Levels of cellular organization
820 likes | 3.48k Vues
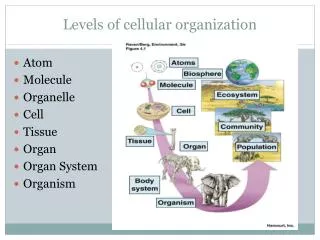
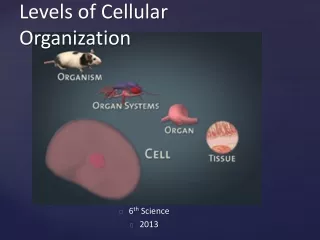
Levels of cellular organization. Atom Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism. Division of Cells. Eukaryotic Cells Literally means “True nucleus” Have a ________ _______ Cells Have membrane-bound __________ Organisms made of eukaryotic cells are called “________”

Levels of cellular organization
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Levels of cellular organization Atom Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
Division of Cells • Eukaryotic Cells • Literally means “True nucleus” • Have a ________ • _______ Cells • Have membrane-bound __________ • Organisms made of eukaryotic cells are called “________” Examples: Animals, Plants, Fungi, Unicellular organisms like paramecium and amoeba
Cellular Components • Cytoplasm • ___-_____ substance ______ the cell where organelles are found • Cytoskeleton • “Cell skeleton” • Network of _______ fibers that maintain the ______ and structure of cell • Composed of three networks of fibers • Microtubules: _______; hollow tubes made of protein; determine cell shape; scaffolding • ______________ Filaments: Provide strength of cell • Actin Filaments: ________; contractile string-like proteins that allow for cell ________
Cellular Components • Cell Membrane • ______-permeable barrier that _________ the cell • Regulates what _____ and ______ the cell • Provides protection • Found in ____ types of cells • Cell Wall • Porous, ______ barrier found _________ the ____ ________ • Adds additional layer of support and protection • _____ found in _______ cells
Organelles • Nucleus • Houses the ______ material (DNA) needed for replication of the cell • “______ Center” of the cell • Contains the instructions for the creation of proteins (made from DNA) • Exterior: Surrounded by nuclear envelope: double-layered ________ that encloses the DNA; contains nuclear pores: small ________ that allow for the passage of molecules between the _________ and the _______ • Interior: DNA in the form of ___________(string-like) • Nucleolus: where ribosomes are made; very _______ region
Organelles • Endoplasmic Reticulum • A grouping of sac-like structures • _____ types of ER: • ______ ER: contain ribosomes (creating ‘rough’ appearance); involved in the process of _______ synthesis • ______ ER: no ribosomes; involved in ______ synthesis • Ribosomes • Location where _______ are made (protein synthesis)
Organelles • Golgi Apparatus • Looks like a stack of membranes (pancake-like appearance) • Modifies, ____, and _______proteins received from the ER. • Break off from the golgi apparatus; float ________ in the cell or travel to _______________where it will eventually___the cell. • Creation of _____________
Organelles • Lysosomes • Contain _______ necessary for_______ of cell food or waste • Can break down lipids, carbs, proteins • Digest non-functional organelles, ‘_______ ___’ the cell
Organelles • Vacuoles • Sac-like structure responsible for _______ of various materials (e.g. water, carbs, proteins, etc.)
Organelles • Mitochondria • The “___________” of the cell • Convert _____ energy into energy that is used by the _____ itself (for growth, development, movement, etc.) via cellular respiration • ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) • _________ structure
Organelles • Chloroplast • Site of _____________ • Energy from ____ is captured and converted into chemical energy • Contain the pigment ________ which absorbs solar energy used in photosynthesis • Responsible for the ______ color of plants
Organelles • Centrioles • Made of ______________ • Located ______ nucleus • ___________ microtubules within the cytoskeleton prior to cell division