MORE FOSSIL FUEL
380 likes | 533 Vues
This document explores the critical aspects of fossil fuels, particularly crude oil and natural gas. It details their formation, extraction methods, and the historical context of oil production, including major crises and legislative responses. The text discusses the environmental consequences of fossil fuel extraction, notable oil spills, and advancements like hybrid engines and the strategic petroleum reserve. The current state of oil reserves and their future sustainability is examined, along with alternative energy developments.

MORE FOSSIL FUEL
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MORE FOSSIL FUEL What is burned by cars late at night? midnight oil
OIL Crude Oil (petroleum): sludgelike mix of different hydrocarbons. Formed below ground Oil refineries: separate crude oil into gasoline and other products
HYDRO CARBONS • Methane • Ethane • Propane • Butane • Octane (gasoline) • Diesel
Balance equations for each hydrocarbon on previousslide • hydrocarbon + oxygen gas --> carbon dioxide + water • example: 1 CH4 + 2 O2 --> 1 CO2 + 2 H2O • Build models for the reactants of any two equations except methane. Sketch & label. Rearrange models to make products for same equations. Sketch & label
SOME OIL HISTORY Surface tar used ~4000 years ago Modern extraction started in 1859 in Pennsylvania Today, oil is the most-used fuel worldwide 1st oil well Drake Well Titusville, PA
SAVE THE WHALES Take notes: _________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
OIL DRILLING Liquid oil found in pores in underground rock layers. Oil is extracted using a pressure differential. Gusher: oil naturally under pressure As more oil is removed, it becomes harder to extract. PRIMARY EXTRACTION: initial extraction of available oil SECONDARY EXTRACTION: forcing oil out by pumping liquid or gas into rock
1970’s Energy Crisis • Petroleum production in U.S. peaked in 1960’s, worldwide peaked in 1970’s • 1973 Oil Crisis caused by the Arab Oil Embargo • 1979 Energy Crisis caused by the Iranian Revolution
1973 Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) placed an embargo on oil exports for any country supporting Israel during the Yom Kippur War. Japan & European allies tried to separate themselves from U.S. OPEC also raised prices.
After Iranian Revolution, exports were reduced, causing prices to go up. ~4% reduction in production worldwide. Widespread panic drove prices even higher.
LESSONS LEARNED FROM 1970’S? Creation of Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPRs). In U.S. about 4.1 billion barrels are held. Development of hybrid engines National speed limit of 55 mph Department of Energy was created National Energy Act of 1978 - directed at conservation. (Grants for weatherizing, using alternate energy sources, etc.) Daylight saving time implemented Building of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS) from Prudhoe Bay to Valdez, Alaska
Pump Stations $8 x 109+ 800 miles
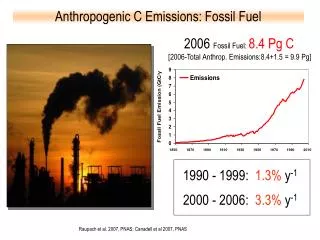
HOW MUCH OIL IS LEFT? HOW LONG WILL IT LAST? Peak Oil Production - Hubbert predicted 1970 for USA Proven reserves - to - production ratio = total remaining reserves divided by the annual rate of production 2010 WORLDWIDE ESTIMATE 1400 Gigabarrels / 29Gigabarrels/year =~48 yrs but . . . these number change. Why?
OIL POLLUTION ACT1990 • PROVIDES AUTHORITY FOR EPA TO RESPOND TO OIL SPILLS • Response to the Exxon Valdez spill
NOTABLE SPILLS • GULF WAR, 1991, KUWAIT • RETREATING IRAQI FORCES OPENED VALVES OF WELLS & PIPELINES TO SLOW AMERICAN TROOPS
IXTOC 1 1979 • BAY OF CAMPECHE, MEXICO • WELL COLLAPSED AFTER AN ACCIDENTAL EXPLOSION
ATLANTIC EMPRESS • WEST INDIES • 1979 • 2 FULL SUPERTANKERS COLLIDED IN CARIBBEAN SEA
DEEPWATER HORIZON(BP OIL SPILL) • 2010 • GULF OF MEXICO • LARGEST MARINE SPILL • ~53,000 BARRELS PER DAY FOR 3 MONTHS (4.9 X 106 BARRELS)
EXXON VALDEZ1989 • Full tanker ran aground • Largest in U.S. waters until the BP spill • Notable not because of size of spill, but for damage to a remote, pristine, fragile ecosystem and efforts to clean and protect habitat for salmon, sea otters, seals, seabirds, etc.)
NATURAL GAS mostly methane (CH4) FORMED IN TWO WAYS . . . Biogenic - shallow depths by anaerobic decomposition of organic matter by bacteria. Thermogenic - formed at deep depths where geothermal heating separates hydrocarbons from organic matter
PRODUCTION & USE Russia produces most USA uses most What happened after the 1970’s crisis? TAPS completed.
PRODUCTION & USE USA uses most. Who? Losses = energy consumed by generation, transmission of electricity
OTHER FOSSIL FUELS Tar sands - dense oily substances that can be mined Shale oil - sedimentary rock filled with organic matter that was not buried deep enough to form oil Methane hydrates - gas trapped or dissolved in ice formed in deep-sea sediments PROS? CONS? TAKE NOTES
Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) Technique used to release natural gas & petroleum from rock formations. RESEARCH: METHODS, PROS, CONS, LAWS Notes: __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF FOSSIL FUEL COMBUSTION AIR POLLUTION DRIVE CLIMATE CHANGE CHANGES BALANCE OF CARBON CYCLE WATER POLLUTION from acid deposition, runoff & oil spills (more on these to come)
So does it matter the source of the fuel used to generate electricity?
RESEARCH COMBUSTION OF OIL, NATURAL GAS & COAL PROS OF EACH ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ CONS OF EACH ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
ENERGY CONSERVATION practice of reducing use to extend nonrenewable resources and reduce environmental impact COGENERATION increase efficiency of power plants by capturing excess heat.
LABS - Due_____ • Bitumen from Oil Sands RESEARCH & PRESENT Due_______ ANWR Debate Exxon Valdez Nigeria, Bonga Field 2011 Yellowstone River Oil Spill Deepwater Horizon Gulf War Spill