Understanding Sequential Circuit Analysis: States, Outputs, and Models
100 likes | 235 Vues
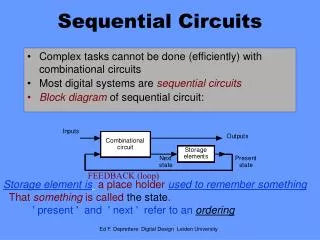
This document provides a comprehensive analysis of sequential circuits, focusing on the behavior of state, inputs, and outputs over time. It details how the current state at time (t) is stored in flip-flops and how the next state at time (t+1) and outputs depend on both current state and inputs. The differences between Mealy and Moore machines are explained, along with examples of state diagrams and state tables. Learn to derive output functions and next state functions, key features in designing and analyzing complex digital systems.

Understanding Sequential Circuit Analysis: States, Outputs, and Models
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SequentialCircuits Analysis
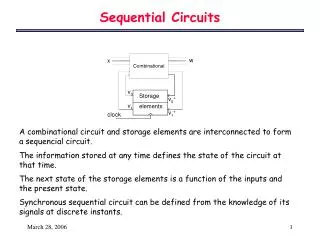
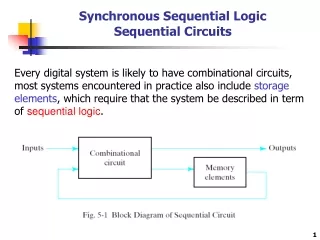
Inputs Combina-tional Logic Outputs Storage Elements Next State State CLK Sequential Circuit Analysis • Current Stateat time (t) is stored in an array of flip-flops. • Next State at time (t+1) is a Boolean function of State and Inputs. • Outputsat time (t) are a Boolean function of State (t) and (sometimes) Inputs (t).
Example of a SequentialCircuit Input: x(t) Output:y(t) State:(A(t), B(t)) • What is theOutput Function? • What is the Next State Function? x A Q D A Q C Next State B Q D CP Q' C y Output
Present State Input Next State Output Present Next State Output A(t) B(t) x(t) A(t+1) B(t+1) y(t) State x(t)=0 x(t)=1 x(t)=0 x(t)=1 0 0 0 0 0 0 A(t) B(t) A(t+1)B(t+1) A(t+1)B(t+1) y(t) y(t) 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 State Table A(t+1) = A(t)x(t)+B(t)x(t) B(t+1) =A (t)x(t) y(t) =x (t)(B(t)+A(t))
x=0/y=0 x=0/y=1 x=1/y=0 A B 1 0 0 0 x=0/y=1 x=1/y=0 x=1/y=0 x=0/y=1 1 1 0 1 x=1/y=0 State Diagrams • The sequential circuit function can be represented in graphical form as a state diagram
MEALY MACHINE MOORE MACHINE Inputs X(t) Outputs Z(t) Inputs X(t) Combinational circuits Combinational circuits Storage Element S(t) Storage Element S(t) Outputs Z(t) Moore and Mealy Models • Moore Model • Outputs are a function ONLY of states • Mealy Model • Outputs are a function of inputs AND states
x=1/y=0 x=0/y=0 1 0 Present Next State Output x=0/y=0 State x=0 x=1 x=0 x=1 x=1/y=1 0 0 1 0 0 x=0 1 0 1 0 1 0/0 x=0 Present Next State Output x=1 State x=0 x=1 x=1 x=0 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 2/1 1/0 2 0 2 1 x=1 Moore and Mealy Example StateDiagrams Mealy Moore
0/0 1/0 S0 S1 0/1 0 1 1/0 0/1 S0/0 S1 0/1 S2 0/1 1/0 1/0 0/1 0/0 1/0 1/0 S0 S1 S3 S2 0/1 1/0 1/0 Equivalent States • Twostatesareequivalentif: • Outputproducedforeachinput is identical • Thenextstatesforeachinputaresameorequivalent
A Z D Q Q C R B D Q Q C R C D Q Clock Q C R Reset SequentialAnalysisExample • Variables • Inputs: None • Outputs: Z • State Variables: A, B, C • FlipFlopInputEquations • A(t+1) = • B(t+1) = • C(t+1) = • Z = Mealy? Moore? StateTable? StateDiagram?