Computed Tomography
140 likes | 506 Vues
Computed Tomography. DANGER DETECTOR production. Typical CT scanner. So how old is the CT scanner?. http://www.impactscan.org/slides/impactcourse/basic_principles_of_ct/img24.html. 2 nd generation. http://www.impactscan.org/slides/impactcourse/basic_principles_of_ct/img25.html.

Computed Tomography
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Computed Tomography DANGER DETECTOR production
So how old is the CT scanner? http://www.impactscan.org/slides/impactcourse/basic_principles_of_ct/img24.html
2nd generation http://www.impactscan.org/slides/impactcourse/basic_principles_of_ct/img25.html
3rd generation http://www.impactscan.org/slides/impactcourse/basic_principles_of_ct/img26.html
4th generation http://www.impactscan.org/slides/impactcourse/basic_principles_of_ct/img27.html
Tomographic Reconstruction • Projection at each θ is made up of line integrals • Each line integral represents total X-ray attenuation • We can relate the attenuation to the original image • Infinite 1D projections at infinite angles perfect reconstruction
Filtered Back Projection • Only have finite number of projections • Approximate the original by “back projecting” • Run ray sums back through to simulate original • Krithika forbade me from discussing this further
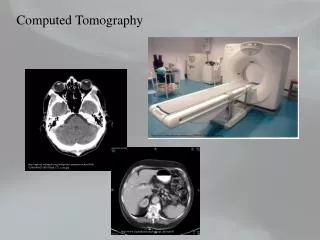
Uses of CT scanners • Non-invasive medical imaging • Examine examine chest, abdomen, and pelvis areas by imaging blood, bone, and soft tissue • radiation exposure of 2 – 10 mSv = 3 years of background radiation
Why do we care? • CT scanners are used to detect explosives in checked baggage • Can create detailed, cross-sectional slices of the baggage • The slices are the input to our program