Topographic Maps
130 likes | 256 Vues
This guide explains the essential components of topographic maps, including the concepts of latitude and longitude as measurements of North/South and East/West. It covers the significance of the equator and prime meridian, and how these are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Explore key map elements such as scale, declination, symbols, and contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. Learn how contour lines represent three-dimensional terrain in two dimensions, and understand the importance of contour intervals and gradients in interpreting slopes.

Topographic Maps
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Latitude and Longitude • Latitude tells N/S 0 is equator 90=poles • Longitude tells E/W 0-180 (prime meridian=0) • Measured in Degrees(º), Minutes(´), and Seconds (´´)
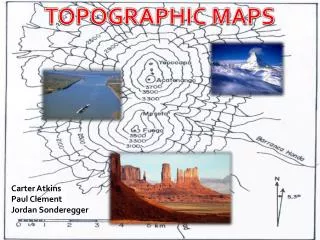
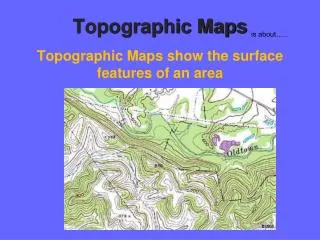
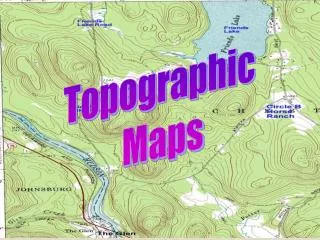
Map Elements • Scale • Declination • Symbols • Contour Lines
Scale • Fractional • Expressed as a ratio 1:250,000 (All the same units) • Graphic • Expressed on Map as a visual bar broken into segments representing a stated distance • Verbal “one inch equals 10 miles”
Declination • The angular difference between true and magnetic north. • True north (geographic) • Magnetic north (where the magnet points toward)
Symbols • Markers used to represent features such as: • Boundaries • Roads • Buildings • Contours • Mines • Rivers • Quarries
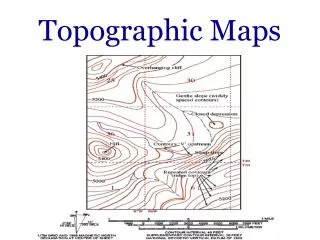
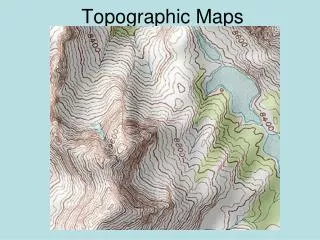
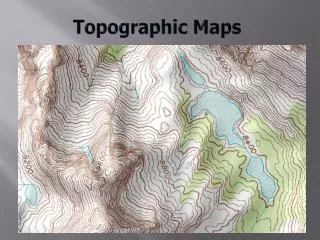
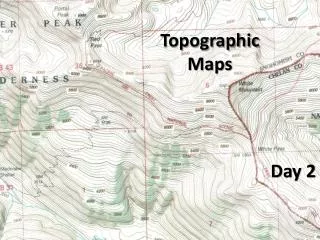
Contour Lines • Lines that connect points of equal elevation • Closer together the steeper the slope of the surface • Contour Interval • The vertical change between two lines
Gradient • Change in elevation divided by Change in horizontal distance Also Known as Slope Total Length on Surface Vertical Change Horizontal Change
Vertical ExaggerationDifferent scales for the vertical and horizontal axes