due to chronic lung disease or pulmonay embolus
Atrial Enlargement (commonly seen in mitral valve disease) B V1 II V1
Ventricular Enlargement Right Ventricular Hypertrophy R in V1 + S in V5-V6 >11 mm R in V1 >7mm R:S in V1 >1 RAD > +90 degrees
Anatomy of Myocardial Infarction *LAD = left anterior descending aretery; LCX = left circumflex artery LM = left main artery; PDA = posterior descending artery; PL = posterolateral branches
Evolution of Infarct ST segment elevation Progressive decrease in ST segment elevation Q wave formation T wave flattening/inversion Q wave with upright T wave
RULES on Q waves • Not significant in aVR • Ignored in V1 unless with abnormalities in other precordial leads • Ignored in III unless with abnormalities in II, AVFmore reliable if with St-T segment changes • Not significant if located in V1-V3 in LBBB • Significant in V1-V2 in the presence of RBBB • Pathologic if >= 0.04 sec and >25% of R wave amplitude